Giải phương trình \(2x^3-15x^2+26x-5=0\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(x^6-6x^5+15x^4-20x^3+15x^2-6x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^6-x^5-5x^5+5x^4+10x^4-10x^3-10x^3+10x^2+5x^2-5x-x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^5\left(x-1\right)-5x^4\left(x-1\right)+10x^3\left(x-1\right)-10x^2\left(x-1\right)+5x\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^5-5x^4+10x^3-10x^2+5x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[x^5-x^4-4x^4+4x^3+6x^3-6x^2-4x^2+4x+x-1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[x^4\left(x-1\right)-4x^3\left(x-1\right)+6x^2\left(x-1\right)-4x\left(x-1\right)+x-1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2\left[x^4-4x^3+6x^2-4x+1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2\left[x^4-x^3-3x^3+3x^2+3x^2-3x-x+1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^3\left[x^3-3x^2+3x-1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^3\left[x^3-x^2-2x^2+2x+x-1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^4\left[x^2-2x+1\right]=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^6=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\)

\(\left(2x^2+3\right)^2-10x^2-15x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^4+12x^2+9-10x^2-15x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^4+2x^2-15x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^4-4x^2+6x^2-6x-9x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2\left(x^2-1\right)+6x\left(x-1\right)-9\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+6x\left(x-1\right)-9\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[4x\left(x+1\right)+6x-9\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2+10x-9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2+10x+\frac{25}{4}+\frac{11}{4}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[\left(2x+\frac{5}{2}\right)^2+\frac{11}{4}\right]=0\)
Vì \(\left(2x+\frac{5}{2}\right)^2+\frac{11}{4}>0\)
=> x - 1 = 0
=> x = 1
Vậy x = 1

\(15x^4+30x^3+13x^2-2x-1=0\)
<=> \(15x^4+15x^3+15x^3+15x^2-2x^2-2x-1=0\)
<=> \(15x^2\left(x^2+x\right)+15x\left(x^2+x\right)-2\left(x^2+x\right)-1\)
<=> \(15\left(x^2+x\right)^2-2\left(x^2+x\right)-1=0\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2+x=\frac{1}{3}\\x^2+x=\frac{1}{5}\end{cases}}\)
Em tự giải tiếp nhé!

CM: 5x^2 +15x+20>0
Ta có: 5x^2 +15x +20
= 5( x^2 + 3x +4)
=5[(x^2 + 2.x.3/2 +9/4) -9/4 +4 ]
=5(x+3/2)^2 -7/4
Vì (x+3/2)^2 >0 với mọi x
=>5(x+3/2)^2 >0 với mọi x
=> 5(x+3/2)^2 - 7/4 >0 với mọi x


Lời giải:
ĐKXĐ: Mọi số thực $x$
\(\text{PT}\Leftrightarrow 8x^2-26x-2+5\sqrt{(x^2-x+1)(2x^2+7x+7)}=0\)
Đặt \(\left\{\begin{matrix} \sqrt{x^2-x+1}=a\\ \sqrt{2x^2+7x+7}=b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\text{PT}\Leftrightarrow 12a^2-2b^2+5ab=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow (4a-b)(3a+2b)=0\)
+) Nếu \(4a-b=0\Rightarrow 16(x^2-x+1)=2x^2+7x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 14x^2-23x+9=0\Leftrightarrow \sqsubset ^{x=1}_{x=\frac{9}{14}}\)
+) Nếu \(3a+2b=0\Rightarrow 3\sqrt{x^2-x+1}+2\sqrt{2x^2+2x+7}=0\)
Vì căn bậc hai của một số thực xác định luôn dương nên \(\left\{\begin{matrix} x^2-x+1=0\\ \\ 2x^2+7x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.(\text{vl})\)
Vậy \(x\in \left \{ 1,\frac{9}{14} \right \}\) là nghiệm của PT

\(b, (2x^2 + 3x-1) - 5(2x^2 + 3x + 2) + 24 =0 \)
Đặt \(2x^2 + 3x + 1 = a \)
\(=> (a-2) - 5(a+2) + 24 = 0\)\(\)
\(=> a - 2 - 5a - 10 + 24 = 0\)
\(=> a = 3=> 2x^2 + 3x + 1 = 3\)
\(<=> 2x^2 + 3x - 2 = 0\)
\(<=> 2x^2 + 4x - x - 2 = 0\)
\(<=> (2x-1)(x+2) = 0 \)
\(<=> 2x - 1 = 0 hoặc x+2 =0\)
\(<=> x = 1/2 hoặc x = -2\)
~~
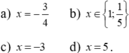
2x3 - 15x2 + 26x - 5 = 0
<=> 2x3 - 10x2 - 5x2 + 25x + x - 5 = 0
<=> 2x2( x - 5 ) - 5x( x - 5 ) + ( x - 5 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 5 )( 2x2 - 5x + 1 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-5=0\\2x^2-5x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
+) x - 5 = 0 <=> x = 5
+) 2x2 - 5x + 1 = 0
Δ = b2 - 4ac = (-5)2 - 4.2.1 = 25 - 8 = 17
Δ > 0, áp dụng công thức nghiệm thu được \(x_1=\frac{5+\sqrt{17}}{4};x_2=\frac{5-\sqrt{17}}{4}\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho có ba nghiệm \(x_1=\frac{5+\sqrt{17}}{4};x_2=\frac{5-\sqrt{17}}{4};x_3=5\)