
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Chiều rộng của mảnh vườn hình chữ nhật là:
\(\dfrac{21}{4}\) : \(\dfrac{7}{3}\) = \(\dfrac{9}{4}\) (m)
Chu vi của mảnh vườn hìn chữ nhật là:
(\(\dfrac{21}{4}\) + \(\dfrac{9}{4}\)) x 2 = 15 (m)
Diện tích của mảnh vườn hình chữ nhật là:
\(\dfrac{21}{4}\) x \(\dfrac{9}{4}\) = \(\dfrac{189}{16}\) (m2)
b; Số tiền thu được khi trồng hoa để bán trên mảnh đất hình chữ nhật đó là:
80 000 x \(\dfrac{189}{16}\) = 945 000 (đồng)
KL...
Bài 5:
a, Chiều rộng mảnh vườn:
\(\dfrac{21}{4}:\dfrac{7}{3}=\dfrac{9}{4}\left(m\right)\)
Chu vi mảnh đất:
\(2\times\left(\dfrac{21}{4}+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)=15\left(m\right)\)
Diện tích mảnh đất:
\(\dfrac{21}{4}\times\dfrac{9}{4}=\dfrac{189}{16}\left(m^2\right)\)
b, Số tiền thu được khi bán hoa:
\(\dfrac{189}{16}\times80000=945000\left(đồng\right)\)

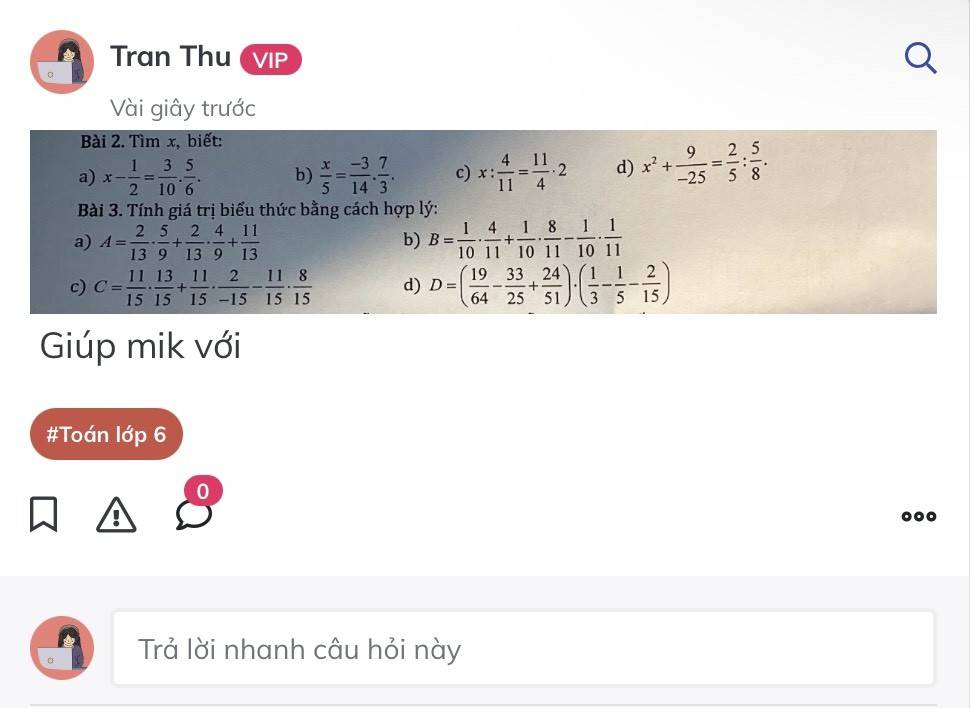
Bài 2:
a; \(x\) - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = \(\dfrac{3}{10}\).\(\dfrac{5}{6}\)
\(x\) - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Vậy \(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{4}\)
b; \(\dfrac{x}{5}\) = \(\dfrac{-3}{14}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{7}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{x}{5}\) = \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\) \(\times\) 5
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{-5}{2}\)
Vậy \(x\) = \(\dfrac{-5}{2}\);
c; \(x\) : \(\dfrac{4}{11}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{4}\) \(\times\) 2
\(x\) : \(\dfrac{4}{11}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{2}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{11}{2}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{4}{11}\)
\(x\) = 2
Vậy \(x\) = 2
d; \(x^2\) + \(\dfrac{9}{-25}\) = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\) : \(\dfrac{5}{8}\)
\(x^2\) - \(\dfrac{9}{25}\) = \(\dfrac{16}{25}\)
\(x^2\) = \(\dfrac{16}{25}\) + \(\dfrac{9}{25}\)
\(x^2\) = \(\dfrac{25}{25}\)
\(x^2\) = 1
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\)\(\in\) {-1; 1}
Bài 3:
a; A = \(\dfrac{2}{13}\)\(\times\) \(\dfrac{5}{9}\)+ \(\dfrac{2}{13}\)\(\times\)\(\dfrac{4}{9}\) + \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
A = \(\dfrac{2}{13}\) \(\times\)(\(\dfrac{5}{9}\) + \(\dfrac{4}{9}\)) + \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
A = \(\dfrac{2}{13}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{9}{9}\) + \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
A = \(\dfrac{2}{13}\) + \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
A = 1
b; B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\).\(\dfrac{4}{11}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{10}\).\(\dfrac{8}{11}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{10}\).\(\dfrac{1}{11}\)
B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) x (\(\dfrac{4}{11}\) + \(\dfrac{8}{11}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{11}\))
B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) x (\(\dfrac{12}{11}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{11}\))
B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) x \(\dfrac{11}{11}\)
B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\)

