2cos x - cos 2 x + 3=0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1: \(\Leftrightarrow\sin^3x=-\cos^3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sin^3x=-\sin^3\left(\dfrac{\Pi}{2}-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sin^3x=\sin^3\left(-\dfrac{\Pi}{2}+x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{\Pi}{2}+x+k2\Pi\\x=\dfrac{\Pi}{2}-x+k2\Pi\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\Pi}{4}+k\Pi\)
2: \(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{1}{2}\sin x+\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\cos x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sin x\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\cdot\cos x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sin x\cdot\dfrac{\cos\Pi}{6}-\cos x\cdot\sin\left(\dfrac{\Pi}{6}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sin\left(x-\dfrac{\Pi}{6}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{\Pi}{6}=k\Pi\)
hay \(x=k\Pi+\dfrac{\Pi}{6}\)

Đáp án D
Tìm điều kiện để phương trình có nghĩa. Sau đó sử dụng công thức 2 cos 2 x = 1 - 2 sin 2 x để đưa phương trình đã cho về phương trình bậc 2 đối với sin x và giải phương trình này để tìm nghiệm. Bước cuối cùng là đối chiếu điều kiện để kết luận nghiệm.
Điều kiện
![]()
Với điều kiện trên phương trình đã cho trở thành
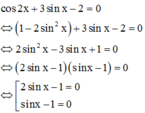
Nếu
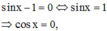
không thỏa mãn điều kiện (1)
Vậy
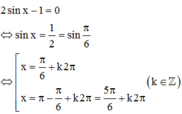

d/
Nhận thấy \(cosx=0\) ko phải nghiệm, chia 2 vế cho \(cos^2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{2}\left(tanx+1\right)=\frac{3}{cos^2x}+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{2}tanx+2\sqrt{2}=3\left(1+tan^2x\right)+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3tan^2x-2\sqrt{2}tanx+5-2\sqrt{2}=0\)
Pt vô nghiệm
c/
\(\Leftrightarrow1-sin^2x+\sqrt{3}sinx.cosx-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3}sinx.cosx-sin^2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx\left(\sqrt{3}cosx-sinx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=0\\\sqrt{3}cosx=sinx\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=0\\tanx=\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=k\pi\\x=\frac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(sina+sinb+sinc+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(sina+1\right)+\left(sinb+1\right)+\left(sinc+1\right)=0\)
Do \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sina\ge-1\\sinb\ge-1\\sinc\ge-1\end{matrix}\right.\) ;\(\forall a;b;c\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(sina+1\right)+\left(sinb+1\right)+\left(sinc+1\right)\ge0\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi \(sina=sinb=sinc=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow cosa=cosb=cosc=0\Rightarrow cosa+cosb+cosc+10=10\)
b/ \(sinx=1-sin^2x\Rightarrow sinx=cos^2x\)
\(\Rightarrow sin^2x=cos^4x\Rightarrow1-cos^2x=cos^4x\)
\(\Rightarrow cos^4x+cos^2x=1\Rightarrow\left(cos^4x+cos^2x\right)^2=1\)
\(\Rightarrow cos^8x+2cos^6x+cos^4x=1\)


\(cosx=cos2.\left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right)=cos^2\dfrac{x}{2}-sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}\)
\(sinx=sin2\left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right)=2sin\dfrac{x}{2}cos\dfrac{x}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{sinx+cosx}{sinx}=\dfrac{sinx+cos^2\dfrac{x}{2}-sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}}{2sin\dfrac{x}{2}cos\dfrac{x}{2}}\)

Đáp án D
Dùng công thức cos a.cos b+ sin a. sin b= cos (a-b) để biến đổi phương trình không chứa
α
về dạng giống phương trình có chứa
α
Ta có
\(\Leftrightarrow2cosx-\left(2cos^2x-1\right)+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2cos^2x+2cosx+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=-1\\cosx=2>1\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pi+k2\pi\)