
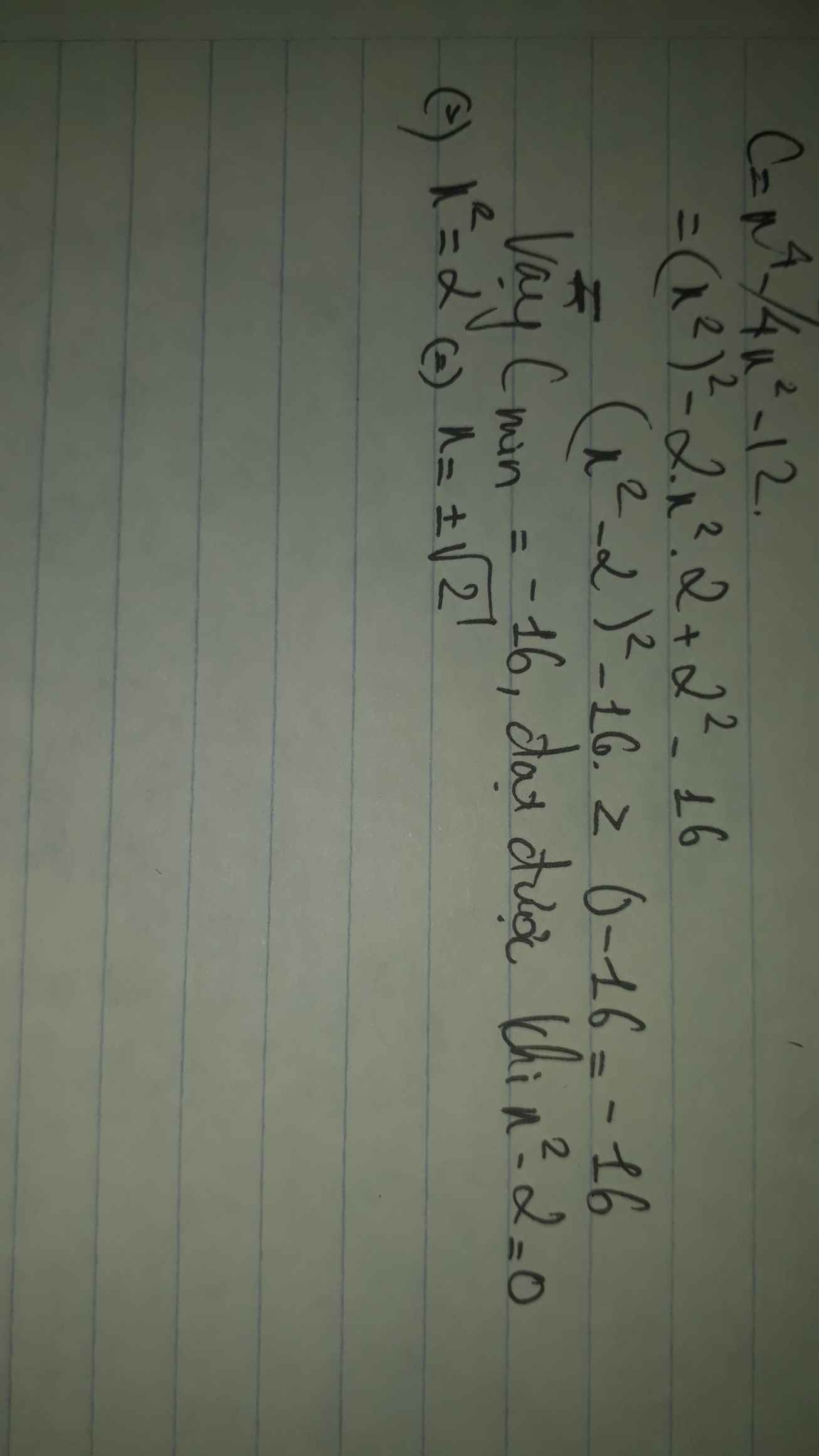
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

