tập nghiệm phương trình căn của 4x+1=giá trị tuyệt đối của x-5
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Không làm mất tính tổng quát, giả sử \(0< x\le y\le z\)
=> \(x+y+z\le3z\Leftrightarrow xyz\le3z\Leftrightarrow xy\le3\)
Mà x;y;z là các số nguyên dương => \(xy\in\left\{1;2;3\right\}\)
Ta xét các trường hợp:
TH1: \(xy=1\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\y=1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow2+z=z\Leftrightarrow2=0\) (vô lý!)
TH2: \(xy=2\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\y=2\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow z=3\) (thỏa mãn)
TH3: \(xy=3\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\y=3\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow z=2\) (thỏa mãn)
Vậy (x;y;z) là các hoán vị của (1;2;3)

a: \(\text{Δ}=\left[-\left(m+3\right)\right]^2-4\cdot2\cdot m\)
\(=\left(m+3\right)^2-8m\)
\(=m^2-2m+9=\left(m-1\right)^2+8>0\forall m\)
=>Phương trình (1) luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt
b: Theo Vi-et, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=\dfrac{m+3}{2}\\x_1\cdot x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{m}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(A=\left|x_1-x_2\right|=\sqrt{\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2}\)
\(=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}\left(m+3\right)^2-4\cdot\dfrac{m}{2}}\)
\(=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}\left(m^2+6m+9\right)-2m}\)
\(=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}m^2+\dfrac{3}{2}m+\dfrac{9}{4}-2m}\)
\(=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}m^2-\dfrac{1}{2}m+\dfrac{9}{4}}\)
\(=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}\left(m^2-2m+9\right)}\)
\(=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}\left(m^2-2m+1+8\right)}\)
\(=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}\left(m-1\right)^2+2}>=\sqrt{2}\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi m-1=0
=>m=1

Chọn đáp án A
x 2 + 2x - 5 = 0 phương trình có ac < 0 ⇒ phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
Theo định lí Vi-et ta có:

![]()
![]()

\(x^2-2\left(m-1\right)x+m-5=0\)
Xét \(\Delta=4\left(m-1\right)^2-4\left(m-5\right)=4m^2-12m+24\)\(=\left(2x-3\right)^2+15>0\forall m\)
=>Pt luôn có hai nghiệm pb
Theo viet:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=m-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đặt \(A=\left|x_1-x_2\right|\)
\(\Rightarrow A^2=\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2\)
\(=4\left(m-1\right)^2-4\left(m-5\right)=4m^2-12m+24\)
\(=\left(2m-3\right)^2+15\ge15\)
\(\Rightarrow A\ge\sqrt{15}\)
\(A_{min}=\sqrt{15}\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
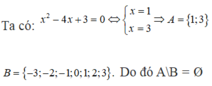
\(\left|x-5\right|=4x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=4x+1\\x-5=-4x-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=\dfrac{4}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy \(S=\left\{-2;\dfrac{4}{5}\right\}\)