Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



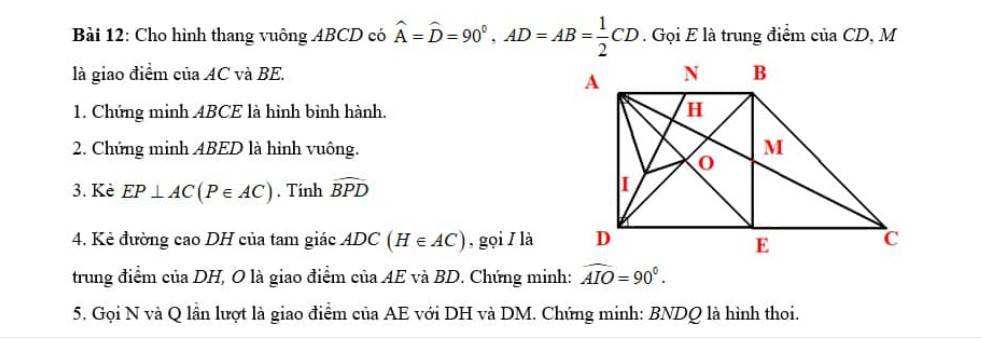
a: Xét tứ giác DIHK có
góc DIH=góc DKH=góc KDI=90 độ
nên DIHK là hình chữ nhật
b: Xét tứ giác IHAK có
IH//AK
IH=AK
Do đó: IHAK là hình bình hành
=>B là trung điểm chung của IA và HK
Xét ΔIKA có IC/IK=IB/IA
nên BC//KA
Xét ΔIDA có IB/IA=IM/ID
nên BM//DA
=>B,C,M thẳng hàng

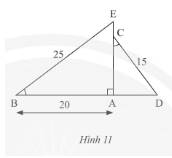
Những hình khối có dạng ở hình 11 được gọi là hình chóp tứ giác đều.

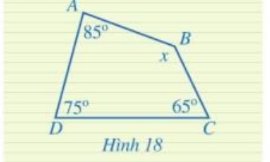
Xét tứ giác ABCD có:
\(\begin{array}{l} \widehat A + \widehat B + \widehat C + \widehat D = {360^0}\\{85^0} + x + {65^0} + {75^0} = {360^0}\\x = {360^0} - {85^0} - {65^0} - {75^0} = {135^0}\end{array}\)

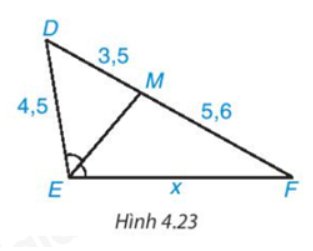
Trong Hình 4.23 có \(\widehat {DME} = \widehat {MEF}\) nên EM là tia phân giác của \(\widehat {{\rm{DEF}}}\).
Áp dụng tính chất đường phân giác của tam giác, ta có:
\(\dfrac{{E{\rm{D}}}}{{EF}} = \dfrac{{M{\rm{D}}}}{{MF}}\) hay \(\dfrac{{4,5}}{x} = \dfrac{{3,5}}{{5,6}}\)
Suy ra: \(x = \dfrac{{5,6.4,5}}{{3,5}} = 7,2\)(đvđd)
Vậy x = 7,2 (đvđd).

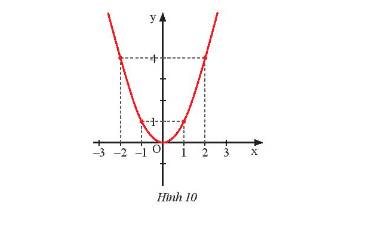
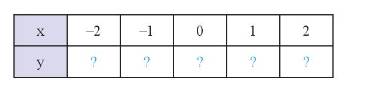
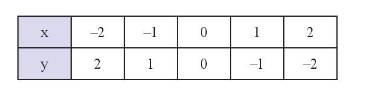
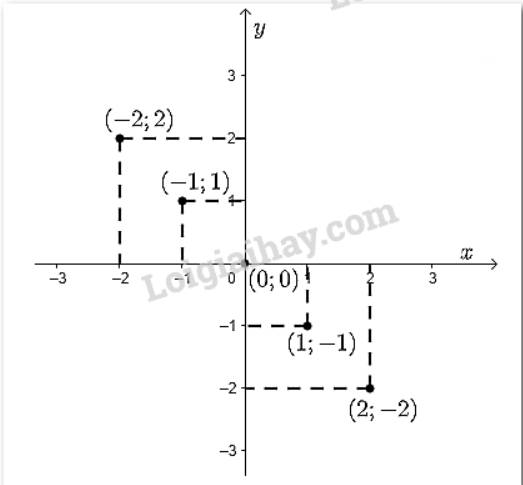
Đồ thị hàm số là tập hợp các điểm có tọa độ \(\left( { - 2;2} \right);\left( { - 1;1} \right);\left( {0;0} \right);\left( {1; - 1} \right);\left( {2; - 2} \right)\) được vẽ trên mặt phẳng tọa độ như hình dưới đây:

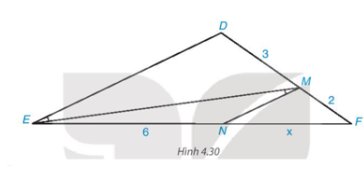
Trong Hình 4.30 có \(\widehat {DEM} = \widehat {EMN}\) mà hai góc này ở vị trí so le trong nên MN // DE.
Áp dụng định lí Thalès vào tam giác DEF có MN // DE, ta có:
\(\dfrac{{MF}}{{M{\rm{D}}}} = \dfrac{{NF}}{{NE}}\) hay \(\dfrac{2}{3} = \dfrac{x}{6}\)
Suy ra \(x = \dfrac{{2.6}}{3} = 4\) (đvđd).
Vậy x = 4 (đvđd).

Xét \(\Delta ABE\) và \(\Delta ACD\) có:
\(\widehat {EBA} = \widehat {ACD}\) (giả thuyết)
\(\widehat {BAE} = \widehat {CAD} = 90^\circ \)
Do đó, \(\Delta ABE\backsim\Delta ACD\) (g.g)
Vì \(\Delta ABE\backsim\Delta ACD\) nên \(\frac{{AB}}{{AC}} = \frac{{EB}}{{CD}}\) (các cặp cạnh tương ứng)
Thay số, \(\frac{{20}}{{AC}} = \frac{{25}}{{15}} \Rightarrow AC = \frac{{20.15}}{{25}} = 12\)cm.
Áp dụng định lí Py – ta – go cho \(\Delta ABE\) vuông tại \(A\) ta có:
\(B{E^2} = A{E^2} + A{B^2} \Leftrightarrow A{E^2} = B{E^2} - A{B^2} = {25^2} - {20^2} = 225 \Rightarrow AE = \sqrt {225} = 15\)cm.
Độ dài \(CE\) là:
15 – 12 = 3cm
Vậy \(CE = 3cm.\)