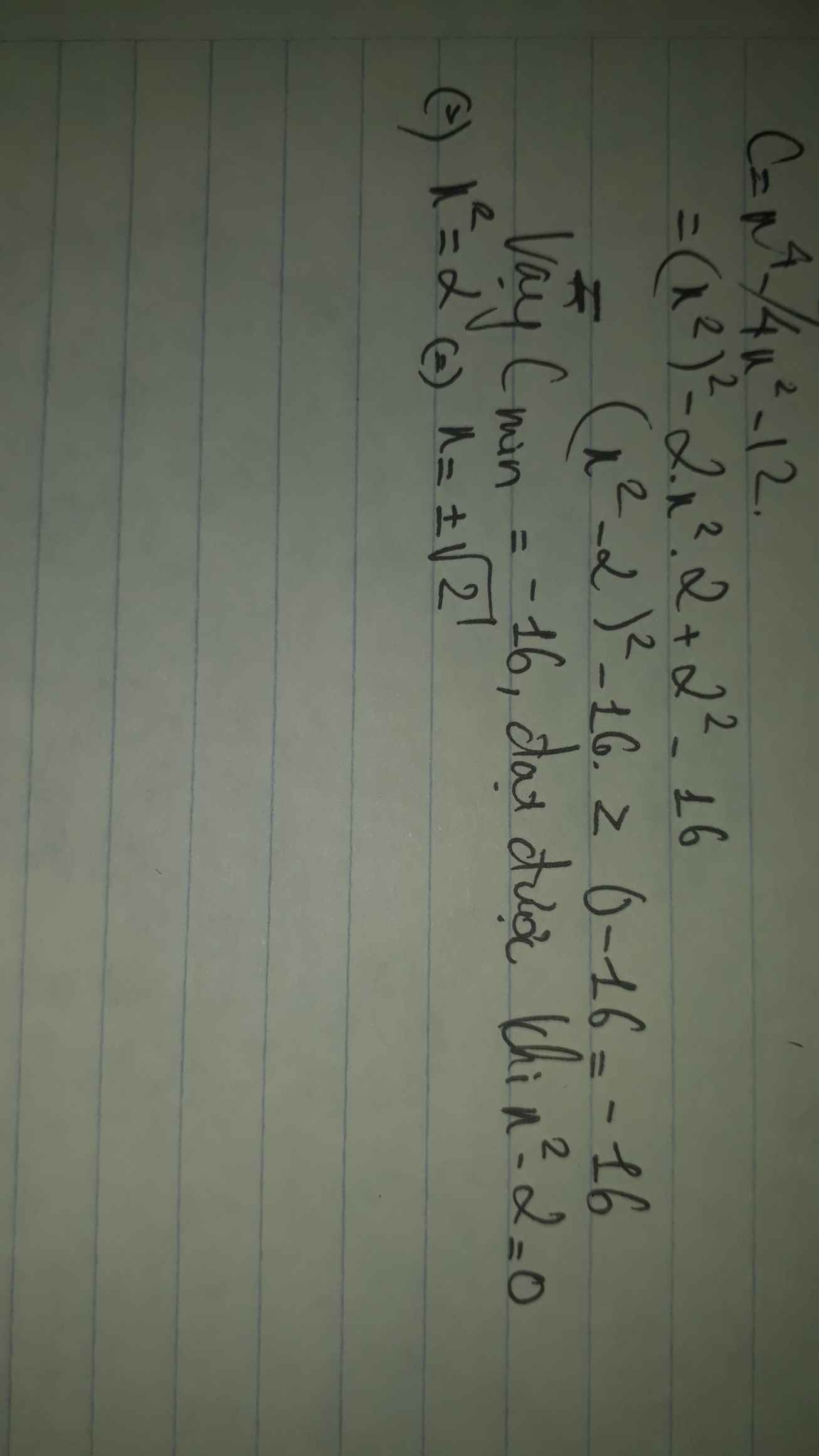

\(4x-x^2-12=-x^2+4x-4-8=-\left(x-4x+4\right)-8=-\left(x-2\right)^2-8\le8\)
=> GTLN của đa thức là 8
<=> x-2 = 0
<=> x = 2
\(x^2+y^2-x+6y+15\)
\(=x^2-2.x.\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{4}+y^2+2.y.3+9+\frac{23}{4}\)
\(=\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\left(y+3\right)^2+\frac{23}{4}\ge\frac{23}{4}\)
=> GTNN của đa thức là 23/4
<=> x-1/2=0 và y+3=0
<=> x=1/2 và y=-3

A = x^2 - 4x + 12 = x^2 - 4x + 4 + 8 = ( x+ 2 )^2 + 8 >= 8 ( với mọi x)
VẬy GTNN của BT klaf 8 khi x - 2 = 0 => x = 2
b) 1 + 6x - x^2 = - ( x^2 - 6x - 1 ) = - ( x^2 - 6x + 9 - 10 )=- ( x - 3 )^2 + 10 <= -10
VẬy GTLN là -10 khi x = 3
sửa lại:
a) \(A=x^2-4x+12\)
\(=\left(x^2-4x+2^2\right)+8\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)^2+8\)
mà (x + 2)2 > 0
Vậy giá trị nhỏ nhất của A = 8 tại x = 2
b) \(A=1+6x-x^2\)
\(=-\left(x^2-6x+3^2\right)+10\)
\(=-\left(x-3\right)^2+10\)
mà -(x - 3)2 < 0
Vậy giá trị lớn nhất của A = 10 tại x = 3


