
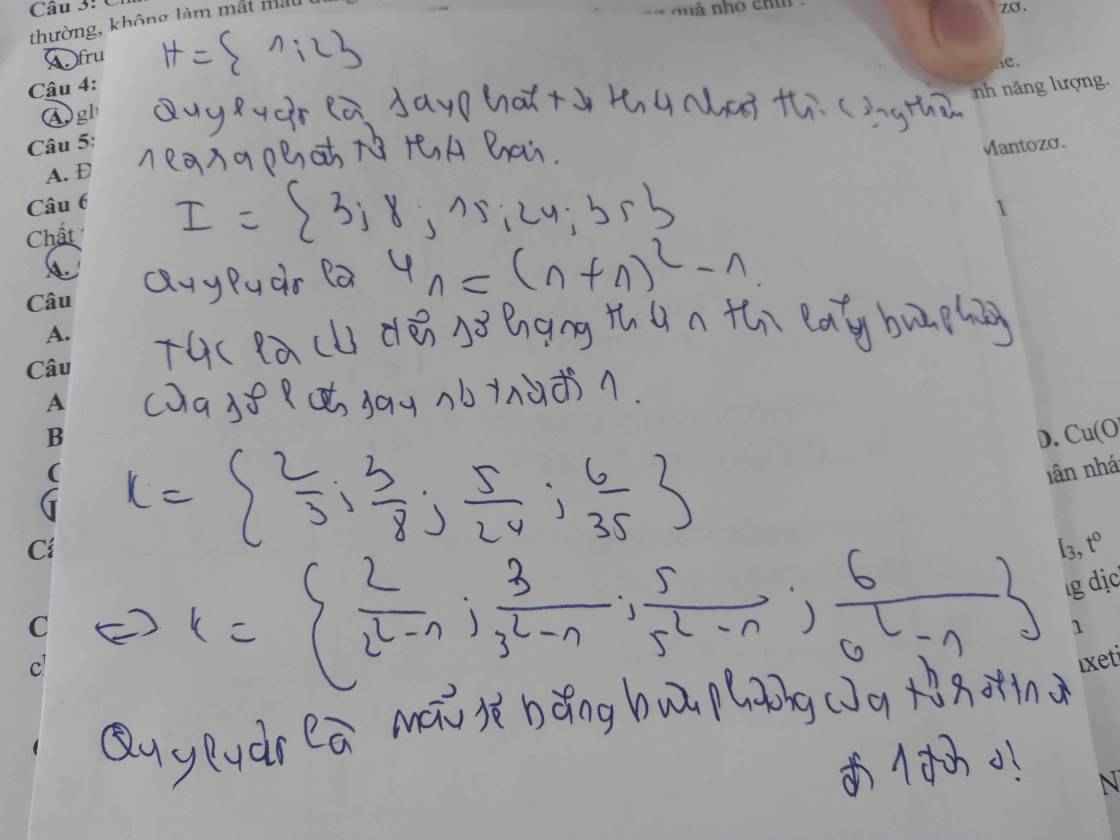
I= {3;8;15;24;35}
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

