
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a)
`x^2+3x+2=0`
`<=>x^2+2x+x+2=0`
`<=>x(x+2)+(x+2)=0`
`<=>(x+2)(x+1)=0`
`<=>x+2=0` hoặc `x+1=0`
`<=>x=-2` hoặc `x=-1`
b)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3y=5\\3x+2y=4\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-9y=15\\3x+2y=4\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-11y=11\\x-3y=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-1\\x-3\cdot\left(-1\right)=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

Tham khảo :
a) \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-y=14\\3x-4y=1\end{cases}}\)
b) \(\hept{\begin{cases}14x+27y=25\\4x+y=1\end{cases}}\)

a) Phương trình bậc nhất một ẩn là phương trình có dạng ax + b = 0 (với a ≠ 0)
Ví dụ: 2x + 4 = 0
a = 2; b = 4
b) Công thức tính thể tích hình hộp chữ nhật:
V = Sh
Với V là thể tích, S là diện tích 1 đáy, h là chiều cao
c) 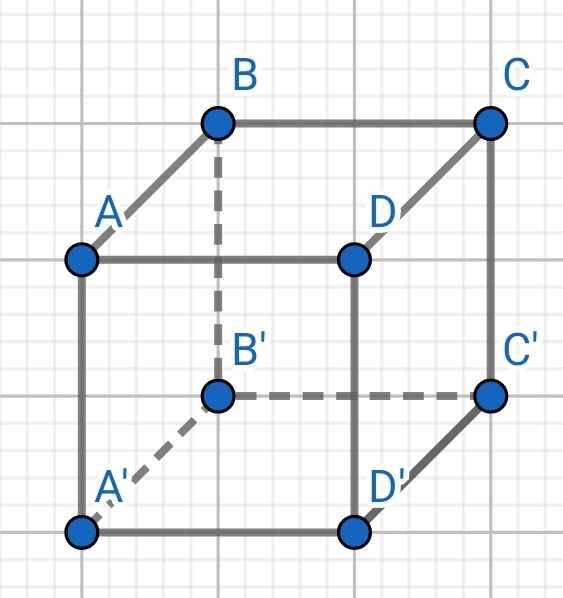
Thể tích:
V = AB.AD.AA'
= 12 . 16 . 25 = 4800 (cm³)
a: ax+b=0(a<>0) là phương trình bậc nhất một ẩn
b: V=a*b*c
a,b là chiều dài, chiều rộng
c là chiều cao
c: V=12*16*25=4800cm3

\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}10x-8y=12\\10x+15y=35\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

e.
$x^4-4x^3-8x^2+8x=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x^3-4x^2-8x+8)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x[x^2(x+2)-6x(x+2)+4(x+2)]=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x+2)(x^2-6x+4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x+2=0$ hoặc $x^2-6x+4=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x=-2$ hoặc $x^2-6x+4=0$
Xét riêng pt $x^2-6x+4=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-3)^2=5$
$\Leftrightarrow x-3=\pm \sqrt{5}$
$\Leftrightarrow x=3\pm \sqrt{5}$
Vậy.........
f.
$2x^2+3xy+y^2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (2x^2+2xy)+(xy+y^2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x(x+y)+y(x+y)=)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+y)(2x+y)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x+y=0$ hoặc $2x+y=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-y$ hoặc $x=\frac{-y}{2}$

a. Thay m = 1 vào hệ ta dc: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-y=1\\\frac{x}{2}+\frac{y}{3}=8\end{cases}}\) <=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-y=1\\3x+2y=48\end{cases}}\) <=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}3x-3y=3\\3x+2y=48\end{cases}}\)<=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-y=1\\-5y=-45\end{cases}}\)<=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x=y+1=9+1=10\\y=9\end{cases}}\)
Vậy no cua hpt khi m = 1 là: (10;9)
b. Xét hệ: \(\hept{\begin{cases}mx-y=1\\3x+2y=48\end{cases}}\) <=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}2mx-2y=2\\3x+2y=48\end{cases}}\)<=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}\left(2m+3\right)x=50\left(1\right)\\3x+2y=48\end{cases}}\)
Hệ pt vô nghiệm <=> (1) vô nghiệm 2m + 3 = 0 <=> m = \(-\frac{3}{2}\)
Vậy khi m = -3/2 thì hệ pt vô nghiệm

Xét hệ phương trình :\(\hept{\begin{cases}mx-y=1\\\frac{x}{2}-\frac{y}{3}=334\end{cases}}\)
a, Khi m = 1 ta có hệ phương trình : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-y=1\\3x-2y=2004\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=2002\\y=2001\end{cases}}}\)
b, \(\hept{\begin{cases}mx-y=1\\\frac{x}{2}-\frac{y}{3}=334\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}mx-y=1\\3x-2y=2004\end{cases}}}\)
Hệ phương trình vô nghiệm khi \(\frac{m}{3}=\frac{1}{2}\ne\frac{1}{2004}\Leftrightarrow m=\frac{3}{2}\)
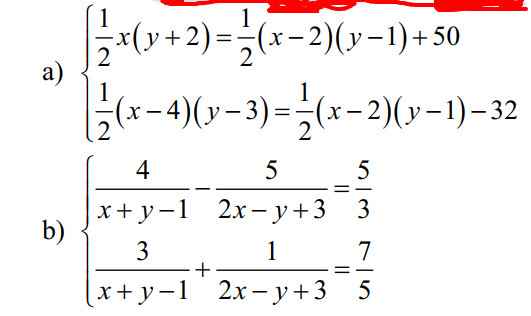

 giải hệ phương trình:(
giải hệ phương trình:(
a.
HPT \(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x(y+2)=(x-2)(y-1)+100\\ (x-4)(y-3)=(x-2)(y-1)-64\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} 2x=-x-2y+102\\ -3x-4y+12=-x-2y-62\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} 3x+2y=102\\ 2x+2y=74\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x=28\\ y=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
b. Đặt $\frac{1}{x+y-1}=a; \frac{1}{2x-y+3}=b$ thì hpt trở thành:
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} 4a-5b=\frac{5}{3}\\ 3a+b=\frac{7}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} a=\frac{26}{57}\\ b=\frac{3}{95}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x+y-1=\frac{57}{26}\\ 2x-y+3=\frac{95}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x+y=\frac{83}{26}\\ 2x-y=\frac{86}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x=\frac{2485}{234}\\ y=\frac{-869}{117}\end{matrix}\right.\)