x2+x=0
Tìm x
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(ac=-m^2-1< 0;\forall m\Rightarrow\) phương trình luôn có 2 nghiệm trái dấu với mọi m
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=m\\x_1x_2=-m^2-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2\left(-m^2-1\right)=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3m^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=\pm\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
xét delta
m2 + 4m2 + 4 = 5m2 + 4 > 0
=> phương trình luôn có 2 nghiệm x1x2
theo Vi-ét ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x1+x2=m\\x1x2=-m^2-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
x12 + x22 = 3
<=> ( x1 +x2 )2 - 2x1x2 = 3
<=> m2 + 2m2 + 2 = 3
<=> 3m2 = 1
=> m2 = \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
=> m = +- \(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)

Chọn A.
Với x >1 ta có hàm số f(x) = x2 liên tục trên khoảng (1; +∞). (1)
Với 0 < x < 1 ta có hàm số 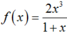 liên tục trên khoảng (0; 1). (2)
liên tục trên khoảng (0; 1). (2)
Với x < 0 ta có f(x) = x.sinx liên tục trên khoảng (-∞; 0). (3)
Với x = 1 ta có f(1) = 1; 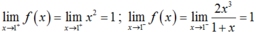
Suy ra ![]() .
.
Vậy hàm số liên tục tại x = 1.
Với x = 0 ta có f(0) = 0; 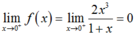 ;
;
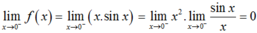 suy ra
suy ra ![]() .
.
Vậy hàm số liên tục tại x = 0. (4)
Từ (1), (2), (3) và (4) suy ra hàm số liên tục trên R.
Chọn A.

Chắc là tìm n?
\(\Delta'=\left(n-1\right)^2+n+1=n^2-n+2=\left(n-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{4}>0;\forall n\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Phương trình luôn có 2 nghiệm pb với mọi n
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(n-1\right)\\x_1x_2=-n-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đặt \(P=\left|x_1-x_2\right|\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\sqrt{\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2}=\sqrt{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2}\)
\(=\sqrt{4\left(n-1\right)^2+4\left(n+1\right)}=2\sqrt{n^2-n+2}\)
\(=2\sqrt{\left(n-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{4}}\ge\sqrt{7}\)
\(P_{min}=\sqrt{7}\) khi \(n-\dfrac{1}{2}=0\Rightarrow n=\dfrac{1}{2}\)

PT có 2 nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=\left(k-2\right)^2-\left(-2k-5\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k^2-4k+4+2k+10\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow k^2-2k+14\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow k\in R\)
Vậy PT luôn có 2 nghiệm
Áp dụng Viét: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(k-2\right)\left(1\right)\\x_1x_2=-2k-5\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lại có \(2x_1-x_2=7\left(3\right)\)
\(\left(1\right)\left(3\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(k-2\right)\\2x_1-x_2=7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x_1=2k+3\\x_2=2x_1-7\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{2k+3}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{4k+6}{2}-7=\dfrac{4k-8}{2}=2k-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay vào \(\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(2k+3\right)\left(2k-4\right)}{2}=-2k-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2k+3\right)\left(k-2\right)=-2k-5\\ \Leftrightarrow2k^2-k-6+2k+5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2k^2+k-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}k=\dfrac{1}{2}\\k=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)

Lời giải:
Để pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt $x_1,x_2$ thì:
$\Delta=(m+1)^2+8(m-1)>0$
$\Leftrightarrow m^2+10m-7>0(*)$
Áp dụng định lý Viet:
$x_1+x_2=\frac{m+1}{2}$
$x_1x_2=\frac{m-1}{2}$
Khi đó:
$x_1-x_2=x_1x_2$
$\Rightarrow (x_1-x_2)^2=(x_1x_2)^2$
$\Leftrightarrow (x_1+x_2)^2-4x_1x_2=(x_1x_2)^2$
$\Leftrightarrow (\frac{m+1}{2})^2-2(m-1)=(\frac{m-1}{2})^2$
$\Leftrightarrow m=2$ (thỏa mãn $(*)$)
Vậy......

\(x^2+2xy+y^2+6\left(x+y\right)+8=-y^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y\right)^2+6\left(x+y\right)+8\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y+2\right)\left(x+y+4\right)\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow-4\le x+y\le-2\)
\(\Rightarrow2016\le B\le2018\)
\(B_{min}=2016\) khi \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(-4;0\right)\)
\(B_{max}=2018\) khi \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(-2;0\right)\)

Ta có:
\(\text{∆}'=\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(m^2+m\right)\)
\(=m^2+2m+1-\left(m^2+m\right)=m+1\)
Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1, x2
\(\Leftrightarrow\text{∆}'>0\Leftrightarrow m+1>0\Leftrightarrow m>-1\)
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-ét, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1.x_2=m^2+m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{1}{x_1^2}+\dfrac{1}{x^2_2}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x_1^2+x^2_2}{x_1^2.x_2^2}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8[\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1.x_2]=x_1^2.x_2^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8[[2\left(m+1\right)]^2-2\left(m^2+m\right)]=\left(m^2+m\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8\left[4m^2+8m+4-2m^2-2m\right]=m^4+2m^3+m^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(8\left[2m^2+6m+4\right]=m^4+2m^3+m^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^4+2m^3-15m^2-48m-32=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m+1\right)\left(m^3+m^2-16m-32\right)=0\)
Vì m>-1
\(\Leftrightarrow m^3+m^2-16m-32=0\)
Đến đây nghiêm xấu bạn xem lại đề hoặc có thể sử dụng CTN Cardano

a=1; b=-4; c=-m^2+3
Δ=(-4)^2-4*1*(-m^2+3)
=16+4m^2-12=4m^2+4>=4>0
=>Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt
5x1+x2=0 và x1+x2=4
=>4x1=-4 và x1+x2=4
=>x1=-1 và x2=5
x1x2=-m^2+3
=>-m^2+3=-5
=>m^2-3=5
=>m^2=8
=>\(m=\pm2\sqrt{2}\)
Tìm x :
x2 + x = 0
=> x ( x + 1 ) = 0
=> x = 0 hoặc x + 1 = 0
=> x = 0 hoặc x = -1