tìm giá trị ϵ z nguyên tìm giá trị lớn nhất của x để Phân số C= \(\dfrac{x}{2x-1}\) ai help với
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Để C có giá trị là một số nguyên
⇒ 6x-1 : 3x+2
3x+2 : 3x+2
⇒ 6x-1 : 3x+2
2(3x+2) : 3x+2
⇒ 6x-1 : 3x+2
6x+4 : 3x+2
⇒ (6x+4) - (6x-1) :3x+2
⇒ 6x+4 - 6x+1 : 3x+2
⇒ 5 : 3x+2
⇒3x+2 thuộc Ư(5) = 5;-5;-1;1
⇒x = 1;-1

A = \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}\)
a, A là phân số ⇔ \(x\) + 2 # 0 ⇒ \(x\) # -2
b, Để A là một số nguyên thì 2\(x-1\) ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ 2\(x\) + 4 - 5 ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ 2(\(x\) + 2) - 5 ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ 5 ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ \(x\) + 2 \(\in\) { -5; -1; 1; 5}
⇒ \(x\) \(\in\) { -7; -3; -1; 3}
c, A = \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}\)
A = 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\)
Với \(x\) \(\in\) Z và \(x\) < -3 ta có
\(x\) + 2 < - 3 + 2 = -1
⇒ \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) > \(\dfrac{5}{-1}\) = -5 ⇒ - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\)< 5
⇒ 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) < 2 + 5 = 7 ⇒ A < 7 (1)
Với \(x\) > -3; \(x\) # - 2; \(x\in\) Z ⇒ \(x\) ≥ -1 ⇒ \(x\) + 2 ≥ -1 + 2 = 1
\(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) > 0 ⇒ - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) < 0 ⇒ 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) < 2 (2)
Với \(x=-3\) ⇒ A = 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{-3+2}\) = 7 (3)
Kết hợp (1); (2) và(3) ta có A(max) = 7 ⇔ \(x\) = -3

a: ĐểA nguyên thì x^2+2x+x+2-3 chia hết cho x+2
=>-3 chia hết cho x+2
=>x+2 thuộc {1;-1;3;-3}
=>x thuộc {-1;-3;1;-5}
b: B nguyên khi x^2+x+3 chia hết cho x+1
=>3 chia hết cho x+1
=>x+1 thuộc {1;-1;3;-3}
=>x thuộc {0;-2;2;-4}

Bổ sung phần c và d luôn:
c, C = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{x^2-1}{2x^2+3}\) = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5(x2 - 1) = 2(2x2 + 3)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5x2 - 5 = 4x2 + 6
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = 11
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 - 11 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) (x - \(\sqrt{11}\))(x + \(\sqrt{11}\)) = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\sqrt{11}=0\\x+\sqrt{11}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{11}\left(TM\right)\\x=-\sqrt{11}\left(TM\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
d, Ta có: \(\dfrac{x^2-1}{2x^2+3}\) = \(\dfrac{x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}-\dfrac{5}{2}}{2\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) - \(\dfrac{5}{4\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\)
C nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{5}{4\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\) nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\) 5 \(⋮\) 4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) \(\in\) Ư(5)
Xét các TH:
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = 5 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-1}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = -5 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-11}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{11}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = 1 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-5}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{5}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = -1 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-7}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{7}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
Vậy không có giá trị nào của x \(\in\) Z thỏa mãn C \(\in\) Z
Chúc bn học tốt! (Ko bt đề sai hay ko nữa :v)

a)để A là phân số => x khác 1/2
b) Để A\(\in\)Z
=> \(2x+5⋮2x-1\)
ta có : 2x-1\(⋮\)2x-1
=>(2x+5)-(2x-1)\(⋮\)2x-1
=>6\(⋮\)2x-1
=> 2x-1\(\in\)Ư(6)={\(\pm\)1;\(\pm\)2;\(\pm\)3;\(\pm\)6}
ta có bảng :
| 2x-1 | 1 | -1 | 2 | -2 | 3 | -3 | 6 | -6 |
| x | 1 | 0 | \(\frac{3}{2}\) | \(\frac{-1}{2}\) | 2 | -1 | \(\frac{7}{2}\) | \(-\frac{5}{2}\) |
Mà A \(\in\)Z
Vậy x\(\in\){\(\pm\)1;0;2}
c) ta có :A= \(\frac{2x-5}{2x-1}=\frac{2x-1-4}{2x-1}=\frac{2x-1}{2x-1}-\frac{4}{2x-1}=1-\frac{4}{2x-1}\)
để A lớn nhất
=>\(1-\frac{4}{2x-1}\)lớn nhất
=> 2x-1<0 và 2x-1 lớn nhất
=> 2x-1=-1
=>2x=0
=>x=0
Vậy tại x =0 thì A đạt giá trị lớn nhất
a)để A là phân số => x khác 1/2
b) Để A∈∈Z
=> 2x+5⋮2x−12x+5⋮2x−1
ta có : 2x-1⋮⋮2x-1
=>(2x+5)-(2x-1)⋮⋮2x-1
=>6⋮⋮2x-1
=> 2x-1∈∈Ư(6)={±±1;±±2;±±3;±±6}
ta có bảng :
| 2x-1 | 1 | -1 | 2 | -2 | 3 | -3 | 6 | -6 |
| x | 1 | 0 | 3232 | −12−12 | 2 | -1 | 7272 | −52−52 |
Mà A ∈∈Z
Vậy x∈∈{±±1;0;2}
c) ta có :A= 2x−52x−1=2x−1−42x−1=2x−12x−1−42x−1=1−42x−12x−52x−1=2x−1−42x−1=2x−12x−1−42x−1=1−42x−1
để A lớn nhất
=>1−42x−11−42x−1lớn nhất
=> 2x-1<0 và 2x-1 lớn nhất
=> 2x-1=-1
=>2x=0
=>x=0
Vậy tại x =0 thì A đạt giá trị lớn nhất

\(P=\dfrac{x-5}{x-4}:\dfrac{x-5}{2x}=\dfrac{2x}{x-4}\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(\dfrac{2x}{x-4}\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(\dfrac{2\left(x-4\right)+8}{x-4}\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(2+\dfrac{8}{x-4}\in Z\Rightarrow\)\(\dfrac{8}{x-4}\in Z\Rightarrow x-4\inƯ\left(8\right)=\left\{...\right\}\)
Bạn làm tiếp nhé!

a)
\(A=\dfrac{2x+3}{x-2}=\dfrac{2\left(x-2\right)+7}{x-2}=2+\dfrac{7}{x-2}\)
Vì x nguyên nên để A có giá trị nguyên thì \(\dfrac{7}{x-2}\) có giá trị nguyên
Khi đó x - 2 ∈ Ư(7) = {-7; -1; 1; 7}
| x-2 | -7 | -1 | 1 | 7 |
| x | -5 | 1 | 2 | 9 |
Vậy x ∈ {-5; 1; 2; 9}.

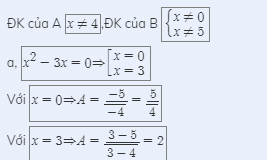
 Z để phân số có giá trị nguyên
Z để phân số có giá trị nguyên
help
Để C là số nguyên thì x chia hết cho 2x-1
=>2x chia hết cho 2x-1
=>2x-1+1 chia hết cho 2x-1
=>\(2x-1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
mà x lớn nhất
nên 2x-1=1
=>x=1