\(x^2-12x+37=0\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) x2 + y2 - 12x + 2y + 37 = 0
<=> (x2 - 12x + 36) + (y2 + 2y + 1) = 0
<=> (x - 6)2 + (y + 1)2 = 0
<=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-6=0\\y+1=0\end{cases}}\) <=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x=6\\y=-1\end{cases}}\)
b) x2 + 2y2 - 2xy - 2x + 2 = 0
<=> (x2 - 2xy + y2) - 2(x - y) + 1 + (y2 - 2y + 1) = 0
<=> (x - y)2 - 2(x - y) + 1 + (y - 1)2 = 0
<=> (x - y - 1)2 + (y - 1)2 = 0
<=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-y-1=0\\y-1=0\end{cases}}\) <=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x=y+1\\y=1\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x=2\\y=1\end{cases}}\)
a) x2 + y2 - 12x + 2y + 37 = 0
⇔ ( x2 - 12x + 36 ) + ( y2 + 2y + 1 ) = 0
⇔ ( x - 6 )2 + ( y + 1 )2 = 0
\(\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x-6\right)^2\ge0\forall x\\\left(y+1\right)^2\ge0\forall y\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\left(x-6\right)^2+\left(y+1\right)^2\ge0\forall x,y\)
Đẳng thức xảy ra ⇔ \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-6=0\\y+1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=6\\y=-1\end{cases}}\)
⇔ x = 6 ; y = -1
b) x2 + 2y2 - 2xy - 2x + 2 = 0
Nhân 2 vào từng vế
⇔ 2( x2 + 2y2 - 2xy - 2x + 2 ) = 2.0
⇔ 2x2 + 4y2 - 4xy - 4x + 4 = 0
⇔ ( x2 - 4xy + 4y2 ) + ( x2 - 4x + 4 ) = 0
⇔ ( x - 2y )2 + ( x - 2 )2 = 0
\(\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x-2y\right)^2\ge0\forall x,y\\\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\forall x\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\left(x-2y\right)^2+\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\forall x,y\)
Đẳng thức xảy ra ⇔ \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-2y=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=2\\y=1\end{cases}}\)
⇔ x = 2 ; y = 1

x2 \(\ge\) 0 => \(5x^2=0\) hoặc \(5x^2\ge5\)
<=> \(5x^2-12x=0\) hoặc \(5x^2-12x\ge-x^2\)
<=> \(5x^2-12x+3=37\) hoặc \(5x^2-12x+37\ge x^2+37\)
=> ĐPCM

Lớp 6 nên chưa pít nhìu :v
\(x^2-12x+37\)
\(=x^2-6x-6x+36+1\)
\(=x\left(x-6\right)-6\left(x-6\right)+1\)
\(=\left(x-6\right)\left(x-6\right)+1\)
\(=\left(x-6\right)^2+1\)
\(\left(x-6\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-6\right)^2+1>0\rightarrowđpcm\)

( 7.x - 15 ) : 3 = 2
7.x - 15 = 6
7.x = 6 + 15
7.x = 21
x = 3
không biết vì chưa học
88 - 3 ( 7 + x ) = 64
3 ( 7 + x ) = 88 - 64
3 ( 7 + x ) = 24
7 + x = 8
x = 1
(7.x -15):3=2
7.x-15=2.3
7.x-15=6
7.x=6+15
7.x=21
x=21:7
x=3
12.(x+37)=504
x+37=504:12
x+37=42
x=42-37
x=5
88-3(7+x)=64
3(7+x)=88-64
3(7+x)=24
7+x=24:3
7+x=8
x=8-7
x=1
dấu . là nhân nhé

TXĐ: \(D=R\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=4x^3-24x\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\sqrt{6}\\x=-\sqrt{6}\left(loai\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\begin{matrix}f\left(0\right)=-1\\f\left(\sqrt{6}\right)=-37\\f\left(9\right)=5588\end{matrix}\)
suy ra chọn D