a)
\(175\cdot19+38\cdot175+43\cdot175\\ =175\cdot19+175\cdot38+175\cdot43\\ =175\cdot\left(19+38+43\right)\\ =175\cdot100\\ =17500\)
b)
\(125\cdot75+125\cdot13-80\cdot125\\ =125\cdot75+125\cdot13-125\cdot80\\ =125\cdot\left(75+13-80\right)\\ =125\cdot10\\ =125\cdot8\\ =1000\)
a, 175. 19 + 38. 175 + 43. 175
= 175. 19 + 175. 38 + 175. 43
= 175.(19 + 38 + 43)
= 175. 100
= 17500

Vì có tia Oz nằm giữa 2 tia Ox và Oy
=> \(\widehat{xOz}+\widehat{zOy}=\widehat{xOy}\)
=> \(\widehat{zOy}=\widehat{xOy}-\widehat{xOz}\)
Thay \(\widehat{xOy}=110^o;\widehat{xOz}=80^o\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{zOy}=110^o-80^o=30^o\)

Lời giải:
a.
$=\frac{3}{5}-\frac{7}{4}=\frac{12-35}{20}=\frac{-23}{20}$
b.
$=-(2+\frac{5}{8})=-\frac{21}{8}$
c.
$=-(\frac{1}{8}+\frac{5}{9})=-\frac{9+8.5}{8.9}=\frac{-49}{72}$
d.
$=\frac{6}{13}-\frac{14}{39}=\frac{18}{39}-\frac{14}{39}=\frac{4}{39}$
e.
$=\frac{-3}{4}+\frac{5}{7}=\frac{5}{7}-\frac{3}{4}$
$=\frac{20-21}{7.4}=\frac{-1}{28}$

Bài 5
1) x ∈ Ư(18) = {1; 2; 3; 6; 9; 18}
x ∈ B(4) = {0; 4; 8; 12; 16; 20; ...}
Vậy không tìm được x thỏa mãn đề bài
2) x ∈ Ư(20) = {1; 2; 4; 5; 10; 20}
x ∈ B(2) = {0; 2; 4; 6; 8; 10; 12; 14; 16; 18; 20; ...}
⇒ x ∈ {2; 4; 10; 20}
3) x ∈ B(12) = {0; 12; 24; 36; 48; ...; 96; 108; ...}
Mà 30 ≤ x ≤ 100
⇒ x ∈ {36; 48; ...; 96}
4) x ∈ Ư(150) = {1; 2; 3; 5; 6; 10; 15; 25; 30; 50; 75; 150}
Mà x ≤ 50
⇒ x ∈ {1; 2; 3; 5; 6; 10; 15; 25; 30; 50}
5) 70 ⋮ x và 168 ⋮ x
⇒ x ∈ ƯC(70; 168)
Ta có:
70 = 2.5.7
168 = 2³.3.7
⇒ ƯCLN(70; 168) = 2.7 = 14
⇒ x ∈ ƯC(70; 168) = Ư(14) = {1; 2; 7; 14}
Mà x > 10
⇒ x = 14
6) Ta có:
(1995 + 2005 + x) ⋮ 5
1995 ⋮ 5
2005 ⋮ 5
⇒ x ⋮ 5
⇒ x ∈ B(5) = {0; 5; 10; 15; 20; 25; 30; 35; 40; ...}
Mà 23 < x ≤ 35
⇒ x ∈ {25; 30; 35}
Bài 6
1) Do 17x2y chia hết cho 2 và 5 nên y = 0
⇒ Số đã cho có dạng: 17x20
Để 17x20 chia hết cho 3 thì (1 + 7 + x + 2 + 0) ⋮ 3
⇒ (10 + x) ⋮ 3
⇒ x ∈ {2; 5; 8}
Vậy x ∈ {2; 5; 8}; y = 0
2) Do 234xy chia hết cho 2 và 5 nên y = 0
⇒ Số đã cho có dạng: 234x0
Để 234x0 chia hết cho 9 thì (2 + 3 + 4 + x + 0) ⋮ 9
⇒ (9 + x) ⋮ 9
⇒ x ∈ {0; 9}
Vậy x ∈ {0; 9}; y = 0
3) Do 4x6y chia hết cho 2 và 5 nên y = 0
Mà x - y = 4
⇒ x = 4 + y
⇒ x = 4
Vậy x = 4; y = 0
4) Do 57x2y chia hết cho 5 nhưng không chia hết cho 2 nên y = 5
⇒ Số đã cho có dạng 57x25
Để 57x25 chia hết cho 9 thì (5 + 7 + x + 2 + 5) ⋮ 9
⇒ (19 + x) ⋮ 9
⇒ x = 8
Vậy x = 8; y = 5




