Tìm m để pt sau vô nghiệm: (m2 -1)x = 4x+m+1
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) Thay m=3 vào pt ta được:
\(9x+6=4x+9\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{5}\)
Vậy...
b) Thay x=-1,5 vào pt ta được:
\(m^2\left(-1,5\right)+6=4.\left(-1,5\right)+3m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-3}{2}m^2-3m+12=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=2\\m=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...
c)Pt \(\Leftrightarrow x\left(m^2-4\right)=3m-6\)
Để pt vô nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3m-6\ne0\\m^2-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne2\\m=\pm2\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow m=-2\)
Để pt có vô số nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3m-6=0\\m^2-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=2\\m=\pm2\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow m=2\)
d)Để pt có nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow m^2-4\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne\pm2\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3m-6}{m^2-4}=\dfrac{3\left(m-2\right)}{\left(m-2\right)\left(m+2\right)}=\dfrac{3}{m+2}\)
Để \(x\in Z\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{m+2}\in Z\)
Vì \(m\in Z\Leftrightarrow m+2\in Z\).Để \(\dfrac{3}{m+2}\in Z\Leftrightarrow m+2\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{-1;-3;1;3\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=\left\{-3;-5;-1;1\right\}\) (tm)
Vậy...

Ta có: \(\Delta=4\left(m-3\right)^2-4.\left(m^2-1\right)\)
a. Để phương trình vô nghiệm thì \(\Delta< 0\Leftrightarrow\left(m-3\right)^2< m^2-1\Leftrightarrow m^2-6m+9< m^2-1\Leftrightarrow6m>10\Leftrightarrow m>\dfrac{10}{6}=\dfrac{5}{3}\)
b. Để phương trình có nghiệm thì:
\(\Delta\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left(m-3\right)^2\ge m^2-1\Leftrightarrow m^2-6m+9\ge m^2-1\Leftrightarrow6m\le10\Leftrightarrow m\le\dfrac{10}{6}=\dfrac{5}{3}\)
c. Để phương trình có nghiệm kép thì:
\(\Delta=0\Leftrightarrow\left(m-3\right)^2=m^2-1\Leftrightarrow m^2-6m+9=m^2-1\Leftrightarrow6m=10\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{10}{6}=\dfrac{5}{3}\)
Nghiệm kép của phương trình là: \(\dfrac{-b}{2a}=\dfrac{2\left(m-3\right)}{2.1}=\dfrac{2\left(\dfrac{5}{3}-3\right)}{2}=-\dfrac{4}{3}\)
d. Để phương trình có nghiệm phân biệt thì:
\(\Delta>0\Leftrightarrow\left(m-3\right)^2>m^2-1\Leftrightarrow m^2-6m+9>m^2-1\Leftrightarrow6m< 10\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{10}{6}=\dfrac{5}{3}\)
a, Để pt vô nghiệm
\(\Delta'=\left(m-3\right)^2-\left(m^2-1\right)=-6m+9+1=-6m+10< 0\Leftrightarrow m>\dfrac{5}{3}\)
b, Để pt có nghiệm
\(\Delta'=-6m+10\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\le\dfrac{5}{3}\)
c, Để pt có nghiệm kép
\(\Delta'=-6m+10=0\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{5}{3}\)
\(x_1=x_2=\dfrac{2\left(m-3\right)}{2}=m-3\)
d, Để pt có 2 nghiệm pb
\(\Delta=-6m+10>0\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{5}{3}\)

Lời giải:
PT $\Leftrightarrow x(m-2)=m^2-4$
a) Để pt nhận $1$ là nghiệm thì $1(m-2)=m^2-4$
$\Leftrightarrow m-2=m^2-4=(m-2)(m+2)$
$\Leftrightarrow (m-2)(m+2-1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (m-2)(m+1)=0\Rightarrow m=2$ hoặc $m=-1$
b) Để pt có nghiệm thì:
\(\left[\begin{matrix} m-2\neq 0\\ m-2=m^2-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} m\neq 2\\ m=2\end{matrix}\right.\) hay $m\in\mathbb{R}$
Vậy pt có nghiệm với mọi $m\in\mathbb{R}$
c) Kết quả phần b suy ra không tồn tại giá trị của $m$ để pt vô nghiệm.

