Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Lời giải:
Vì $a,b$ là số tự nhiên nên $2a+1,b-2$ là số nguyên
$(2a+1)(b-2)=12$ nên $2a+1$ là ước của $12$
Mà $2a+1$ là số tự nhiên lẻ nên $2a+1\in\left\{1;3\right\}$
Nếu $2a+1=1$ thì $b-2=12:1=12$
$\Rightarrow a=0; b=14$ (thỏa mãn)
Nếu $2a+1=3$ thì $b-2=12:3=4$
$\Rightarrow a=1; b=6$ (thỏa mãn)

Bạn dùng phương pháp chặn `b` rồi tìm `a` nhé.
`8a^2 + 31b^2 = 2468 <=> 31b^2 <= 2468 <=> b^2 < 81 -> b = 1 -> 8.`
Từ đây tìm `a` theo `b` và nhớ thử lại nhé.

=>3b(4a-3)+20a-15=2820
=>(4a-3)(3b+5)=2820
=>a chia 4 dư 1, b chia 3 dư 2
Do đó: \(\left(a,b\right)\in\varnothing\)

=>2ab-3a+b-9=0
=>b(2a+1)-3a-4,5-*4,5=0
=>b(2a+1)-1,5(2a+1)=4,5
=>(2a+1)(b-1,5)=4,5
=>(2a+1)(2b-3)=9
=>\(\left(2a+1;2b-3\right)\in\left\{\left(1;9\right);\left(3;3\right);\left(9;1\right)\right\}\)
=>\(\left(a,b\right)\in\left\{\left(0;6\right);\left(1;3\right);\left(4;2\right)\right\}\)

\(\dfrac{2\text{x}-1}{3}=\dfrac{3\text{x}+1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow=\dfrac{4\left(2\text{x}-1\right)}{12}=\dfrac{3\left(3\text{x}+1\right)}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8\text{x}-4=9\text{x}+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8\text{x}-9\text{x}=3+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-7\)

\(2^{x+3}.2=2^2.3+52\)
\(=>2^{x+3}.2=64\)
\(=>2^{x+3}=64:2\)
\(=>2^{x+3}=32\)
\(=>2^{x+3}=2^5\)
=>x+3=5
=>x=5-3
=>x=2
Vậy ...........
2x + 3 . 2 = 22 . 3 + 52
2x + 3 . 2 = 4 . 3 + 52
2x + 3 . 2 = 12 + 52
2x + 3 . 2 = 64
2x + 3 = 64 : 2
2x + 3 = 32
2x + 3 = 25
x + 3 = 5
x = 5 - 3
x = 2
Vậy x = 2
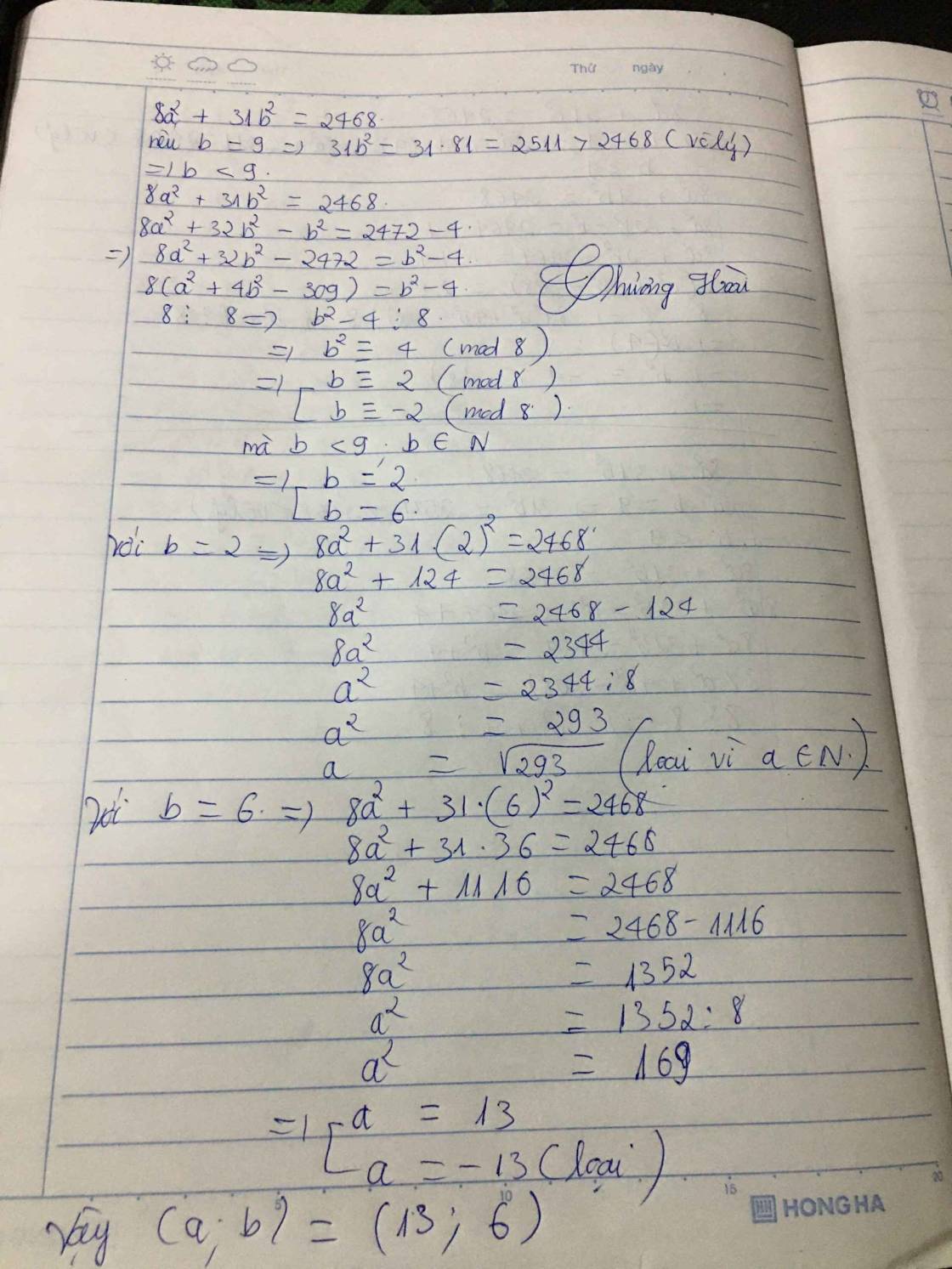
(n+3) ⋮ (2n-1)
=> 2.(n+3)⋮2n-1
=> 2n+6 ⋮ 2n-1
=> (2n-1)+7⋮2n-1
mà 2n-1⋮2n-1
=> 7⋮2n-1
=>2n-1∈Ư(7)={1;7}
=>2n∈{2;8}
=>n∈{1;4}
Vậy n∈{1;4}