Giải phương trình: 2x2(x-3)=3x(x+2)-5
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(2x^2-2x+\left(x+1-\sqrt{3x+1}\right)+2\left(x+2-\sqrt[3]{19x+8}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-2x+\dfrac{x^2-x}{x+1+\sqrt[]{3x+1}}+\dfrac{\left(x+7\right)\left(x^2-x\right)}{\left(x+2\right)^2+\left(x+2\right)\sqrt[3]{19x+8}+\sqrt[3]{\left(19x+8\right)^2}}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x\right)\left(2+\dfrac{1}{x+1+\sqrt[]{3x+1}}+\dfrac{x+7}{\left(x+2\right)^2+\left(x+2\right)\sqrt[3]{19x+8}+\sqrt[3]{\left(19x+8\right)^2}}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

(x + 2)( x 2 – 3x + 5) = (x + 2) x 2
⇔ (x + 2)( x 2 – 3x + 5) – (x + 2) x 2 = 0
⇔ (x + 2)[( x 2 – 3x + 5) – x 2 ] = 0
⇔ (x + 2)( x 2 – 3x + 5 – x 2 ) = 0
⇔ (x + 2)(5 – 3x) = 0
⇔ x + 2 = 0 hoặc 5 – 3x = 0
x + 2 = 0 ⇔ x = -2
5 – 3x = 0 ⇔ x = 5/3
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = -2 hoặc x = 5/3

a: \(x\left(x-1\right)+2x^2-2=0\)
=>\(x\left(x-1\right)+2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2x+2\right)=0\)
=>(x-1)(3x+2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(9x^2-1=\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-3\right)\)
=>\(\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)-\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-3\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-1-2x+3\right)=0\)
=>(3x+1)(x+2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)

Bài 2:
a: =>2x^2-4x+1=x^2+x+5
=>x^2-5x-4=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{41}}{2}\)
b: =>11x^2-14x-12=3x^2+4x-7
=>8x^2-18x-5=0
=>x=5/2 hoặc x=-1/4

Điều kiện của phương trình x 2 + 3 x + 7 > 0
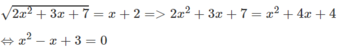
Phương trình cuối vô nghiệm, do đó phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm.

\(a,PT\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2+x^2-x\sqrt{3x-2}=0\left(x\ge\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-3x+2\right)+\dfrac{x\left(x^2-3x+2\right)}{x+\sqrt{3x-2}}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\left(1+\dfrac{x}{x+\sqrt{3x-2}}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(1+\dfrac{x}{x+\sqrt{3x-2}}\right)=0\)
Vì \(x\ge\dfrac{2}{3}>0\Leftrightarrow1+\dfrac{x}{x+\sqrt{3x-2}}>0\)
Do đó \(x\in\left\{1;2\right\}\)
\(b,ĐK:0\le x\le4\\ PT\Leftrightarrow x+2\sqrt{x}+1=6\sqrt{x}-3-\sqrt{4-x}\\ \Leftrightarrow x-4\sqrt{x}+4=-\sqrt{4-x}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)^2=-\sqrt{4-x}\)
Vì \(VT\ge0\ge VP\Leftrightarrow VT=VP=0\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}-2=0\\\sqrt{4-x}=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=4\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy PT có nghiệm \(x=4\)

2x^2(x-3)=3x(x+2)-5
2x^2*x-2x^2*3=3x*x+3x*2-5
2x^3-6x^2=3x^2+6x-5
2x^3-6x^2-3x^2-6x+5
2x^3-9x^2-6x+5
2x^3-x^2-8x^2+4x-10x+5
x^2(2x-1)-4x(2x-1)-5(2x-1)
(2x-1)(x^2-4x-5)
(2x-1)(x^2+x-5x-5)
(2x-1)[x(x+1)-5(x+1)]
(2x-1)(x+1)(x-5)
hơi dài so vs cách cô chữa nhưg cũg đc