Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) Xét pt \(x^2-\left(2m-3\right)x+m^2-3m=0\)
Ta có \(\Delta=\left[-\left(2m-3\right)^2\right]-4.1\left(m^2-3m\right)\)\(=4m^2-12m+9-4m^2+12m\)\(=9>0\)
Vậy pt đã cho luôn có 2 nghiệm phân biệt với mọi m.
Câu b mình nhìn không rõ đề, bạn sửa lại nhé.

\(\Delta'=\left(m-1\right)^2+2m=m^2+1>0;\forall m\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Pt luôn có 2 nghiệm pb với mọi m
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=-2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Cộng vế với vế: \(x_1x_2+x_1+x_2=-2\) (1)
\(x_1^2+x_1-x_2=5-2m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2+x_1-x_2=5+x_1x_2\) (2)
Cộng vế với vế (1) và (2):
\(\Rightarrow x_1^2+2x_1=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2+2x_1-3=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=1\Rightarrow x_2=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\x_1=-3\Rightarrow x_2=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) (thế \(x_1\) vào (1) để tính ra \(x_2\))
Thế vào \(x_1x_2=-2m\Rightarrow m=-\dfrac{x_1x_2}{2}\Rightarrow m=\pm\dfrac{3}{4}\)

a, - Thay m = 6 vào phương trình ta được : \(x^2-5x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
b, - Xét phương trình trên có : \(\Delta=b^2-4ac=25-4m\)
- Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt <=> \(m< \dfrac{25}{4}\)
- Theo viet ta có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=5\\x_1x_2=m\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Ta có : \(\left|x_1-x_2\right|=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2_1+x^2_2-2\left|x_1x_2\right|=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2\left(x_1x_2+\left|x_1x_2\right|\right)=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m+\left|m\right|=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=4\)
Vậy ...

a: Thay m=3 vào pt, ta được:
\(x^2-4x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=5\)
hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{5}+2\\x=-\sqrt{5}+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(-4\right)^2-4\left(-2m+5\right)\)
\(=16+8m-20=8m-4\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm thì 8m-4>=0
hay m>=1/2
Theo đề, ta có: \(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2+3x_1x_2-3\left(x_1+x_2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4^2-3\cdot4+3\left(-2m+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4-6m+15=0\)
=>-6m+19=0
hay m=19/6(nhận)

a: Để phương trình có hai nghiệm trái dấu thì \(\left(m^2-m-6\right)\cdot1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-3\right)\left(m+2\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2< m< 3\)

a, bạn tự làm
b, Thay x = 3 vào pt trên ta được
\(9-3m-3=0\Leftrightarrow6-3m=0\Leftrightarrow m=2\)
Thay m = 2 vào ta được \(x^2-2x-3=0\)
Ta có a - b + c = 1 + 2 - 3 = 0
vậy pt có 2 nghiệm x = -1 ; x = 3
c, \(\Delta=m^2-4\left(-3\right)=m^2+12>0\)
vậy pt luôn có 2 nghiệm pb
\(x_1x_2+5\left(x_1+x_2\right)-1997=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-3+5m-1997=0\Leftrightarrow5m-2000=0\Leftrightarrow m=400\)

a: \(\Delta=\left(2m-2\right)^2-4\left(-m-3\right)\)
\(=4m^2-8m+4+4m+12\)
\(=4m^2-4m+16\)
\(=\left(2m-1\right)^2+15>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt
b: Theo đề, ta có:
\(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2>=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-2\right)^2-2\left(-m-3\right)>=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4+2m+6-10>=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-6m>=0\)
=>m<=0 hoặc m>=3/2

b) phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(m-1\right)\left(m+3\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+1-m^2-3m+m+3\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4m+4\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le1\)
Ta có: \(x_1^2+x_1x_2+x_2^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=1\)
Theo viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[-2\left(m-1\right)^2\right]-2\left(m+3\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4-2m-6-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-10m-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(ktm\right)\\m_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\)