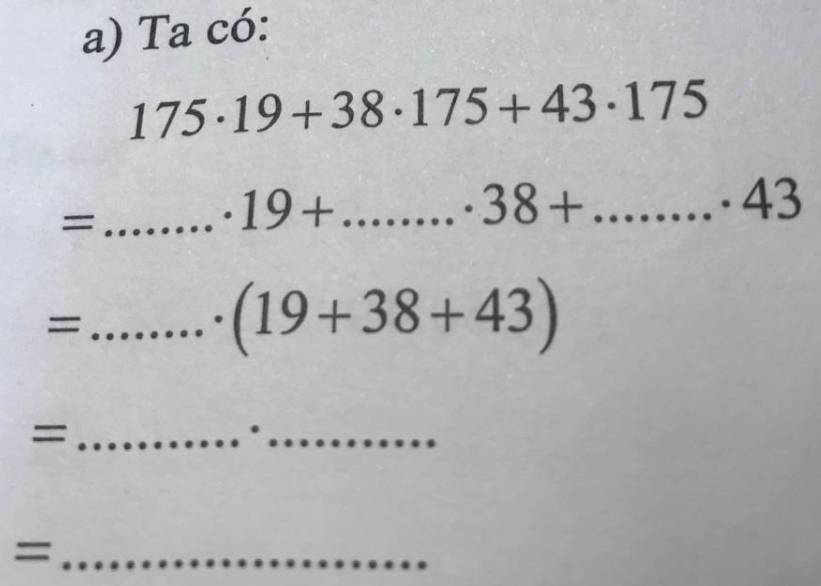
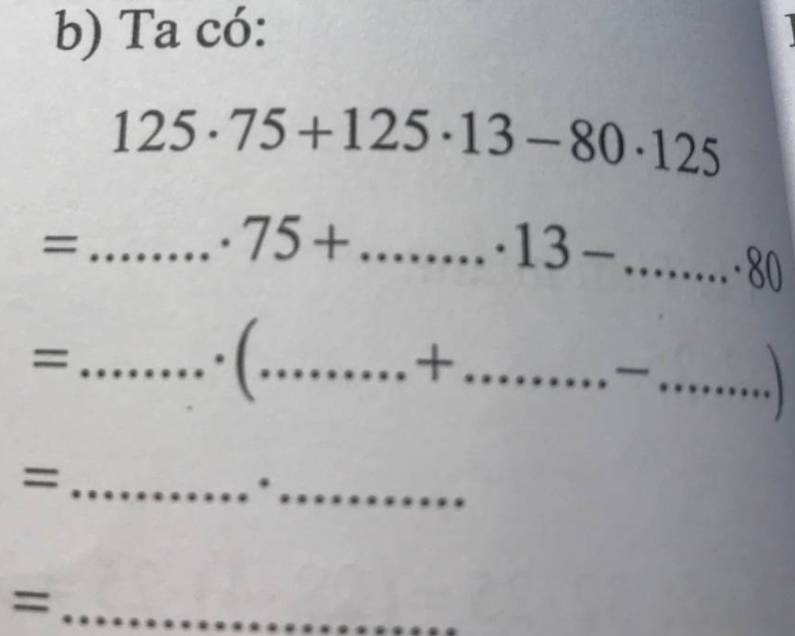
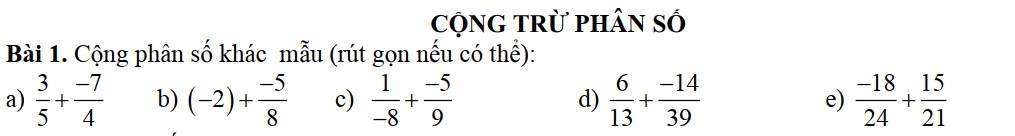

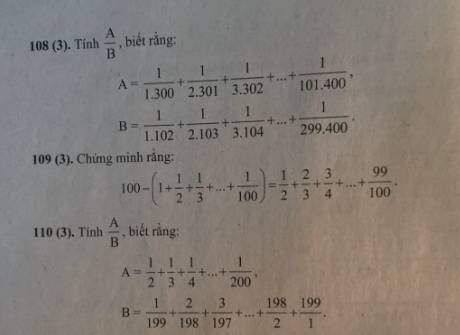
Bài 1:
e; \(\dfrac{10}{21}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{8}\) : \(\dfrac{15}{4}\)
= \(\dfrac{10}{21}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{8}\) x \(\dfrac{4}{15}\)
= \(\dfrac{10}{21}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{10}\)
= \(\dfrac{100}{210}\) - \(\dfrac{21}{210}\)
= \(\dfrac{79}{210}\)
f; (\(\dfrac{2}{3}\) + \(\dfrac{3}{4}\)).(\(\dfrac{5}{7}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{14}\))
= (\(\dfrac{8}{12}\) + \(\dfrac{9}{12}\)).(\(\dfrac{10}{14}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{14}\))
= \(\dfrac{17}{12}\).\(\dfrac{15}{14}\)
= \(\dfrac{85}{56}\)