
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(\dfrac{17}{6}-x\left(x-\dfrac{7}{6}\right)=\dfrac{7}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{17}{6}-x^2+\dfrac{7}{6}x-\dfrac{7}{4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2+\dfrac{7}{6}x+\dfrac{13}{12}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12x^2+14x+13=0\)
\(\Delta=14^2-4\cdot\left(-12\right)\cdot13=196+624=820\)
Vì Δ>0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{14-2\sqrt{205}}{-24}=\dfrac{-7+\sqrt{205}}{12}\\x_2=\dfrac{14+2\sqrt{2015}}{-24}=\dfrac{-7-\sqrt{205}}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(\dfrac{3}{35}-\left(\dfrac{3}{5}-x\right)=\dfrac{2}{7}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{5}-x=\dfrac{3}{35}-\dfrac{10}{35}=\dfrac{-7}{35}=\dfrac{-1}{5}\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{3}{5}-\dfrac{-1}{5}=\dfrac{3}{5}+\dfrac{1}{5}=\dfrac{4}{5}\)

Bài 1 :
\(\frac{x-1}{x-5}=\frac{6}{7}\Leftrightarrow7x-7=6x-30\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-23\)
\(\frac{x-2}{x-1}=\frac{x+4}{x+7}\)ĐK : \(x\ne1;-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+7\right)=\left(x+4\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+5x-14=x^2+3x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-10=0\Leftrightarrow x=5\)

a: =>1/2x-3/4x=-5/6+7/3
=>-1/4x=14/6-5/6=3/2
=>x=-3/2*4=-6
b: =>4/5x-3/2x=1/2+6/5
=>-7/10x=17/10
=>x=-17/7
c: =>6/5x+6/20=6/5-1/3x
=>6/5x+1/3x=6/5-3/10=12/10-3/10=9/10
=>x=27/46
d: =>6x+3/2+4/5=1/2-2x
=>8x=1/2-3/2-4/5=-1-4/5=-9/5
=>x=-9/40

bài 1 : a,ta có 3/x-1 =4/y-2=5/z-3 => x-1/3=y-2/4=z-3/5
áp dụng .... => x-1+y-2+z-3 / 3+4+5 = x+y+z-1-2-3/3+4+5 = 12/12=1
do x-1/3 = 1 => x-1 = 3 => x= 4 ( tìm y,z tương tự
Bài 1:
a) Ta có: 3/x - 1 = 4/y - 2 = 5/z - 3 => x - 1/3 = y - 2/4 = z - 3/5 áp dụng ... =>x - 1 + y - 2 + z - 3/3 + 4 + 5 = x + y + z - 1 - 2 - 3/3 + 4 + 5 = 12/12 = 1 do x - 1/3 = 1 => x - 1 = 3 => x = 4 ( tìm y, z tương tự )

a, \(\left(5x-1\right)\left(2x-\frac{1}{3}\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}5x-1=0\\2x-\frac{1}{3}=0\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}5x=1\\2x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{5}\\x=\frac{1}{6}\end{cases}}\)
b. \(\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2+1=0\\x-4=0\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2=-1\left(Voly\right)\\x=4\end{cases}\Rightarrow x=4}\)
c, \(2x^2-\frac{1}{3}x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x-\frac{1}{3}\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\2x-\frac{1}{3}=0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{1}{6}\end{cases}}\)
d, \(\left(\frac{4}{5}\right)^{5x}=\left(\frac{4}{5}\right)^7\)
\(\Rightarrow5x=7\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{7}{5}\)
e, Ta có: \(A=\frac{x+5}{x-2}=\frac{\left(x-2\right)+7}{x-2}=1+\frac{7}{x-2}\)
Để A ∈ Z <=> (x - 2) ∈ Ư(7) = { ±1; ±7 }
| x - 2 | 1 | -1 | 7 | -7 |
| x | 3 | 1 | 9 | -5 |
Vậy....
a) \(\left(5x-1\right)\left(2x-\frac{1}{3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}5x-1=0\\2x-\frac{1}{3}=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}5x=1\\2x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{5}\\x=\frac{1}{6}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy : ....
b) \(\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2+1=0\\x-4=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2=-1\left(loại\right)\\x=4\end{cases}}\)
c) \(2x^2-\frac{1}{3}x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x-\frac{1}{3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\2x-\frac{1}{3}=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{1}{6}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy :...

a ) x + 5/12 = -2/3
=> x = -2/3 - 5/12
=> x = -8/12 - 5/12
=> x = -13/12
b ) 4/5 + 3/4 : x = 1/2
=> 3/4 : x = 1/2 - 4/5
=> 3/4 : x = 5/10 - 8/10
=> 3/4 : x = -3/10
=> x = 3/4 : -3/10
=> x = -5/2
c ) x/2 + x/3 = 1/4
=> 3x/6 + 2x/6 = 1/4
=> ( 3x + 2x )/6 = 1/4
=> 5x/6 = 1/4
=> 20x/24 = 6/24
=> 20x = 6
=> x = 6 : 20
=> x = 0 , 3
Chúc bạn học giỏi !!!


