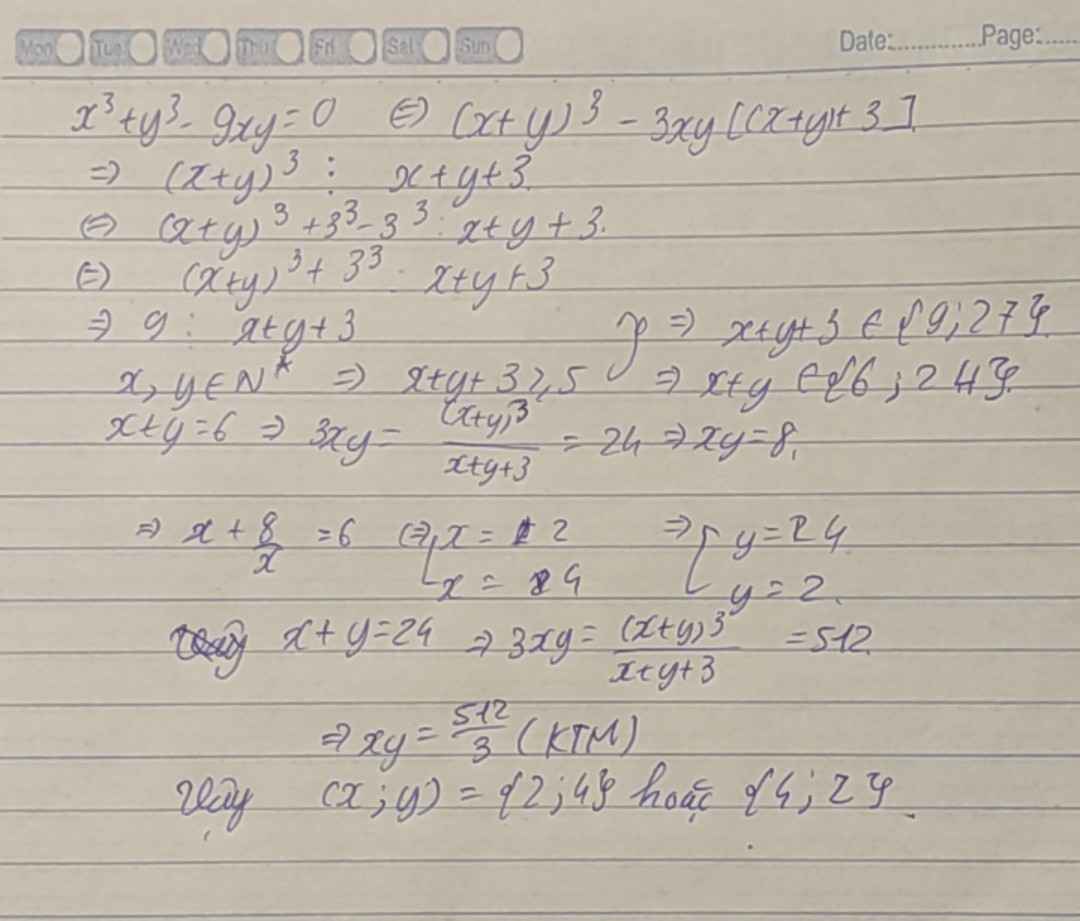tìm (x,y) nguyên dương thỏa \(x^3+y^3-9xy=0\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(x^3+y^3-9xy=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y\right)^3-3x^2y-3xy^2-9xy=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y\right)^3+27-3xy\left(x+y+3\right)=27\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y+3\right)\left[\left(x+y\right)^2-3\left(x+y\right)+9\right]-3xy\left(x+y+3\right)-27=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y+3\right)\left(x^2+2xy+y^2-3x-3y+9-3xy\right)-27=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y+3\right)\left(x^2-xy+y^2-3x-3y+9\right)-27=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y+3\right)\left(2x^2-2xy+2y^2-6x-6y+18\right)-54=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y+3\right)\left[\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(x-3\right)^2+\left(y-3\right)^2\right]=54\)
Do x, y > 0 => x + y + 3 > 3
Mà x, y nguyên dương => \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y+3\in Z^+\\\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(x-3\right)^2+\left(y-3\right)^2\in Z^+\end{matrix}\right.\)
Và \(\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(x-3\right)^2+\left(y-3\right)^2⋮2\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y+3=9\\\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(x-3\right)^2+\left(y-3\right)^2=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=6\\x^2-xy+y^2-3x-3y=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x\left(6-x\right)+\left(6-x\right)^2-3x-3\left(6-x\right)=-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\left(tm\right)\Leftrightarrow y=2\left(tm\right)\\x=2\left(tm\right)\Leftrightarrow y=4\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y+3=27\\\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(x-3\right)^2+\left(y-3\right)^2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=24\\x^2-xy+y^2-3x-3y=-8\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x\left(24-x\right)+\left(24-x\right)^2-3x-3\left(24-x\right)=-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-72x+512=0\) (vô nghiệm)
KL: Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm (x;y) = [(2;4);(4;2)]

