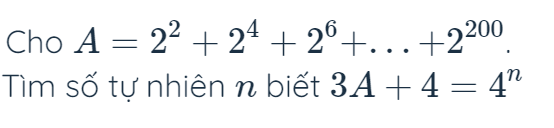
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Vì \(\left(2x-3\right)^4\ge0\left(\forall x\right)\) (mũ 4 luôn luôn là một số dương)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^4-2\ge-2\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow2x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3}{2}\)
Vậy GTNN của biểu thức bằng -2 <=> x = 3/2

\(C_2^2+C_3^2+...+C_n^2=C_3^3+C_3^2+C_4^2+...+C_n^2\) (do \(C_2^2=C_3^3=1\))
\(=C_4^3+C_4^2+C_5^2+...+C_n^2=C_5^3+C_5^2+...+C_n^2\)
\(=...=C_n^3+C_n^2=C_{n+1}^3\)
Do đó:
\(2C_{n+1}^3=3A_{n+1}^2\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2.\left(n+1\right)!}{3!.\left(n-2\right)!}=\dfrac{3.\left(n+1\right)!}{\left(n-1\right)!}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n-1=9\Rightarrow n=10\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\left(1-x-3x^3\right)^{10}=\sum\limits^{10}_{k=0}C_{10}^k\left(-x-3x^3\right)^k\)
\(=\sum\limits^{10}_{k=0}C_{10}^k\left(-1\right)^k\left(x+3x^3\right)^k=\sum\limits^{10}_{k=0}\sum\limits^k_{i=0}C_{10}^kC_k^i\left(-1\right)^kx^i.3^{k-i}.x^{3\left(k-i\right)}\)
\(=\sum\limits^{10}_{k=0}\sum\limits^k_{i=0}C_{10}^kC_k^i\left(-1\right)^k.3^{k-i}.x^{3k-2i}\)
Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}0\le i\le k\le10\\i;k\in N\\3k-2i=4\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left(i;k\right)=\left(1;2\right);\left(4;4\right)\)
Hệ số: \(C_{10}^2C_2^1\left(-1\right)^2.3^1+C_{10}^4C_4^4.\left(-1\right)^4.3^0=...\)

\(\Rightarrow he-so:\left[{}\begin{matrix}C^9_{10}C^1_9\left(-3\right)^{10-9}\left(-1\right)=270\\C^{10}_{10}C^4_{10}\left(-3\right)^{10-10}.\left(-1\right)^4=210\end{matrix}\right.\)

+ Biểu thức nguyên:
\(3x^2y-5x\left(y^2+3\right)\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3a}x^n-4x^2+\dfrac{x}{a+3}\)
+ Biểu thức phân:
\(\dfrac{5\left(x-4\right)\left(x^2+y\right)}{6xy-1}\)

Đa thức biểu thị kết quả thứ nhất: K = (x + 1)2
Đa thức biểu thị kết quả thứ hai: H = (x – 1)2
Đa thức biểu thị kết quả cuối cùng:
Q = K – H = (x + 1)2 - (x – 1)2
= (x+1).(x+1) - (x – 1). (x – 1)
= x.(x+1) + 1.(x+1) - x(x-1) + (-1). (x-1)
= x.x + x.1 + 1.x + 1.1 –[ x.x – x .1 + (-1).x + (-1) . (-1)]
= x2 + x + x + 1 – (x2 – x – x + 1)
= x2 + x + x + 1 – x2 + x + x – 1
= (x2 - x2 ) + (x+x+x+x) + (1- 1)
= 4x
Để tìm x, ta lấy kết quả cuối cùng chia cho 4

n x (n + 1) = 2 + 4 + 6 + 8 + ... + 2500
n x (n + 1) = 2 x (1 + 2 + 3 + ... + 1250)
n x (n + 1) = 2 x (1 + 1250) x 1250 : 2
n x (n + 1) = 1251 x 1250
=> n = 1250
n x (n + 1) = 2 + 4 + 6 + 8 + ... + 2500
n x (n + 1) = 2 x (1 + 2 + 3 + ... + 1250)
n x (n + 1) = 2 x (1 + 1250) x 1250 : 2
n x (n + 1) = 1251 x 1250
=> n = 1250

Để A có giá trị nguyên hay A \(\in\)Z thì ( 3 - n ) \(\in\)Ư(4) .
Mà : Ư(4) = { 1 ; 2 ; 4 ; -1 ; - 2 ; -4 }
Nếu : 3 - n = 1 => n = 2
3 - n = 2 => n = 1
3 - n = 4 => n = -1
3 - n = -1 => n = 4
3 - n = -2 => n = 5
3 - n = -4 => n = 7
Vậy : n \(\in\){ 2 ; 1 ; -1 ; 4 ; 5 ; 7 }

a) gtnn bạn ạ
GTNN A= -4 vì 2/3x-1/ >= 0
b) gtln bạn ạ
GTLN B = 10 vì 4/x-2/ >=0
\(A=2^2+2^4+2^6+...+2^{200}\\ 2^2A=2^4+2^6+...+2^{202}\\ 4A-A=\left(2^4+2^6+2^8+...+2^{202}\right)-\left(2^2+2^4+2^6+...+2^{200}\right)\\ 3A=2^{202}-2^2\)
\(=>3A+4=2^{202}-2^2+4=2^{202}-4+4=2^{202}\)
\(=>2^{202}=4^n\\ =>2^{202}=\left(2^2\right)^n\\ =>2^{202}=2^{2n}\\ =>2n=202\\ =>n=101\)