\(A=2x^2+4x+1=2\left(x^2+2x+1\right)-1=2\left(x+1\right)^2-1\ge-1\)
\(A_{min}=-1\) khi \(x=-1\)
Câu B chỉ có max, ko có min
\(B=-x^2+3x+4=-\left(x^2-3x+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)+\dfrac{25}{4}=-\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{25}{4}\le\dfrac{25}{4}\)
\(B_{max}=\dfrac{25}{4}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Câu C cũng chỉ có max, không có min
\(C=-4x^2+8x=-4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+4=-4\left(x-1\right)^2+4\le4\)
\(C_{max}=4\) khi \(x=1\)
Câu D cũng chỉ có max, không có min
\(D=\dfrac{3}{4x^2-4x+1+4}=\dfrac{3}{\left(2x-1\right)^2+4}\le\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(C_{max}=\dfrac{3}{4}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
(4 câu có 3 câu sai đề)
Nhầm đề bài Sorrry
đáng lẽ là ntn này giúp con dc ko ạ
\(\dfrac{3}{4x^{2_-}4x+5}\) Giúp con :(


\(\text{a)}\left(2x-1\right)^2+x+2\)
\(=4x^2-4x+1+x+2\)
\(=4x^2-3x+3\)
\(=\left(4x^2-3x+\frac{9}{16}\right)+\frac{39}{16}\)
\(=\left(2x+\frac{3}{4}\right)^2+\frac{39}{16}\)
\(\text{Vì}\left(2x-\frac{3}{4}\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\text{nên }\left(2x-\frac{3}{4}\right)^2+\frac{39}{16}\ge\frac{39}{16}\)
Vậy \(GTNN=\frac{39}{16}\),dấu bằng xảy ra khi \(x=\frac{3}{8}\)
\(\text{b)}4-x^2+2x\)
\(=\left(-x^2+2x-1\right)+5\)
\(=-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+5\)
\(=-\left(x-1\right)^2+5\)
\(\text{Vì }-\left(x-1\right)^2\le0\)
\(\text{nên }-\left(x-1\right)^2+5\le5\)
Vậy \(GTLN=5\), dấu bằng xảy ra khi \(x=1\)
\(\text{c)}4x-x^2\)
\(=\left(-x^2+4x-4\right)+4\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x+4\right)-4\)
\(=-\left(x-4\right)^2-4\)
\(\text{Vì }-\left(x-4\right)^2\le0\)
\(\text{nên }-\left(x-4\right)^2-4\le-4\)
Vậy \(GTLN=-4\), dấu bằng xảy ra khi \(x=4\)
\(a,\left(2x-1\right)^2+\left(x+2\right)=4x^2-4x+1+x+2\)
\(=4x^2-3x+3\)
\(=4x^2-2.2.\frac{3}{4}x+\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)^2-\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)^2+3\)
\(=\left(2x-\frac{3}{4}\right)^2+\frac{39}{16}\ge\frac{39}{16}\)
Dấu bằng xảy ra khi \(2x-\frac{3}{4}=0\Rightarrow x=\frac{3}{8}\)
Vậy \(x=\frac{3}{8}\)thì biểu thức đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất là \(\frac{39}{16}\)
\(b,4-x^2+2x=-\left(x^2-2x-4\right)\)
\(=-\left(\left(x-2\right)^2-8\right)\)
\(\left(x-2\right)^2-8\ge-8\)
\(-\left(\left(x-2\right)^2-8\right)\le8\)
Dấu bằng xảy ra khi \(x-2=0\Rightarrow x=2\)
Vậy \(x=2\)thì biểu thức đạt giá trị lớn nhất là 8
\(c,4x-x^2=-\left(x^2-4x\right)\)
\(=-\left(\left(x-2\right)^2-4\right)\)
\(\left(x-2\right)^2-4\ge-4\)
\(\Rightarrow-\left(\left(x-2\right)^2-4\right)\le4\)
Dấu bằng xảy ra khi \(x-2=0\Rightarrow x=2\)
Vậy giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức là 4 khi x = 2

Ta có C=x^2-4x-4 / x^2-4x+5
=x^2-4x+4-8/x^2-4x+4+1
=(x^2-4x+4)-8 / (x^2-4x+4)+1
=(x-2)^2 -8/ (x-2)^2 +1
=Vì (x-2)^2 >hoặc = 0
=>(x-2)^2-8 > hoặc = -8 và (x-2)^2+1> hoặc =1 (với mọi x)
Dấu ''='' xảy ra <=> (x-2)^2 =0
<=>x - 2 = 0
<=>x =2
<=> Giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức C là -8/1=-8
Vậy giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức C là minC= - 8 khi x=2
Chúc bạn làm bài tốt ! Mình ko chắc câu trả lời của mình đúng đâu , nhưng cũng ko phải là sai