Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_2^22x+log_2\left(\frac{2x}{8}\right)-9< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log^2_22x+log_22x-12< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4< log_22x< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{32}< x< 4\)

a)
Có:
\(log_2^{\left(2^x+1\right)}.log_2^{\left(2^{x+1}+2\right)}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_2^{\left(2^x+1\right)}.\left[1+log_2^{\left(2^{x+1}\right)}\right]=2\)
Đặt \(t=log_2^{\left(2^x+1\right)}\), ta có phương trình \(t\left(1+t\right)=2\Leftrightarrow t^2+t-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=1\\t=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_2^{\left(2^x+1\right)}=1\\log_2^{\left(2x+1\right)}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2^x+1=2\\2^x+1=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2^x=1\\2^x=-\dfrac{3}{4}\left(không-t.m\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
b)
Với điều kiện \(x>0\), ta có:
\(log.\left(x^{log9}\right)=log9.logx\) và \(log\left(9^{logx}=logx.log9\right)\)
nên \(log\left(x^{log9}\right)=log\left(9^{logx}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x^{log9}=9^{logx}\)
Đặt \(t=x^{log9}\), ta được phương trình \(2t=6\Leftrightarrow t=3\Leftrightarrow x^{log9}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log\left(x^{log9}\right)=log3\Leftrightarrow log9.logx=log3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow logx=\dfrac{log3}{log9}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt{10}\) (thỏa mãn điều kiện \(x>0\)).
c)
Với điều kiện \(x>0\), lấy lôgarit thập phân hai vế của phương trình đã cho, ta được:
\(\left(3log^3x-\dfrac{2}{3}logx\right).logx=\dfrac{7}{3}\)
Đặt \(t=logx\), ta được phương trình:
\(3t^4-\dfrac{2}{3}t^2-\dfrac{7}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9t^4-2t^2-7=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t^2=1\\t^2=-\dfrac{7}{9}\left(không-t.m\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=1\\t=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}logx=1\\logx=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=10\\x=\dfrac{1}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d)
Đặt \(t=log_5^{\left(x+2\right)}\) với điều kiện \(x+2>0\), \(x+2\ne1\), ta có:
\(1+\dfrac{2}{t}=t\Leftrightarrow t^2-t-2=0,t\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=-1\\t=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_5^{\left(x+2\right)}=-1\\log_5^{\left(x+2\right)}=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2=\dfrac{1}{5}\\x+2=25\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{9}{5}\\x=23\end{matrix}\right.\)

ĐKXĐ: \(6-5^x>0\Rightarrow5^x< 6\)
\(log_5\left(6-5^x\right)=1-x\Leftrightarrow6-5^x=5^{1-x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5^x-6+\frac{5}{5^x}=0\Leftrightarrow\left(5^x\right)^2-6.5^x+5=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5^x=1\\5^x=5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\sum x=0+1=1\)

Lời giải:
a) ĐKXĐ:......
Ta có: \(\log_{2x+1}(3-x^2)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 3-x^2=(2x+1)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 5x^2+4x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-2+\sqrt{14}}{5}\\x=\dfrac{-2-\sqrt{14}}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Kết hợp với đkxđ suy ra \(x=\frac{-2+\sqrt{14}}{5}\) là nghiệm
b) ĐKXĐ:....
Đặt \(2-x=a\Rightarrow \log_2(2a+1)=a\) (\(a>\frac{-1}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow 2a+1=2^a\)
Xét hàm \(y(a)=2^a-2a-1\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=\ln 2.2^a-2=0\Leftrightarrow a=\log_2\left(\frac{2}{\ln 2}\right)\)
Lập bảng biến thiên của $y(a)$ với $a>\frac{-1}{2}$ ta thấy đồ thì của $y(a)$ cắt đường thẳng \(y=0\) tại hai điểm, tức là pt có hai nghiệm. Trong đó một nghiệm thuộc \((-\frac{1}{2}; \log_2\left(\frac{2}{\ln 2}\right))\) và nghiệm khác thuộc \((\log_2\left(\frac{2}{\ln 2}\right);+\infty)\)
Thực hiện shift-solve ta thu được \(a=0\) hoặc \(a\approx 2,66\)
Câu c)
ĐKXĐ: \(x>-1\)
Ta có: \(\log_2(x+1)=4-3x\Leftrightarrow x+1=2^{4-3x}\)
Ta thấy:
\((x+1)'=1>0\) nên hàm vế trái đồng biến trên KXĐ
\((2^{4-3x})'=-3.\ln 2.2^{4-3x}<0\) nên hàm vế phải nghịch biến trên KXĐ
Do đó, PT chỉ có thể có duy nhất một nghiệm
Thấy \(x=1\) thỏa mãn nên $x=1$ là nghiệm duy nhất của phương trình


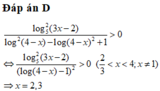
Chọn A.
Điều kiện x > 0.
Đặt t = log2x , phương trình trở thành : t2 + (x - 1) t + 2x – 6 = 0
Hay t2 – t – 6 + x(t + 2) = 0
(t + 2) (t - 3) + x(t + 2) = 0
Xét hàm số f(x) = log2x + x - 3 với x > 0, có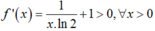
Suy ra f(x) là hàm đồng biến trên khoảng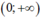
Khi đó phương trình f(x) = 0 có nhiều nhất một nghiệm trên khoảng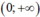
Mà f(2) = 0 nên x = 2 là nghiệm duy nhất của phương trình (*)
Vậy tổng các nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là 9/4.