
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



m2 -8m -16 =0
m2 -2.4m -4\(^2\) =0
(m - 4)\(^2\) = 0
=> m -4 = 0
=> m = 4
HT
m2 - 8m - 16 = 0 <=> m2 - 8m + 16 - 32 = 0
<=> ( m - 4 )2 - ( 4√2 )2 = 0 <=> ( m - 4 - 4√2 )( m - 4 + 4√2 ) = 0
<=> m = 4 ± 4√2


\(\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{y}{2}-\frac{\left(x+y\right)}{5}=0,1\\\frac{y}{5}-\frac{\left(x-y\right)}{2}=0.1\end{cases}}\)
\(\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{\left(x+y\right)}{5}=\frac{y-0,2}{2}\\\frac{y}{5}-\frac{\left(x-y\right)}{2}=0,1\end{cases}}\)
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x+y=\frac{5y-1}{2}\\\frac{y}{5}-\frac{\left(x-y\right)}{2}=0,1\end{cases}}\)
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5y-1}{2}-\frac{2y}{2}=\frac{3y-1}{2}\\\frac{y}{5}-\frac{\left(x-y\right)}{2}=0,1\end{cases}}\)
Ta thay x vào biểu thức \(\frac{y}{5}-\frac{\left(x-y\right)}{2}\)ta đc
\(\frac{y}{5}-\frac{\left(\frac{3y-1}{2}-y\right)}{2}=0,1\)
\(\frac{3y-1-2y}{2}=\frac{y}{5}-\frac{0,5}{5}\)
\(\frac{y-1}{2}=\frac{y-0,5}{5}\)
\(5y-5=2y-1\Leftrightarrow5y-5-2y+1=0\Leftrightarrow3y-4=0\Leftrightarrow y=\frac{4}{3}\)
Thay y vào biểu thức \(\frac{3y-1}{2}\)ta đc
\(x=\frac{3.\frac{4}{3}-1}{2}=\frac{3}{2}\)
Vậy \(\left\{x;y\right\}=\left\{\frac{3}{2};\frac{4}{3}\right\}\)

Để A là số nguyên thì
\(2x+12\ge x^2+x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3\le x\le4\)
Kết hợp với điều kiện đề bài được
\(1\le x\le4\)
Thế lần lược \(x=1;2;3;4\)cái nào làm cho A nguyên thì chọn

ĐKXĐ : \(x\ge1\)
\(\sqrt{x+2\sqrt{x-1}}-\sqrt{x-2\sqrt{x-1}}=\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x-1}+1\right)^2}-\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x-1}-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\sqrt{x-1}+1-\left|\sqrt{x-1}-1\right|\)
Xét các trường hợp :
1. Nếu \(1\le x\le2\)thì \(\sqrt{x-1}+1-\left|\sqrt{x-1}-1\right|=\sqrt{x-1}+1-\left(1-\sqrt{x-1}\right)=2\sqrt{x-1}\le2\)
2. Nếu \(x>2\) thì
\(\sqrt{x-1}+1-\left|\sqrt{x-1}-1\right|=\sqrt{x-1}+1-\sqrt{x-1}+1=2\)
Gộp hai trường hợp có đpcm.

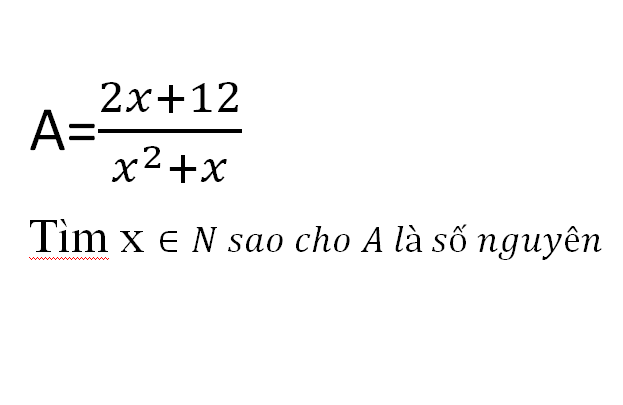

Bài 1: Để căn thức có nghĩa thì \(8x+2\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge\frac{-1}{4}\)
Bài 2: a) \(\sqrt{3}-\frac{1}{3}.\sqrt{27}+2\sqrt{507}=\sqrt{3}-\frac{1}{3}.3\sqrt{3}+2\sqrt{507}=2\sqrt{507}\)
b) \(\frac{1}{3-\sqrt{2}}=\frac{3+\sqrt{2}}{\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(3+\sqrt{2}\right)}=\frac{3+\sqrt{2}}{7}\)
c) \(5\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{\left(5\sqrt{2}-1\right)^2}=5\sqrt{2}-5\sqrt{2}+1=1\)
Bài 2: \(3\sqrt{4x+20}-4\sqrt{5+x}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6\sqrt{x+5}-4\sqrt{x+5}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x+5}=6\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+5}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+5=9\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
Vậy x = 4