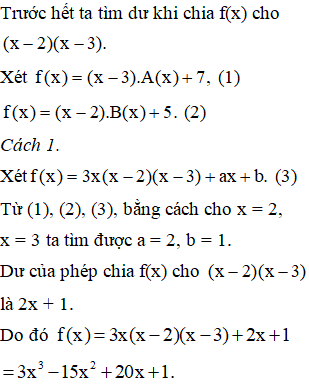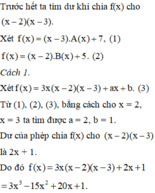Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Vì f(x) chia x-3 dư 7
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(x-3\right)q\left(x\right)+7\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(3\right)=7\)
Vì f(x) chia x-2 dư 5
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(x-2\right)q\left(x\right)+5\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(2\right)=5\)
Ta có f(x) khi chia (x-2)(x-3) thì được thương là 3x và còn dư
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)3x+ax+b\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}f\left(2\right)=2a+b=5\\f\left(3\right)=3a+b=7\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a=2\\b=1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(f\left(x\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)3x+2x+1\)

f(x)= (x-3). Q(x)+2 moi X
f(x)=(x+4).H(x)+9 moi X
=>f(3)= 2
f( -4)= 9
f(x)= (x^2+x-12).(x^2+3)+ ax +b
=(x-3)(x+4). (x^2+3) +ax+b
=>f(3)= 3a+b=2
f(-4)=b -4a=9
=>a= -1; b=5
=> f(x)=(x^2+x-12)(x^2+3)-x+5
= x^4+x^3-9x^2+2x-31
Ta thấy :
x2 +x -12 = x2 +4x - 3x-12
= x(x+4) - 3(x+4)
= (x-3)(x+4)
Vì :
f(x) chia (x-1)(x+4) được x2 + 3 và còn dư
Mà số dư có bậc không vượt quá 1
=> f(x) = (x-3)(x+4)(x2 + 3) +ax +b
Ta có :
f(x) chia (x-3) dư 2
=> f(3)=2
=> 3a+b=2
f(x) chia (x+4) dư 9
=> f(-4)=9
=> b-4a=9
=> 3a+b-b+4a = 2-9
7a = -7
=> a= -1
=> -3 + b =2
b=5
Vậy đa thức f(x) = (x-3)(x+4)(x2 + 3) - x + 5

Gọi thương của phép chia f(x) cho x-2 là A(x); cho x-3 là B(x)
Ta có: f(x) = (x-2).A(x) + 5
f(x) = (x-3).B(x) + 7
Ap dụng định lý Bơ-du ta có:
f(2) = 5
f(3) = 7
Gọi dư của phép chia f(x) cho (x-2)(x-3) là ax+b
Ta có:
f(x) = (x-2)(x-3).(x2-1) + ax + b
\(\Rightarrow\)f(2) = 2a + b = 5
f(3) = 3a + b =7
\(\Rightarrow\)a = 2; b = 1
vậy f(x) = (x-2)(x-3)(x2 - 1) + 2x + 1
= x4 - 5x3 + 5x2 + 7x - 5
cho mình hỏi tại sao dư của f(x) cho (x-2)(x-3) lại phải là ax+b mà không phải cái khác vậy bạn

Vì f(x) chia cho x2-5x+6 được thương là 1-x2 và còn dư nên f(x) có bậc 4 và đa thức dư bậc cao nhất là 1.
Gọi f(x)=(x-2)(x-3)(1-x2)+ax+b
Ta có f(2)=2 vaf(3)=7 thay vào tìm đc a và b suy ra đa thức f(x) cần tìm.
Giải giùm nha!!
Câu hỏi của Bạch Quốc Huy - Toán lớp 8 - Học toán với OnlineMath
Em tham khảo bài tương tự tại đây nhé.