Bài 2:
a: \(x^2-4x+3=0\)
=>x=1 hoặc x=3
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=1^2+3^2=10\)
b: \(\dfrac{1}{x_1+2}+\dfrac{1}{x_2+2}=\dfrac{1}{1}+\dfrac{1}{5}=\dfrac{6}{5}\)
c: \(x_1^3+x_2^3=1^3+3^3=28\)
d: \(x_1-x_2=1-3=-2\)

2(m-1)x+3=2m-5
=>x(2m-2)=2m-5-3=2m-8
a: (1) là phương trình bậc nhất một ẩn thì m-1<>0
=>m<>1
b: Để (1) vô nghiệm thì m-1=0 và 2m-8<>0
=>m=1
c: Để (1) có nghiệm duy nhất thì m-1<>0
=>m<>1
d: Để (1) có vô số nghiệm thì 2m-2=0 và 2m-8=0
=>Ko có m thỏa mãn
e: 2x+5=3(x+2)-1
=>3x+6-1=2x+5
=>x=0
Khi x=0 thì (1) sẽ là 2m-8=0
=>m=4

a.
Khi \(m=2\) pt trở thành:
\(2x+3=0\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b.
Để pt có nghiệm \(x=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(m^2-m\right).\left(-1\right)+m^2-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-m^2+m+m^2-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=1\)
c.
Pt tương đương:
\(\left(m^2-m\right)x=-\left(m^2-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(m-1\right)x=-\left(m-1\right)\left(m+1\right)\)
Pt vô nghiệm khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\left(m-1\right)=0\\-\left(m-1\right)\left(m+1\right)\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow m=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) pt có nghiệm khi \(m\ne0\)
Pt có vô số nghiệm khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\left(m-1\right)=0\\-\left(m-1\right)\left(m+1\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow m=1\)
Lời giải:
a. Khi $m=2$ thì pt trở thành:
$2x+3=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{3}{2}$
b. Để pt có nghiệm $x=-1$ thì:
$(m^2-m).(-1)+m^2-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow m-1=0\Leftrightarrow m=1$
c.
PT $\Leftrightarrow (m^2-m)x=1-m^2$
Để pt vô nghiệm thì: \(\left\{\begin{matrix} m^2-m=0\\ 1-m^2\neq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} m(m-1)=0\\ (1-m)(1+m)\neq 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=0\)
PT có vô số nghiệm khi \(\left\{\begin{matrix} m^2-m=0\\ 1-m^2= 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=1\)
Để PT có nghiệm thì: $m\neq 0$

\(mx-m+2nx-n-x=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m+2n-1\right)x=m+n+2\)
Pt đã cho có vô số nghiệm khi và chỉ khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+2n-1=0\\m+n+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}n=3\\m=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
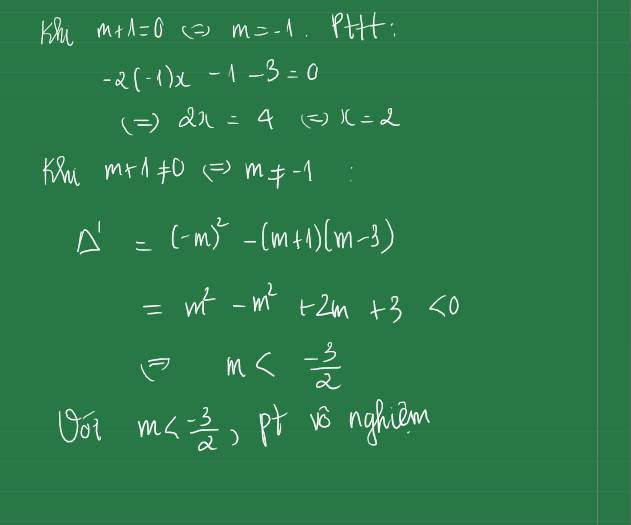
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m^2-5\right)x=m+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{m+1}{m^2-5}\)
Neu \(m=\sqrt{5}\)thi PT vo nghiem