Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Giải như sau.
(1)+(2)⇔x2−2x+1+√x2−2x+5=y2+√y2+4⇔(x2−2x+5)+√x2−2x+5=y2+4+√y2+4⇔√y2+4=√x2−2x+5⇒x=3y(1)+(2)⇔x2−2x+1+x2−2x+5=y2+y2+4⇔(x2−2x+5)+x2−2x+5=y2+4+y2+4⇔y2+4=x2−2x+5⇒x=3y
⇔√y2+4=√x2−2x+5⇔y2+4=x2−2x+5, chỗ này do hàm số f(x)=t2+tf(x)=t2+t đồng biến ∀t≥0∀t≥0
Công việc còn lại là của bạn !

a) M(x) = A(x) - 2B(x) + C(x)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)M(x) = 2x5 - 4x3 + x2 - 2x + 2 - 2(x5 - 2x4 + x2 - 5x + 3) + x4 + 4x3 + 3x2 - 8x + \(4\frac{3}{16}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)M(x) = 2x5 - 4x3 + x2 - 2x + 2 - 2x5 - 4x4 - 2x2 + 10x - 6 + x4 + 4x3 + 3x2 - 8x + \(4\frac{3}{16}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)M(x) = (2x5 - 2x5) + (-4x3 + 4x3) + (x2 - 2x2 + 3x2) + (-2x + 10x - 8x) + (2 - 6 + \(4\frac{3}{16}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\)M(x) = 2x2 + \(\frac{3}{16}\)
b) Thay \(x=-\sqrt{0,25}\)vào M(x), ta được:
\(M\left(x\right)=2\left(-\sqrt{0,25}\right)^2+\frac{3}{16}\)
\(M\left(x\right)=2.0,25+\frac{3}{16}\)
\(M\left(x\right)=0,5+\frac{3}{16}\)
\(M\left(x\right)=\frac{11}{16}\)
c) Ta có : \(x^2\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+\frac{3}{16}\ge\frac{3}{16}\)
Vậy để \(M\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)

a: ĐKXĐ: x<>2; x<>3
\(Q=\dfrac{2x-9-x^2+9+2x^2-4x+x-2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-x-2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}\)
b: Để P<1 thì P-1<0
=>\(\dfrac{x+1-x+3}{x-3}< 0\)
=>x-3<0
=>x<3

\(P\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+Q\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=-5.\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3+3\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{2}{2}+5-5\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3+6\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{2}{2}+5\)
\(P\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+Q\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=-\dfrac{5.1}{8}+\dfrac{3.1}{4}+6-\dfrac{5.1}{8}+\dfrac{6.1}{4}+6\)
\(P\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+Q\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=-\dfrac{5}{8}+\dfrac{3}{4}+6-\dfrac{5}{8}+\dfrac{3}{2}+6\)
\(P\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+Q\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=13\)

a: \(P\left(x\right)=A\left(x\right)+B\left(x\right)=2x^2-x^3+x^3-x^2-3x+4=x^2-3x+4\)
b: Theo đề, ta có: Q(-1)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow5-5+a^2-a=0\)
=>a(a-1)=0
=>a=0 hoặc a=1
a, \(P\left(x\right)=2x^2-x^3+x^3-x^2+4-3x=x^2-3x+4\)
b, Ta có \(Q\left(-1\right)=5-5+a^2+a=a^2+a=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a\left(a+1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow a=0;a=-1\)

\(Ta\)\(có\)
\(P\left(x\right)=-F\left(x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^3+2x^2+x-1=\left(x^3-2x^2+3x+5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^3+2x^2+x-1=-x^3+2x^2-3x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=-3x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
\(Vậy\)\(......\)
sorry \(-x^3+2x^2+x-1=-\left(x^3-2x+3x+5\right)\)
mik thiếu dấu trừ nha

