
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(A=\left|3,7-x\right|+2,5\)
\(\Rightarrow GTLN\)là 2,5
Khi 3,7 - x = 0
x = -3,7



\(3,\\ a,\dfrac{2011}{2010}=1+\dfrac{1}{2010};\dfrac{3011}{3010}=1+\dfrac{1}{3010}\\ \dfrac{1}{2010}>\dfrac{1}{3010}\left(2010< 3010\right)\Rightarrow\dfrac{2011}{2010}>\dfrac{3011}{3010}\\ b,A=1-\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{3}+...+\dfrac{1}{99}-\dfrac{1}{100}\\ A=\left(1+\dfrac{1}{3}+...+\dfrac{1}{99}\right)-\left(\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}+...+\dfrac{1}{100}\right)\\ A=\left(1+\dfrac{1}{3}+...+\dfrac{1}{99}\right)+\left(\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}+...+\dfrac{1}{100}\right)-2\left(\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}+...+\dfrac{1}{100}\right)\\ A=\left(1+\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{3}+...+\dfrac{1}{100}\right)-\left(1+\dfrac{1}{2}+...+\dfrac{1}{50}\right)\\ A=\dfrac{1}{51}+\dfrac{1}{52}+....+\dfrac{1}{100}=B\)
\(4,\\ a,\dfrac{x+5}{x+1}=1+\dfrac{4}{x+1}\in Z\Leftrightarrow4⋮x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1\inƯ\left(4\right)=\left\{-4;-2;-1;1;2;4\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-5;-3;-2;0;1;3\right\}\\ b,\dfrac{2x+4}{x+3}=\dfrac{2\left(x+3\right)-2}{x+3}=2-\dfrac{2}{x+3}\in Z\\ \Leftrightarrow2⋮x+3\Leftrightarrow x+3\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{-2;-1;1;2\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-5;-4;-2;-1\right\}\)
\(5,\\ -\left|3x+\dfrac{1}{5}\right|\le0\\ \Leftrightarrow A=2017-\left|3x+\dfrac{1}{5}\right|\le2017\\ A_{max}=2017\Leftrightarrow3x+\dfrac{1}{5}=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{15}\\ 6,\\ \left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\\\left|2y-\dfrac{3}{4}\right|\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow A=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\left|2y-\dfrac{3}{4}\right|+\dfrac{175}{3}\ge\dfrac{175}{3}\\ A_{min}=\dfrac{175}{3}\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{1}{2}=0\\2y-\dfrac{3}{4}=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\y=\dfrac{3}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 5:
\(A=-\left|3x+\dfrac{1}{5}\right|+2017\le2017\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x=-\dfrac{1}{15}\)

ta có P(x)=x^2+ax+b ; Q(x)=x^2+cx+d
ta có x1 và x2 là nghiêm của P(x)Dán
nên \(x_1^2+ax_1+b=0;x_2^2+ax_2+b=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x_1^2=-ax_1-b\) và \(x_2^2=-ax_2-b\) (1)
Ta có x1,x2 là nghiêm của Q(x)
nên \(x_1^2+cx_1+d=0;x_2^2+cx_2+d=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x_1^2=-cx_1-d\)và \(x_2^2=-cx_2-d\) (2)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra \(-ax_1-b=-cx_1-d\\ -ax_2-b=-cx_2-d\)
Do đó \(ax_1+b=cx_1+d\\ ax_2+b=+cx_2+d\)
Suy ra\(x_1^2+ax_1+b=x^2_1+cx_1+d\\ x^2_2+ax_2+b=x^2_2+cx_2+d\)
Nên P(x)=Q(x)
Q(x) =x2 +ax + b
P(x) = x2 +cx + d
Vì x1;x2 đều là nghiệm của P(x); Q(x)
=>x1;x2 là nghiệm của : P(x) - Q(x)=(c-a)x +(d-b)
=> PT: (c-a)x +(d-b) =0 có 2 nghiệm x1;x2
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}c-a=0\\d-b=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=c\\b=d\end{matrix}\right.\)
Nên => P(x) = Q(x) dpcm

Lời giải:
Để 2 tam giác bằng nhau theo TH g.c.g thì cần thêm điều kiện:
TH1:
$\widehat{A}=\widehat{A'}$
$\widehat{B}=\widehat{B'}$
TH2:
$\widehat{A}=\widehat{A'}$
$\widehat{C}=\widehat{C'}$
TH3:
$\widehat{B}=\widehat{B'}$
$\widehat{C}=\widehat{C'}$
Cách 1:
\(\widehat{A}=\widehat{A'}\) và \(\widehat{B}=\widehat{B'}\)
Cách 2:
\(\widehat{A}=\widehat{A'}\) và \(\widehat{C}=\widehat{C'}\)
Cách 3:
\(\widehat{B}=\widehat{B'}\) và \(\widehat{C}=\widehat{C'}\)