a) \(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{4}{12}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{12}\cdot3=\dfrac{12}{12}=1\)
b) \(\dfrac{x-1}{x-2}=\dfrac{3}{5}\) (Điều kiện : \(x\ne2\))
\(\Rightarrow5\left(x-1\right)=3\left(x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-5=3x-6\Leftrightarrow5x-3x=-6+5\Leftrightarrow2x=-1\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c) \(2x:6=\dfrac{1}{4}\Leftrightarrow2x=\dfrac{1}{4}\cdot6=\dfrac{6}{4}=\dfrac{3}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}:2=\dfrac{3}{2}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{3}{4}\)
d) \(\dfrac{x^2+x}{2x^2+1}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left(x^2+x\right)=2x^2+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2x=2x^2+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2x-2x^2=1\Leftrightarrow2x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\).
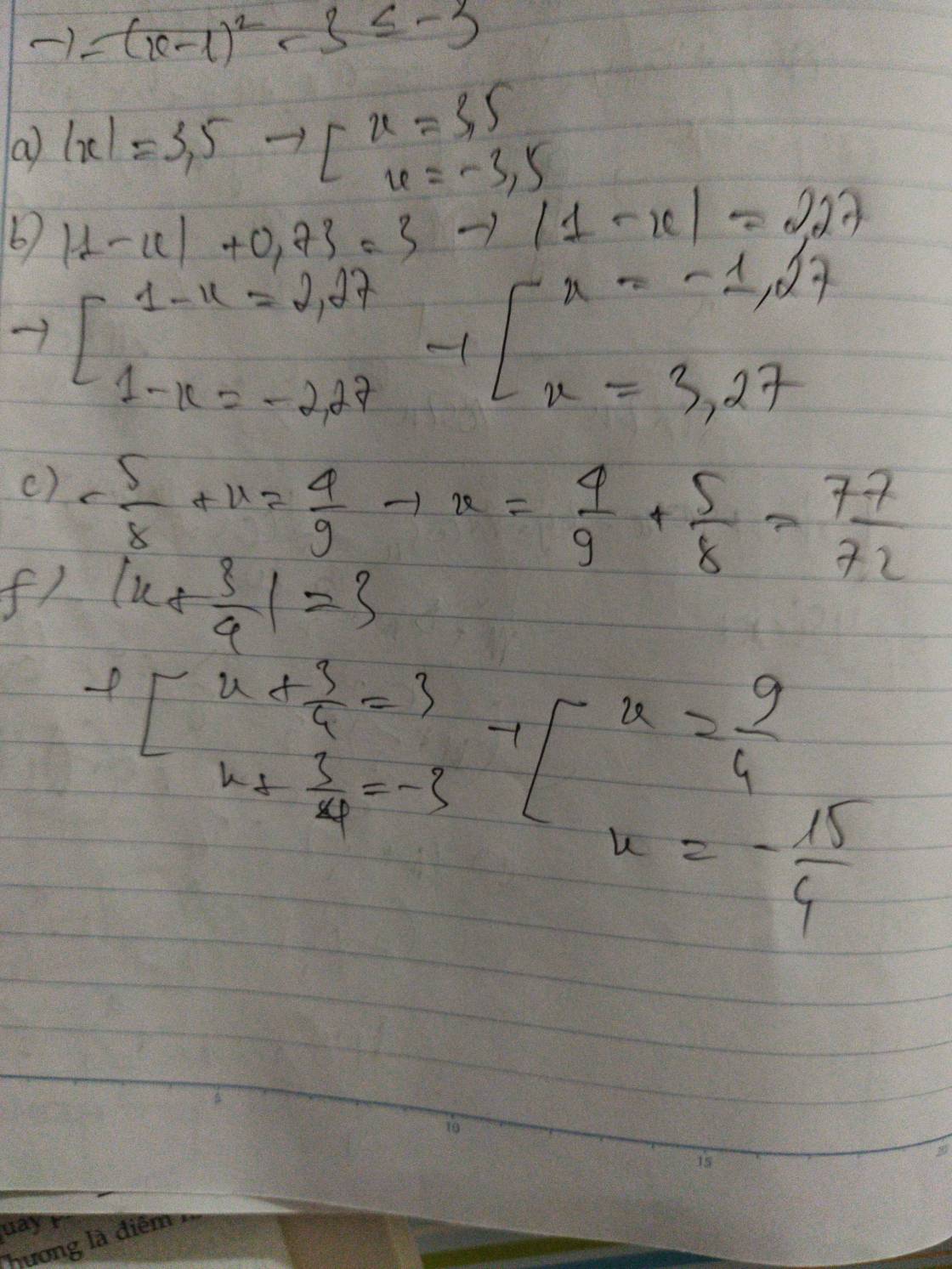
TH1: Với x < 1
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x-1\right)+\left[-\left(x-5\right)\right]=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-x+5-x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-2x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)(nhận)
TH2: Với \(1\le x\le5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)+\left[-\left(x-5\right)\right]=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1+5-x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4=4\) luôn đúng!
TH3: Với x > 5
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-5\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1+x-5=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-6=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=5\) (loại)
Vậy \(1\le x\le5\)