a, bạn tự làm
b, \(\Delta'=\left(m+2\right)^2-\left(m^2+m+3\right)=m^2+4m+4-m^2-m-3\)
\(=3m+1\)để pt có 2 nghiệm \(m\ge-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Ta có \(\dfrac{x_1^2+x_2^2}{x_1x_2}=4\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2}{x_1x_2}=4\Rightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-6x_1x_2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow4\left(m+2\right)^2-6\left(m^2+m+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+16m+16-6m^2-6m-18=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2m^2+10m-2=0\Leftrightarrow m^2-5m+1=0\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{21}}{2}\)(tm)
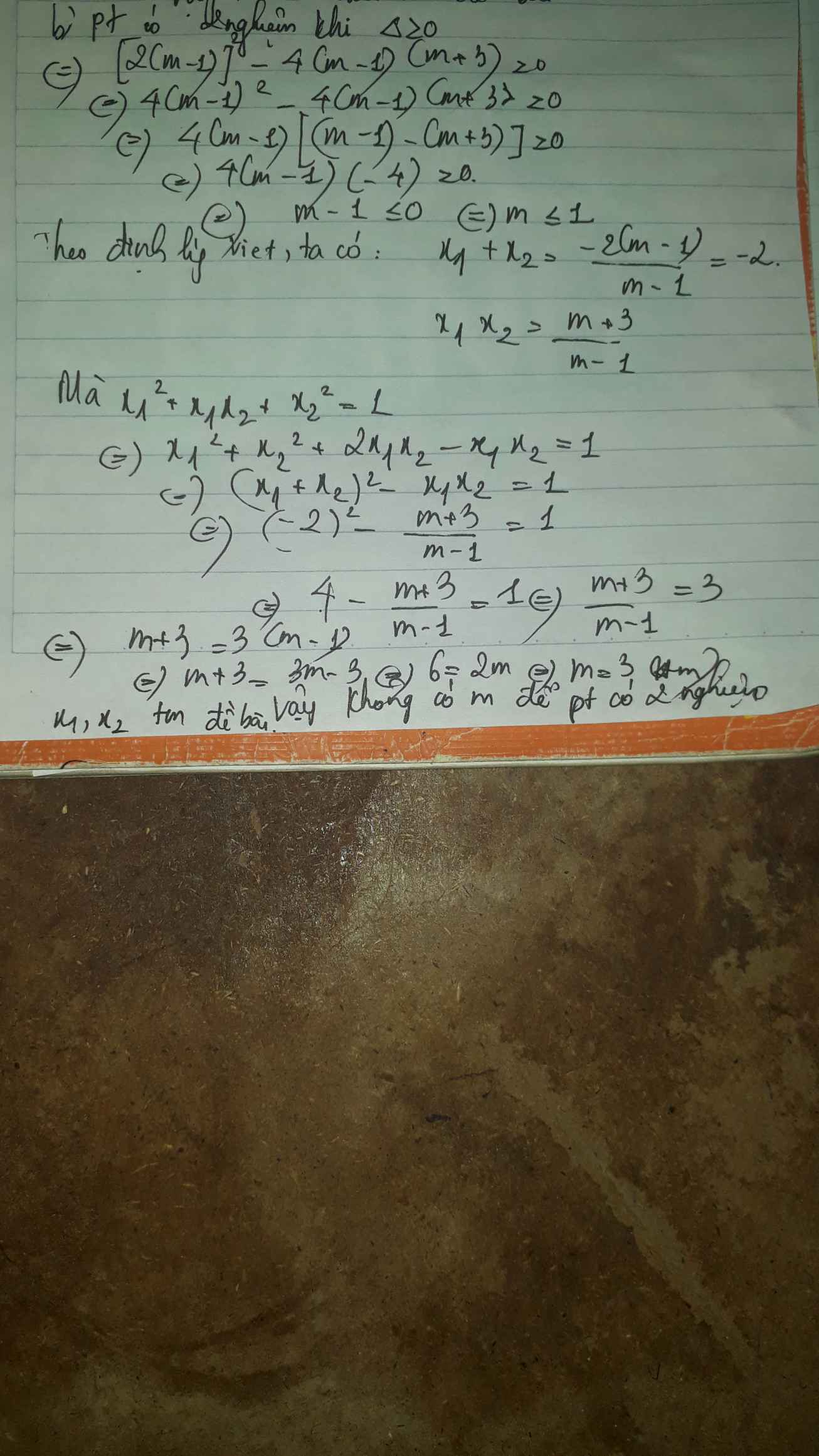
a) Pt đã cho có \(\Delta=\left[-\left(2m-3\right)\right]^2-4\left(m^2-3m\right)=4m^2-12m+9-4m^2+12m\)\(=9>0\). Vậy pt đã cho luôn có 2 nghiệm khi m thay đổi.
b) Pt đã cho cho 2 nghiệm phân biệt:
\(x_1=\dfrac{-\left[-\left(2m-3\right)\right]-\sqrt{9}}{2}=\dfrac{2m-3-3}{2}=m-3\)
\(x_2=\dfrac{-\left[-\left(2m-3\right)\right]+\sqrt{9}}{2}=\dfrac{2m-3+3}{2}=m\)
Vậy để pt đã cho có 2 nghiệm \(x_1,x_2\) thỏa mãn \(1< x_1< x_2< 6\) thì \(1< m-3< m< 6\) \(\Leftrightarrow4< m< 6\)