Giải phương trình 12+(Xx3+5):5=16
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)

4x2 – 1 = (2x + 1)(3x – 5)
⇔ 4x2 – 1 – (2x + 1)(3x – 5) = 0
⇔ (2x – 1)(2x + 1) – (2x + 1)(3x – 5) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)[(2x – 1) – (3x – 5)] = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)(2x – 1 – 3x + 5) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)(4 – x) = 0
⇔ 2x + 1= 0 hoặc 4 – x = 0
+ 2x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 2x = -1 ⇔ x = -1/2.
+ 4 – x = 0 ⇔ x = 4.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 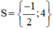

\(a,2x\left(x-5\right)+4\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\2x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;-2\right\}\)
\(b,3x-15=2x\left(x-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x-5\right)-2x\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(-2x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\-2x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
\(c,\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)=\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)-\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2-5x+8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(-2x+6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\-2x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-1\\2x=6\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};3\right\}\)
Câu d xem lại đề

\(\sqrt{x^2+12}-\sqrt{x^2+5}=3x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x^2+12}+\left(x-6\right)\right)-\left(\left(x-5\right)+\sqrt{x^2+5}\right)+\left(-3x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{12\left(x-2\right)}{\sqrt{x^2+12}+6-x}+\frac{10\left(x-2\right)}{\sqrt{x^2+5}+5-x}+-3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(\frac{12}{\sqrt{x^2+12}+6-x}+\frac{10}{\sqrt{x^2+5}+5-x}-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Dùng lượng liên hiệp mà giải đi bạn.
Giải được nghiệm x = 2 đó

ĐK: \(x\in R\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2+12}-4+3-\sqrt{x^2+5}+6-3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-4}{\sqrt{x^2+12}+4}+\dfrac{4-x^2}{3+\sqrt{x^2+5}}+6-3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{x+2}{\sqrt{x^2+12}+4}-\dfrac{x+2}{3+\sqrt{x^2+5}}-3\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\left(1\right)\)
Từ phương trình suy ra \(3x-5=\sqrt{x^2+12}-\sqrt{x^2+5}>0\Rightarrow x>\dfrac{5}{3}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+2}{\sqrt{x^2+12}+4}-\dfrac{x+2}{3+\sqrt{x^2+5}}-3\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x^2+12}+4}-\dfrac{1}{3+\sqrt{x^2+5}}\right)\left(x+2\right)-3< 0\)
Khi đó \(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm \(x=2\)

\(\Leftrightarrow\left(20x-4\right)^2-\left(9x+15\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(20x-4-9x-15\right)\left(20x-4+9x+15\right)=0\)
=>(11x-19)(29x+11)=0
=>x=19/11 hoặc x=-11/29
\(12+\left(x\times3+5\right):5=16\\ \left(x\times3+5\right):5=16-12\\ \left(x\times3+5\right):5=4\\ x\times3+5=4\times5\\ x\times3+5=20\\ x\times3=20-5\\ x\times3=15\\ x=15:3\\ x=5\)
Vậy: ..