Lời giải:
a. Với $n$ nguyên khác -3, để $B$ nguyên thì:
$2n+9\vdots n+3$
$\Rightarrow 2(n+3)+3\vdots n+3$
$\Rightarrow 3\vdots n+3$
$\Rightarrow n+3\in\left\{\pm 1; \pm 3\right\}$
$\Rightarrow n\in\left\{-2; -4; 0; -6\right\}$
b.
$B=\frac{2n+9}{n+3}=\frac{2(n+3)+3}{n+3}=2+\frac{3}{n+3}$
Để $B_{\max}$ thì $\frac{3}{n+3}$ max
Điều này đạt được khi $n+3$ là số nguyên dương nhỏ nhất
Tức là $n+3=1$
$\Leftrightarrow n=-2$
c. Để $B$ min thì $\frac{3}{n+3}$ min
Điều này đạt được khi $n+3$ là số nguyên âm lớn nhất
Tức là $n+3=-1$
$\Leftrightarrow n=-4$

b: AB//CD
=>\(\widehat{ABC}+\widehat{BCD}=180^0\)(hai góc trong cùng phía)
=>\(\widehat{BCD}=180^0-60^0=120^0\)
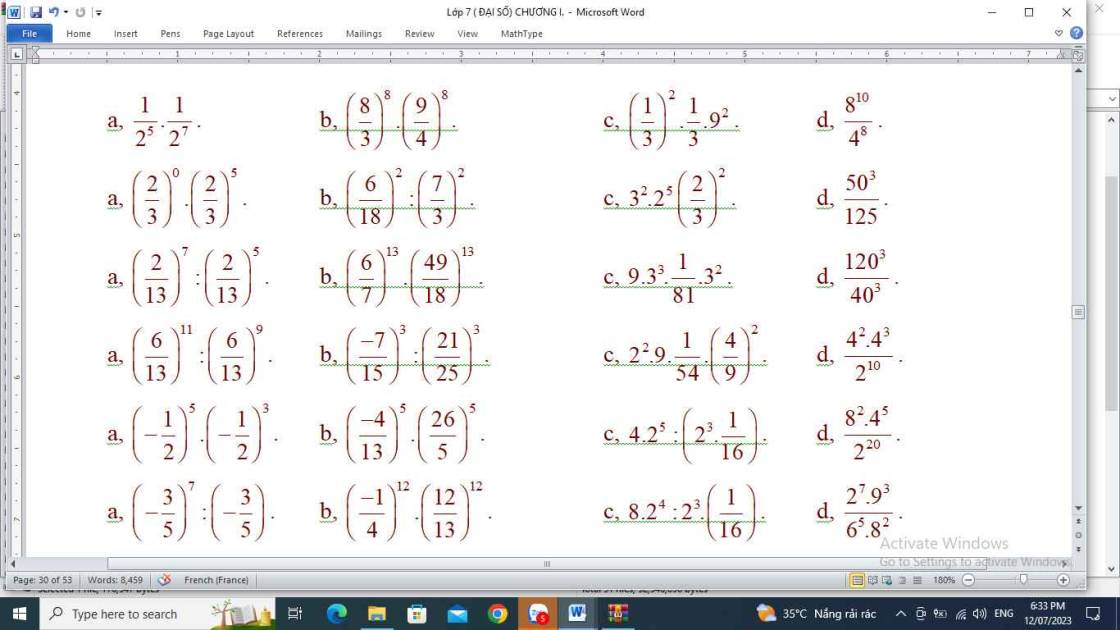 mik cần làm tất cả cột b nha
mik cần làm tất cả cột b nha  Mấy pn giúp mik làm bài 3 nha ! (^^)
Mấy pn giúp mik làm bài 3 nha ! (^^) .
.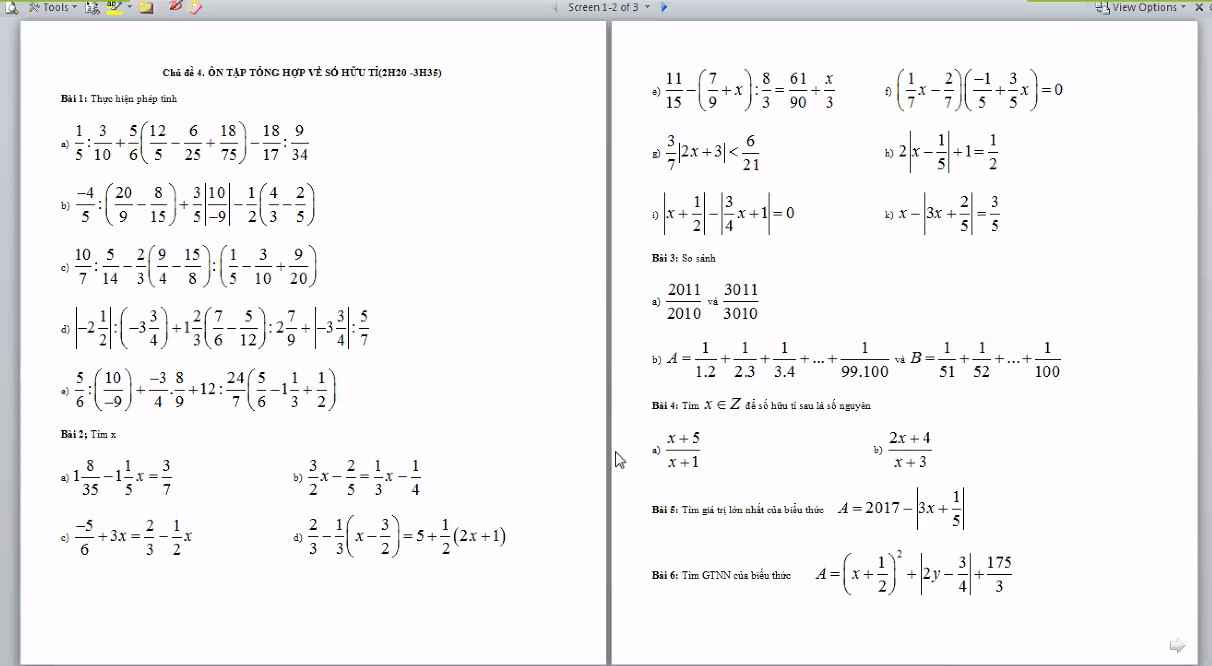



Mình làm rồi nha, bạn check lại tb.