Tìm số nguyên x , y biết
\(\dfrac{5}{8x-2}\)= \(\dfrac{-4}{7-x}\)
Làm chi tiết với ạ!
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(x\) = y.\(\dfrac{3}{4}\) ; z = \(\dfrac{y}{5}\).7
Thay \(x\) = y.\(\dfrac{3}{4}\) và z = \(\dfrac{y}{5}\).7 vào biểu thức:
2\(x\) + 3y - z = 186 ta có:
2.y.\(\dfrac{3}{4}\) + 3y - \(\dfrac{y}{5}\).7 = 186
y.(2.\(\dfrac{3}{4}\) + 3 - \(\dfrac{7}{5}\)) = 186
y.\(\dfrac{31}{10}\) = 186
y = 186 : \(\dfrac{31}{10}\)
y = 60 ; \(x\) = 60. \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) = 45; z = 60.\(\dfrac{7}{5}\) = 84
\(x\) + y + z = 45 + 60 + 84 = 189
Mình không hiểu câu sau của đề bài.
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{4}\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{15}=\dfrac{y}{20}\left(1\right)\)
\(\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{z}{7}\Rightarrow\dfrac{y}{20}=\dfrac{z}{28}\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra:
\(\dfrac{x}{15}=\dfrac{y}{20}=\dfrac{z}{28}\Rightarrow\dfrac{2x}{30}=\dfrac{3y}{60}=\dfrac{z}{28}\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta có:
\(\dfrac{2x}{30}=\dfrac{3y}{60}=\dfrac{z}{28}=\dfrac{2x+3y-z}{30+60-28}=\dfrac{186}{62}=3\)
Do đó:
\(\dfrac{x}{15}=3\Rightarrow x=15.3=45\)
\(\dfrac{y}{20}=3\Rightarrow y=20.3=60\)
\(\dfrac{z}{28}=3\Rightarrow z=28.3=84\)
Tổng là: \(x+y+z=45+60+84=189\)
Vậy....


\(a.\dfrac{12}{3}=\dfrac{20}{5}=4\\ b.\dfrac{9}{-3}=\dfrac{-15}{5}=-3\)
a, Xét \(\dfrac{x}{3}=4\Rightarrow x=12;\dfrac{20}{y}=4\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{20}{4}=5\)
b, \(\dfrac{9}{-x}=-3\Rightarrow-x=-3\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
\(\dfrac{y}{5}=-3\Rightarrow y=-15\)

\(a,\left(\dfrac{31}{35}-\dfrac{4}{7}\right)\times\dfrac{8}{7}:2\\ =\left(\dfrac{31}{35}-\dfrac{4\times5}{35}\right)\times\dfrac{8}{7}:2\\ =\dfrac{11}{35}\times\dfrac{8}{7}:2\\ =\dfrac{88}{245}:2\\ =\dfrac{44}{245}\\ b,\left(1-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\times\left(1-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\times\left(1-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)\times\left(1-\dfrac{1}{5}\right)\\ =\left(\dfrac{2-1}{2}\right)\times\left(\dfrac{3-1}{3}\right)\times\left(\dfrac{4-1}{4}\right)\times\left(\dfrac{5-1}{5}\right)\\ =\dfrac{1}{2}\times\dfrac{2}{3}\times\dfrac{3}{4}\times\dfrac{4}{5}\\ =\dfrac{1}{3}\times\dfrac{3}{4}\times\dfrac{4}{5}\\ =\dfrac{1}{4}\times\dfrac{4}{5}=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
a, ( \(\dfrac{31}{35}\) - \(\dfrac{4}{7}\)) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{8}{7}\): 2
= \(\left(\dfrac{31}{35}-\dfrac{20}{35}\right)\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{8}{7}\) : 2
= \(\dfrac{11}{35}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{8}{7}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
= \(\dfrac{44}{35}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{4}{7}\)
= \(\dfrac{44}{245}\)
b, ( 1 - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)) \(\times\) ( 1 - \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)) \(\times\) ( 1 - \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)) \(\times\) ( 1 - \(\dfrac{1}{5}\))
= \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{2}{3}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{4}{5}\)
= \(\dfrac{1}{5}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{2\times3\times4}{2\times3\times4}\)
= \(\dfrac{1}{5}\)