Lời giải:
Ta có: \(x^3+y^3-9xy=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (x+y)^3-3xy(x+y)-9xy=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (x+y)^3=9xy+3xy(x+y)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (x+y)^3=3xy[(x+y)+3]\)
\(\Rightarrow (x+y)^3\vdots x+y+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (x+y)^3+3^3-3^3\vdots x+y+3\)
Theo phân tích hằng đẳng thức: \((x+y)^3+3^3\vdots x+y+3\)
Suy ra \(3^3\vdots x+y+3(1)\)
Vì \(x,y\in\mathbb{N}^*\Rightarrow x+y+3\geq 5(2)\)
Từ \((1);(2)\Rightarrow x+y+3\in\left\{9;27\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x+y\in\left\{6;24\right\}\)
Nếu \(x+y=6\Rightarrow 3xy=\frac{(x+y)^3}{x+y+3}=24\Rightarrow xy=8\)
Áp dụng hệ thức Viete suy ra $x,y$ là nghiệm của PT: \(X^2-6X+8=0\)
\(\Rightarrow (x,y)=(2,4)\) và hoán vị
Nếu \(x+y=24\Rightarrow 3xy=\frac{(x+y)^3}{x+y+3}=512\Rightarrow xy=\frac{512}{3}\not\in\mathbb{N}\) (loại)
Vậy \((x,y)=(2,4)\) và hoán vị

5x2+2y+y2-4x-40=0
△=(-4)2-4.5.(2y+y2-40)
△=16-40y-20y2+800
△=-(784+40y+20y2)
△=-(32y+8y+16y2+4y2+16+4+764)
△=-[(4y+4)2+(2y+2)2+764]<0
=>PHƯƠNG TRÌNH VÔ NGHIỆM.

a) \(6xy+4x-9y-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x.\left(3y+2\right)-9y-6-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x.\left(3y+x\right)-3.\left(3y+2\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right).\left(3y+2\right)=1\)
Mà \(x,y\in Z\Rightarrow2x-3;3y+2\in Z\)
Tự làm típ
\(A=x^3+y^3+xy\)
\(A=\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2-xy+y^2\right)+xy\)
\(A=x^2-xy+y^2+xy\)( vì \(x+y=1\))
\(A=x^2+y^2\)
Áp dụng bất đẳng thức Bunhiakovxky ta có :
\(\left(1^2+1^2\right)\left(x^2+y^2\right)\ge\left(x\cdot1+y\cdot1\right)^2=\left(x+y\right)^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2+y^2\right)\ge1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+y^2\ge\frac{1}{2}\)
Hay \(x^3+y^3+xy\ge\frac{1}{2}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow x=y=\frac{1}{2}\)


a) \(\left(x+y+1\right)^3=x^3+y^3+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y\right)^3+3\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y+1\right)+1=x^3+y^3+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+y^3+3xy\left(x+y\right)+3\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y+1\right)+1=x^3+y^3+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y+xy+1\right)=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y\right)\left[x\left(1+y\right)+1+y\right]=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(y+1\right)\left(x+y\right)=2\)
\(\Rightarrow x+1,y+1,x+y\) là các ước của 2.
Ta thấy 6 có 2 dạng phân tích thành tích 3 số nguyên là \(\left(2;1;1\right)\) và\(\left(2;-1;-1\right)\).
- Xét trường hợp \(\left(2;1;1\right)\). Ta có 3 trường hợp nhỏ:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=2\\y+1=1\\x+y=1\end{matrix}\right.\) ; \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=1\\y+1=2\\x+y=1\end{matrix}\right.\) ; \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=1\\y+1=1\\x+y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải ra ta có \(\left(x,y\right)=\left(1;0\right),\left(0;1\right)\).
- Xét trường hợp \(\left(2;-1;-1\right)\). Ta có 3 trường hợp nhỏ:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=2\\y+1=-1\\x+y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) ; \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=-1\\y+1=2\\x+y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) ; \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=-1\\y+1=1\\x+y=2\end{matrix}\right.\).
Giải ra ta có: \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;-2\right),\left(-2;1\right)\).
Vậy \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(0;1\right),\left(1;0\right),\left(1;-2\right),\left(-2;1\right)\)
b) \(y^2+2xy-8x^2-5x=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2xy+y^2\right)-\left(9x^2+5x\right)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y\right)^2-9\left(x^2+\dfrac{5}{9}x+\dfrac{25}{324}\right)+\dfrac{25}{36}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y\right)^2-9\left(x+\dfrac{5}{18}\right)^2=\dfrac{47}{36}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6^2.\left(x+y\right)^2-3^2.6^2\left(x+\dfrac{5}{18}\right)^2=47\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+6y\right)^2-\left(18x+5\right)^2=47\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+6y-18x-5\right)\left(6x+6y+18x+5\right)=47\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6y-12x-5\right)\left(24x+6y+5\right)=47\)
\(\Rightarrow\)6y-12x-5 và 24x+6y+5 là các ước của 47.
Lập bảng:
| 6y-12x-5 | 1 | 47 | -1 | -47 |
| 24x+6y+5 | 47 | 1 | -47 | -1 |
| x | 1 | \(\dfrac{-14}{9}\left(l\right)\) | \(\dfrac{-14}{9}\left(l\right)\) | 1 |
| y | 3 | \(\dfrac{50}{9}\left(l\right)\) | \(-\dfrac{22}{9}\left(l\right)\) | -5 |
Vậy pt đã cho có 2 nghiệm (x;y) nguyên là (1;3) và (1;-5)