a, x2 + 10x + 27
Đặt A = x2 + 2. x. 5 + 52 + 2
= ( x + 5 )2 + 2
Vì ( x + 5 )2 \(\ge\)0 với mọi x
=> ( x + 5 )2 + 2 \(\ge\)2 với mọi x
Hay A \(\ge\)2
Dấu " = " xảy ra khi:
( x + 5 )2 = 0
x + 5 = 0
x = - 5
Vậy Min A = 2 khi x = - 5
b, x2 + x + 7
Đặt B = x2 + x + 7
\(=x^2+x+\frac{1}{4}+\frac{27}{4}\)
\(=\left[x^2+2\cdot x\cdot\frac{1}{2}+\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\right]+\frac{27}{4}\)
\(=\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{27}{4}\)
Vì \(\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\)với mọi x
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{27}{4}\ge\frac{27}{4}\)với mọi x
Hay B \(\ge\frac{27}{4}\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra khi:
\(\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2=0\)
\(x+\frac{1}{2}=0\)
\(x=-\frac{1}{2}\)
Vậy Min B = \(\frac{27}{4}\)khi x = \(-\frac{1}{2}\)
a) x2 + 10 x + 27 =( x2 + 2. 5 . x + 52 ) + 2 = ( x + 5 ) 2 + 2
Vì ( x + 5 ) 2 \(\ge\) 0 với mọi x nên ( x + 5 ) 2 + 2 \(\ge\) 2 với mọi x
Dấu bằng xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\)x + 5 = 0 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x = -5
b) x2 + x + 7 = 0 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + 2. x . \(\frac{1}{2}\)+ \(\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\) + \(\frac{27}{4}\) = 0 \(\Leftrightarrow\)( x + 1/2) 2 + 27/4 = 0
Vì ( x + 1/2 )2 \(\ge\) 0 với mọi x nên ( x + 1/2) 2 + 27/4 \(\ge\)27/4 với mọi x
Dấu bằng xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\)x+ 1/2 = 0 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x = ---\(\frac{1}{2}\)
c + d ) Tương tự a, b
e) x2 + 14 x + y2 - 2y +7 = 0 \(\Leftrightarrow\) ( x2 + 2. x. 7 + 72 ) + ( y2 -- 2y + 1 ) -43 = 0 \(\Leftrightarrow\) ( x + 7 ) 2 + ( y -- 1 ) 2 --43 = 0 ( 1 )
Vì ( x + 7 )2 \(\ge\) 0 và ( y -- 1 )2 \(\ge\) 0 với mọi x, y nên ( 1 ) \(\ge\) --43 với mọi x, y
Dấu bằng xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\hept{\begin{cases}x+7=0\\y-1=0\end{cases}}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\hept{\begin{cases}x=-7\\y=1\end{cases}}\)

a) \(x^2-12x+11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2.6.x+36-25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)^2-25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)^2=25=5^2=\left(-5\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=5\\x-6=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=11\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy : \(x\in\left\{11,1\right\}\)
c) \(4x^2-12x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x\right)^2-2.2x.3+9-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^2-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^2=16=4^2=\left(-4\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-3=4\\2x-3=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=7\\2x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{7}{2}\\x=-\frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy : \(x\in\left\{\frac{7}{2},-\frac{1}{2}\right\}\)
Câu b) và d) xíu em làm sau, em hơi bận chút !!
Làm tiếp nha >>>
b) \(4x^2-4x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x\right)^2-2.2x.1+1-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^2-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^2=4=2^2=\left(-2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=2\\2x-1=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=3\\2x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{3}{2}\\x=-\frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy : \(x\in\left\{\frac{3}{2},-\frac{1}{2}\right\}\)
d) \(x^3-6x^2=8-12x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x^2-\left(8-12x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x^2-8+12x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3.x^2.2+3.x.2^2-2^3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy : \(x=2\)
P/s : Hằng đẳng thức với lập phương khó thật, rối câu d) mãi mới nghĩ ra >>
\(\)

a: \(x^2+12x+36=0\)
=>\(x^2+2\cdot x\cdot6+6^2=0\)
=>\(\left(x+6\right)^2=0\)
=>x+6=0
=>x=-6
b: \(4x^2-4x+1=0\)
=>\(\left(2x\right)^2-2\cdot2x\cdot1+1^2=0\)
=>\(\left(2x-1\right)^2=0\)
=>2x-1=0
=>2x=1
=>x=1/2
c: \(x^3+6x^2+12x+8=0\)
=>\(x^3+3\cdot x^2\cdot2+3\cdot x\cdot2^2+2^3=0\)
=>\(\left(x+2\right)^3=0\)
=>x+2=0
=>x=-2

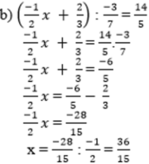
Phương trình đã cho là:
x² − 12x + 37 = 0
Đây là phương trình có dạng tổng quát ax² + bx + c = 0, với các hệ số:
Áp dụng Công thức nghiệm
Công thức nghiệm của phương trình bậc hai là:
x = [ -b ± √(b² − 4ac) ] / 2a
x = [ -(-12) ± √((-12)² − 4 * 1 * 37) ] / (2 * 1)
x = [ 12 ± √(144 − 148) ] / 2
x = [ 12 ± √(-4) ] / 2
Ta biết rằng √(-1) được định nghĩa là đơn vị ảo, ký hiệu là i.
Do đó, √(-4) = √(4 * -1) = √4 * √-1 = 2i.
x = (12 ± 2i) / 2
x = 12/2 ± 2i/2
x = 6 ± i
Vậy, phương trình có hai nghiệm phức là:
\(x^2-12x+37=0\)
\(ax^2+bx+c=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
Nếu \(a=1;b=-12;c=37\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta=\left(-12\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot37\)
\(\Delta=144-148\)
\(\Delta=-4\)
Mà \(\Delta<0\)
\(\rightarrow\) Phương trình vô nghiệm.