Giải các hệ phương trình sau bằng phương pháp cộng đại số:
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x+2y=3\\3x+y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3x+6y=9\\3x+y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7y=8\\-x+2y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{8}{7}\\-x=3-2y=3-2\cdot\dfrac{8}{7}=\dfrac{5}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{5}{7}\\y=\dfrac{8}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{5}{7}\\y=\dfrac{8}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+2\sqrt{3}\cdot y=1\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\sqrt{3}x+6y=\sqrt{3}\\2\sqrt{3}x+4y=-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2y=\sqrt{3}+10\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+10}{2}\\x\sqrt{3}+2\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+10}{2}=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+10}{2}\\x\sqrt{3}=-5-\sqrt{3}-10=-15-\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1-5\sqrt{3}\\y=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+10}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1-5\sqrt{3}\\y=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+10}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Làm mẫu hai câu a, b thôi nha.
a, \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-\sqrt{3}y=0\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{3}y\\\sqrt{3}.\sqrt{3}y+2y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{3}y\\5y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+3}{5}\\y=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{3}}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\approx0,95\\y\approx0,55\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x-\sqrt{5}y=1\\x+\sqrt{5}y=\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}\left(\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{5}y\right)-\sqrt{5}y=1\\x=\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{5}y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2-\sqrt{5}\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)y=1\\x=\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{5}y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{\sqrt{5}}\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y\approx0,19\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-\sqrt{3}y=0\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{3}x-3y=0\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lấy phương trình dưới trừ phương trình trên thu được: \(5y=1+\sqrt{3}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{3}}{5}\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{3}y=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{3}}{5}\)
b) Cộng hai phương trình lại với nhau thu được:
\(\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)x=\sqrt{2}+1\Leftrightarrow x=1\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{\sqrt{5}}\)
c) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x+\sqrt{5}y=2\\x+\sqrt{5}y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lấy phương trình trên trừ phương trình dưới:
\(\left(\sqrt{2}-1\right)x=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2-x}{\sqrt{5}}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\)
d) Hướng dẫn. Nhân phương trình đầu với \(\sqrt{2}\) rồi lấy phương trình thu được trừ phương trình dưới.

a) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x-y=3\\x+\sqrt{2}y=\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x-y=3\\\sqrt{2}x+2y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3y=1\\x+\sqrt{2}y=\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}\cdot\dfrac{-1}{3}=\dfrac{4\sqrt{2}}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{4\sqrt{2}}{3}\\y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{2}-2y=\dfrac{3}{4}\\2x+\dfrac{y}{3}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-8y=3\\2x+\dfrac{1}{3}y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{25}{3}y=\dfrac{10}{3}\\2x-8y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{2}{5}\\2x=3+8y=3+8\cdot\dfrac{-2}{5}=-\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{10}\\y=-\dfrac{2}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{10}\\y=-\dfrac{2}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2x-3y}{4}-\dfrac{x+y-1}{5}=2x-y-1\\\dfrac{x+y-1}{3}+\dfrac{4x-y-2}{4}=\dfrac{2x-y-3}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{5\left(2x-3y\right)}{20}-\dfrac{4\left(x+y-1\right)}{20}=\dfrac{20\left(2x-y-1\right)}{20}\\\dfrac{4\left(x+y-1\right)}{12}+\dfrac{3\left(4x-y-2\right)}{12}=\dfrac{2\left(2x-y-3\right)}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}10x-15y-4x-4y+4=40x-20y-20\\4x+4y-4+12x-3y-6=4x-2y-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x-19y+4-40x+20y+20=0\\16x+y-10-4x+2y+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-34x+y=-24\\12x+3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-102x+3y=-72\\12x+3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-114x=-76\\12x+3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\12\cdot\dfrac{2}{3}+3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\3y=4-8=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\y=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\y=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

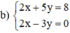 (Hệ số của x ở 2 pt bằng nhau nên ta trừ từng vế của 2pt)
(Hệ số của x ở 2 pt bằng nhau nên ta trừ từng vế của 2pt)
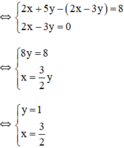
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất 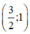

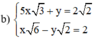 (Chia hai vế pt 2 cho √2 để hệ số của y đối nhau)
(Chia hai vế pt 2 cho √2 để hệ số của y đối nhau)
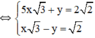 (Hệ số của y đối nhau nên cộng từng vế của 2 pt)
(Hệ số của y đối nhau nên cộng từng vế của 2 pt)
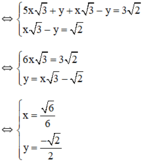
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất 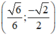

(Các phần giải thích học sinh không phải trình bày).
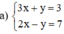 (Vì hệ số của y ở 2 pt đối nhau nên cộng từng vế của 2 pt).
(Vì hệ số của y ở 2 pt đối nhau nên cộng từng vế của 2 pt).
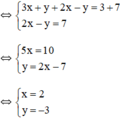
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (2; -3).