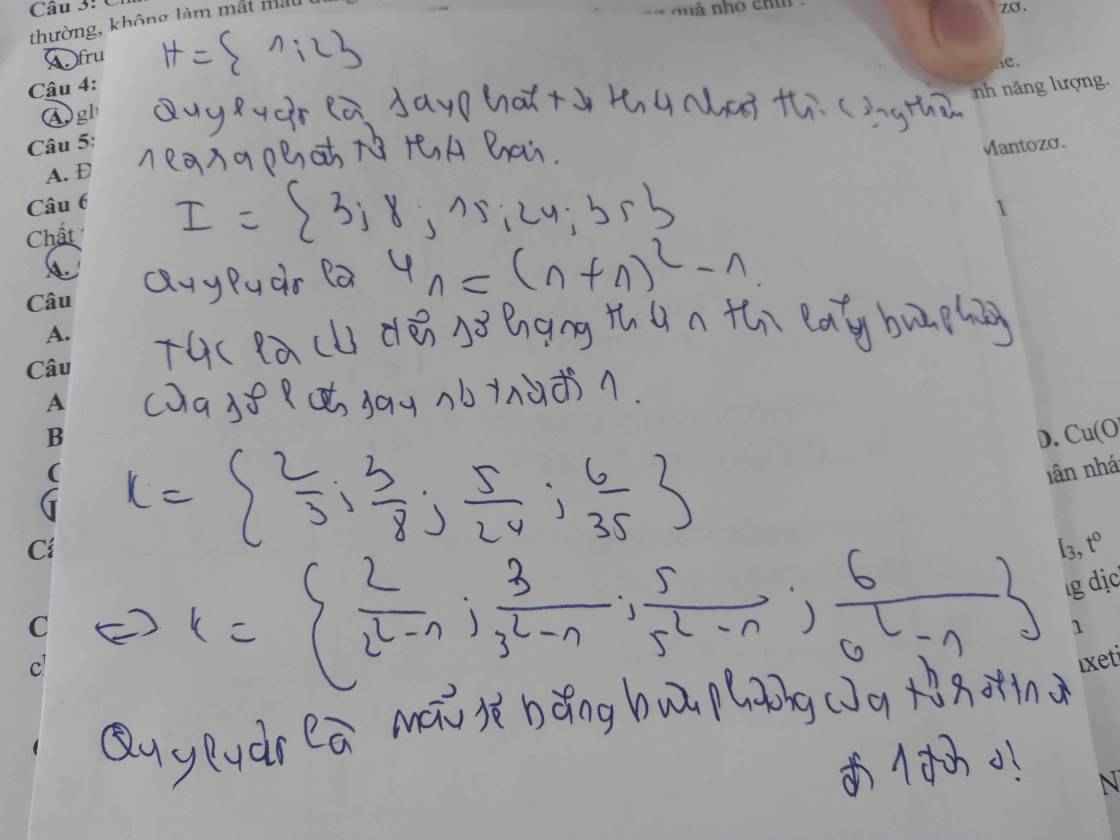

a) A = {\(\dfrac{1}{n\left(n+1\right)}\)| \(n\in\mathbb{N},1\le n\le5\)}
b) B = {\(\dfrac{1}{n^2-1}\)|\(n\in\mathbb{N},2\le n\le6\)\(\)}

Bài 2:
a: A={1/x(x+1)|\(x\in N;1< =x< =5\)}
b: B={x/(x^2-1)|\(x\in N;2< =x< =6\)}

a) \(A=\left\{x\in N|x=3k+1;0\le k\le3;k\in z\right\}\)
b) \(B=\left\{x\in Q^+|x=\dfrac{k}{k^2-1};2\le k\le6;k\in N\right\}\)

Bài 2:
a: \(A=11+\dfrac{3}{13}-2-\dfrac{4}{7}-5-\dfrac{3}{13}\)
\(=4-\dfrac{4}{7}=\dfrac{24}{7}\)
b: \(B=6+\dfrac{4}{9}+3+\dfrac{7}{11}-4-\dfrac{4}{9}\)
\(=5+\dfrac{7}{11}=\dfrac{62}{11}\)
c: \(C=\dfrac{-5}{7}\left(\dfrac{2}{11}+\dfrac{9}{11}\right)+1+\dfrac{5}{7}=1\)
d: \(D=\dfrac{7}{10}\cdot\dfrac{8}{3}\cdot20\cdot\dfrac{3}{8}\cdot\dfrac{5}{28}\)
\(=\dfrac{20}{10}\cdot7\cdot\dfrac{8}{3}\cdot\dfrac{3}{8}\cdot\dfrac{5}{28}=2\cdot\dfrac{5}{4}=\dfrac{5}{2}\)