\(\dfrac{1}{x-3}+\dfrac{3x^2-8x+10}{x^2-5x+6}-\dfrac{2x-4}{x-2}\left(ĐK:x\ne3;x\ne2\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x-3}+\dfrac{3x^2-8x+10}{x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{2x-4}{x-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x-3}+\dfrac{3x^2-8x+10}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{2x-4}{x-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{3x^2-8x+10}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{\left(2x-4\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2+3x^2-8x+10-\left(2x^2-6x-4x+12\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x^2-7x+8-2x^2+10x-12}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+3x-4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+3x-4}{x^2-5x+6}\)

\(\dfrac{x}{y+z+1}\) = \(\dfrac{y}{x+z+2}\) = \(\dfrac{z}{x+y-3}\) = \(x+y+z\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
\(\dfrac{x}{y+z+1}\)=\(\dfrac{y}{x+z+2}\)=\(\dfrac{z}{x+y-3}\)=\(\dfrac{x+y+z}{y+z+1+x+z+2+x+y-3}\)
\(x+y+z\) = \(\dfrac{x+y+z}{2.\left(x+y+z\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) (1)
\(\dfrac{x}{y+z+1}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) ⇒ 2\(x\) = y+z+1
⇒ 2\(x\) + \(x\) = \(x+y+z+1\) (2)
Thay (1) vào (2) ta có: 2\(x\) + \(x\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) + 1
3\(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{2}\) ⇒ \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{y}{x+z+2}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) ⇒ 2y = \(x+z+2\) ⇒ 2y+y = \(x+y+z+2\) (3)
Thay (1) vào (3) ta có: 2y + y = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) + 2
3y = \(\dfrac{5}{2}\) ⇒ y = \(\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Thay \(x=\dfrac{1}{2};y=\dfrac{5}{6}\) vào (1) ta có: \(\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{5}{6}+z\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{5}{6}\) + z = 0 ⇒ z = - \(\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Kết luận: (\(x;y;z\)) = (\(\dfrac{1}{2}\); \(\dfrac{5}{6}\); - \(\dfrac{5}{6}\))

TH1: x + y + z ≠≠ 0
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta có:
xy+z+1��+�+1 = yx+z+2��+�+2 = zx+y−3��+�−3 = x+y+zy+z+1+x+z+2+x+y−3�+�+��+�+1+�+�+2+�+�−3
= x+y+zx+y+z+x+y+z�+�+��+�+�+�+�+� = x+y+z2(x+y+z)�+�+�2(�+�+�) = 12
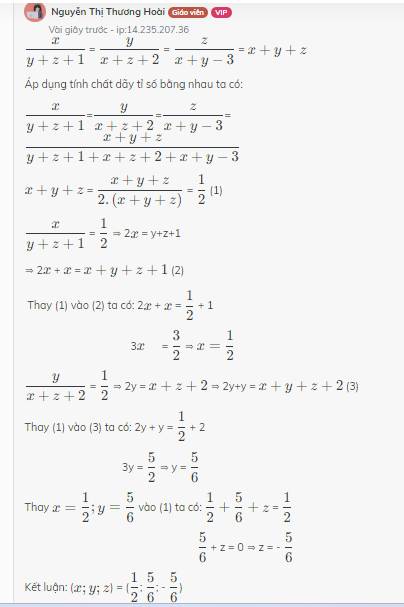
https://olm.vn/cau-hoi/tim-tat-ca-cac-so-xyz-biet-dfracxyz1dfracyxz2dfraczxy-3xyz-giair-chi-tiet-ho-e-vs-a.8297156371934
\(5\left(7-x\right)=-4\left(8x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow35-5x=-32x+8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x+32x=8-35\\ \Leftrightarrow27x=-27\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Mình ko thấy y mà chỉ thấy x thôi ak :))