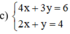 (Nhân cả hai vế của pt 2 với 2 để hệ số của x bằng nhau)
(Nhân cả hai vế của pt 2 với 2 để hệ số của x bằng nhau)
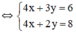 (Hệ số của x bằng nhau nên ta trừ từng vế của 2 pt)
(Hệ số của x bằng nhau nên ta trừ từng vế của 2 pt)
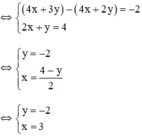
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (3; -2).
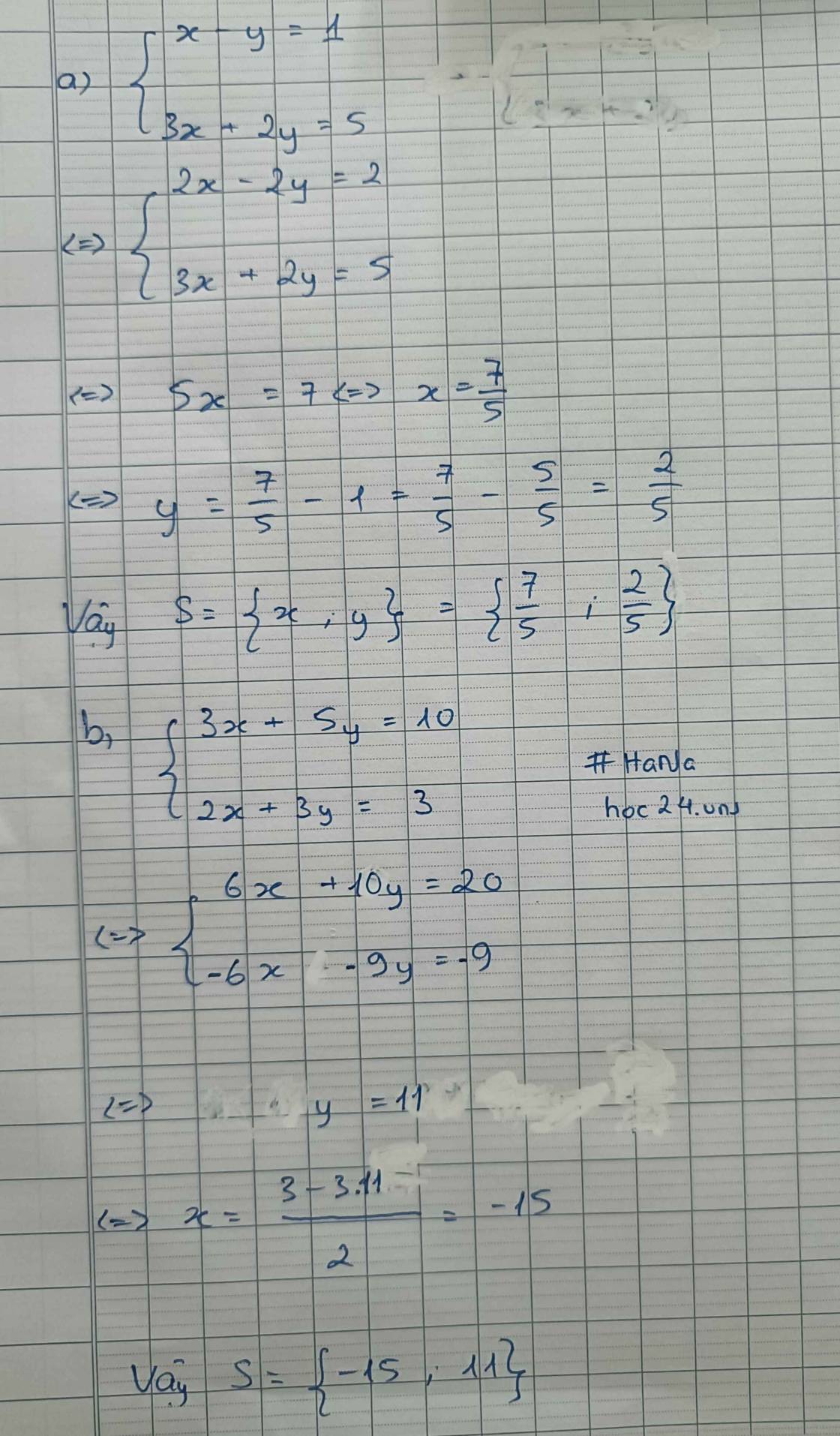
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (5; 3).