tìm x-y biết \(|3x-2y|\)=20x-50-2x2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1) Ta có: \(x^2-4x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
hay x=2
Vậy: S={2}

a/ \(x^2+y^2=0\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow A=0\)
b/ Do \(x=19\Rightarrow20=x+1\)
\(B=x^6-\left(x+1\right)x^5+\left(x+1\right)x^4-\left(x+1\right)x^3+\left(x+1\right)x^2-\left(x+1\right)x+20\)
\(B=x^6-x^6-x^5+x^5+x^4-x^4-x^3+x^3+x^2-x^2-x+20\)
\(B=20-x=20-19=1\)
c/ \(x+y+z=0\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=-z\\x+z=-y\\y+z=-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(C=\frac{\left(x+y\right)}{y}.\frac{\left(y+z\right)}{z}.\frac{\left(x+z\right)}{x}=\frac{-z}{y}.\frac{-x}{z}.\frac{-y}{x}=\frac{-xyz}{xyz}=-1\)

x/2=y/3;y/2=z/5 => x/2=2y/6;3y/6=z/5 => x/4=y/6=z/15
adtcdtsbn:
x/4=y/6=z/15=x+y+z/4+6+15=50/25=2
suy ra : x/4=2=>x=4.2=8
y/6=2=>y=2.6=12
z/15=2 => z=15.2=30


Bài 1:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x+4\ne0\)
=>\(x\ne-4\)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(2x-1\ne0\)
=>\(2x\ne1\)
=>\(x\ne\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\left(y-3\right)\ne0\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne0\\y-3\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne0\\y\ne3\end{matrix}\right.\)
d: ĐKXĐ: \(x^2-4y^2\ne0\)
=>\(\left(x-2y\right)\left(x+2y\right)\ne0\)
=>\(x\ne\pm2y\)
e: ĐKXĐ: \(\left(5-x\right)\left(y+2\right)\ne0\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne5\\y\ne-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 2:
a: \(\dfrac{-12x^3y^2}{-20x^2y^2}=\dfrac{12x^3y^2}{20x^2y^2}=\dfrac{12x^3y^2:4x^2y^2}{20x^2y^2:4x^2y^2}=\dfrac{3x}{5}\)
b: \(\dfrac{x^2+xy-x-y}{x^2-xy-x+y}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x^2+xy\right)-\left(x+y\right)}{\left(x^2-xy\right)-\left(x-y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+y\right)-\left(x+y\right)}{x\left(x-y\right)-\left(x-y\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+y\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+y}{x-y}\)
c: \(\dfrac{7x^2-7xy}{y^2-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{7x\left(x-y\right)}{\left(y-x\right)\left(y+x\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-7x\left(x-y\right)}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}=\dfrac{-7x}{x+y}\)
d: \(\dfrac{7x^2+14x+7}{3x^2+3x}\)
\(=\dfrac{7\left(x^2+2x+1\right)}{3x\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{7\left(x+1\right)^2}{3x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{7\left(x+1\right)}{3x}\)
e: \(\dfrac{3y-2-3xy+2x}{1-3x-x^3+3x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3y-2-x\left(3y-2\right)}{1-3x+3x^2-x^3}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(3y-2\right)\left(1-x\right)}{\left(1-x\right)^3}=\dfrac{3y-2}{\left(1-x\right)^2}\)
g: \(\dfrac{x^2+7x+12}{x^2+5x+6}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+4}{x+2}\)

`-3x=2y `
`=> x/2 = -y/3 `
AD t/c của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có
`x/2 =-y/3 = (x-y)/(2+3) = 6/5`
`=>{(x=2*6/5 = 12/5),(y=-3*6/5 =-18/5):}`
a) `6/x =-3/2`
`=>x =6 :(-3/2) = 6*(-2/3)=-4`
`b)`\(-3x=2y\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{-3}\)
Áp dụng t/c của DTSBN , ta đc :
\(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{-3}=\dfrac{x-y}{2+3}=\dfrac{6}{5}\\ \Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{6}{5}\\\dfrac{y}{-3}=\dfrac{6}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{12}{5}\\y=-\dfrac{18}{5}\end{matrix}\right. \)
`a)`
`6/x=-3/2`
`x=6:(-3/2)`
`x=6*(-2/3)`
`x=-4`

a) x2 + y2 - 6x + 2y + 10 = 0
<=> ( x2 - 6x + 9 ) + ( y2 + 2y + 1 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 3 )2 + ( y + 1 )2 = 0
<=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\y+1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=3\\y=-1\end{cases}}\)
b) 4x2 + y2 - 20x - 2y + 26 = 0
<=> ( 4x2 - 20x + 25 ) + ( y2 - 2y + 1 ) = 0
<=> ( 2x - 5 )2 + ( y - 1 )2 = 0
<=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x-5=0\\y-1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{2}\\y=1\end{cases}}\)
a) x2 + y2 - 6x + 2y + 10 = 0
=> (x2 - 6x + 9) + (y2 + 2y + 1) = 0
=> (x - 3)2 + (y + 1)2 = 0 (1)
Vì \(\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x-3\right)^2\ge0\forall x\\\left(y+1\right)^2\ge0\forall y\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2+\left(y+1\right)^2\ge0\forall x;y\)
Đẳng thức (1) xảy ra <=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\y+1=0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=3\\y=-1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x = 3 ; y = -1
b) 4x2 + y2 + 20x - 2y + 26 = 0
=> (4x2 - 20x + 25) + (y2 - 2y + 1) = 0
=> (2x - 5)2 + (y - 1)2 = 0 (1)
Vì \(\hept{\begin{cases}\left(2x-5\right)^2\ge0\forall x\\\left(y-1\right)^2\ge0\forall y\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\left(2x-5\right)^2+\left(y-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x;y\)
Đẳng thức (1) "=" xảy ra <=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x-5=0\\y-1=0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=2,5\\y=1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x = 2,5 ; y = 1
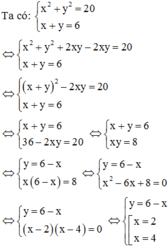

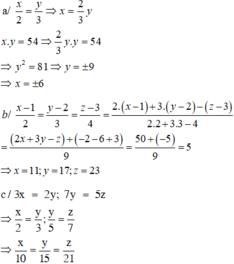
Tìm 2 số x và y hay tìm hiệu x - y ?
\(\left|3x-2y\right|=20x-50-2x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|3x-2y\right|=-2\left(x^2-10x+25\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|3x-2y\right|=-2\left(x-5\right)^2\)
Ta thấy : \(\left|3x-2y\right|\ge0\)
\(-2\left(x-5\right)^2\le0\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra khi và chỉ khi :
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}3x-2y=0\\x-5=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=5\\y=7,5\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-y=5-7,5=-2,5\)
Vậy x - y = -2,5