\(A=2x^2\left(x-3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-3\right)\left(2x^2-x\right)\)
\(=\left(x-3\right)x\left(2x-1\right)\)
Ta có:\(\left|x\right|=4\Rightarrow x=4\left(h\right)x=-4\)
Nếu x=4 thì \(A=\left(4-3\right)4\left(2\cdot4-1\right)=28\)
Nếu \(x=-4\) thì \(A=\left(-4-3\right)\left(-4\right)\left[2\left(-4\right)-1\right]=-252\)
Để \(A=0\) thì \(\left(x-3\right)x\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3=0\left(h\right)x=0\left(h\right)2x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(h\right)x=0\left(h\right)x=\frac{1}{2}\)
Mọi x>3 thì ta luôn có:\(x-3>0;x>0;2x-1>2\cdot3-1=5>0\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\left(x-3\right)x\left(2x-1\right)>0\Rightarrowđpcm\)
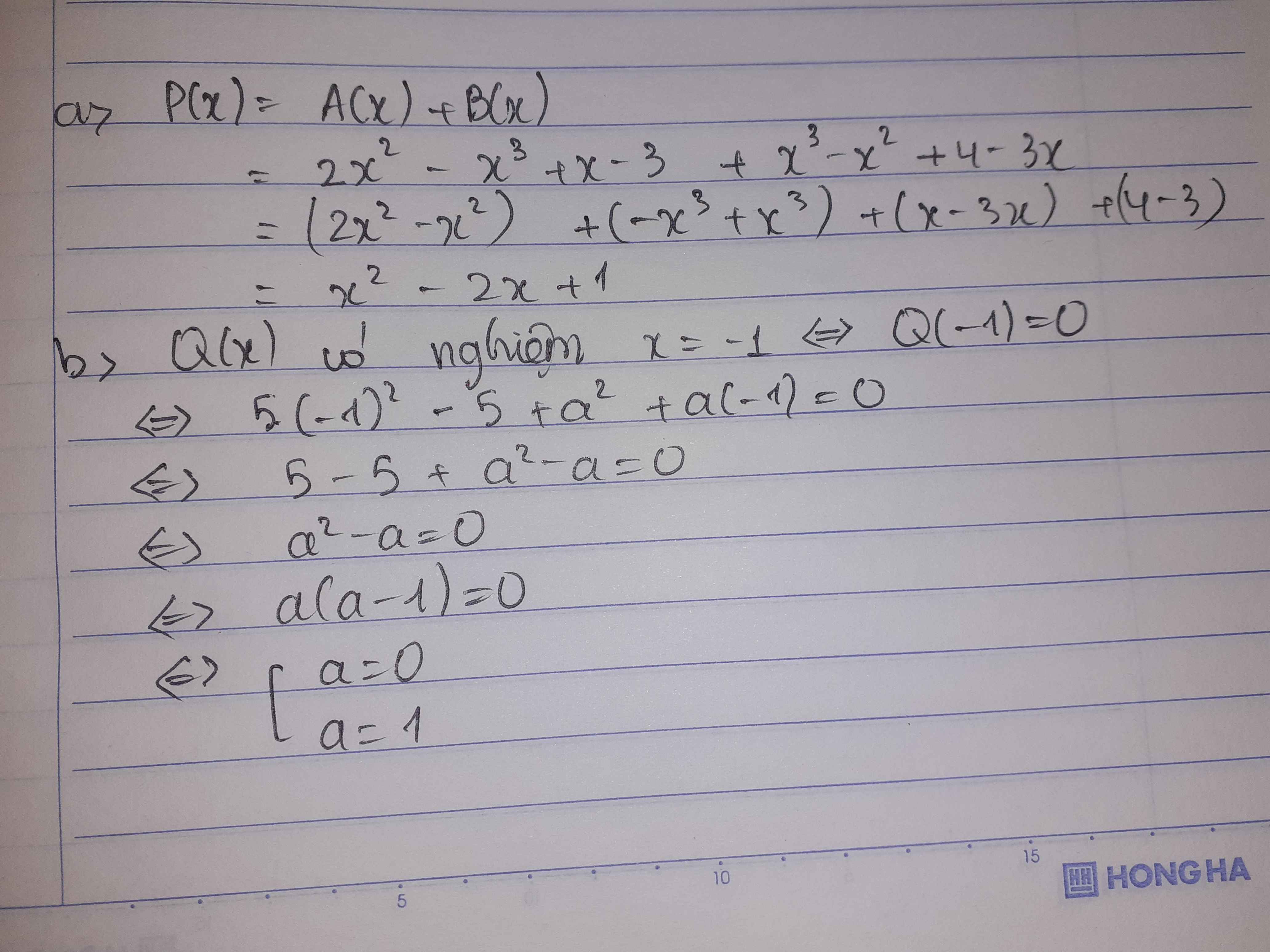
\(P\left(x\right)⋮Q\left(x\right)\)
=>\(x^4-2x^3+x^2+13x-11⋮x^2-2x+3\)
=>\(x^4-2x^3+3x^2-2x^2+4x-6+9x-5⋮x^2-2x+3\)
=>\(\left(x^2-2x+3\right)\cdot\left(x^2-2\right)+9x-5⋮x^2-2x+3\)
=>\(9x-5⋮x^2-2x+3\)
=>9x-5=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{5}{9}\)