Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Chọn A.
Ta có : 
Vậy để hàm số liên tục tại x = 0 thì f(0) = 1.

Chọn C.
Ta có :
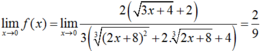
Vậy để hàm số liên tục tại x = 0 ta chọn f(0) = 2/9.

2: ĐKXĐ: x<>1
\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{\left(x^2-3x+3\right)'\left(x-1\right)-\left(x^2-3x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)'}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)-\left(x^2-3x+3\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2-5x+3-x^2+3x-3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
f'(x)=0
=>x^2-2x=0
=>x(x-2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
1:
\(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3-2\sqrt{2}\cdot x^2+8x-1\)
=>\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot3x^2-2\sqrt{2}\cdot2x+8=x^2-4\sqrt{2}\cdot x+8=\left(x-2\sqrt{2}\right)^2\)
f'(x)=0
=>\(\left(x-2\sqrt{2}\right)^2=0\)
=>\(x-2\sqrt{2}=0\)
=>\(x=2\sqrt{2}\)

1) \(y=\dfrac{2x^2+1}{x^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=\dfrac{\left(4x+1\right)x^2-2x\left(2x^2+1\right)}{x^4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y'=\dfrac{4x^3+x^2-4x^3-2x}{x^4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y'=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{x^4}=\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{x^4}=\dfrac{x-2}{x^3}\)
2) \(f\left(x\right)=\sqrt[]{-5x^2+14x-9}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{-10x+14}{2\sqrt[]{-5x^2+14x-9}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{-2\left(5x-7\right)}{2\sqrt[]{-5x^2+14x-9}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{-\left(5x-7\right)}{\sqrt[]{-5x^2+14x-9}}\)
Để \(f'\left(x\right)=0\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{-\left(5x-7\right)}{\sqrt[]{-5x^2+14x-9}}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{5}\)
Vậy tập hợp giá trị để \(f'\left(x\right)=0\) là \(\left\{\dfrac{7}{5}\right\}\)

Đáp án D
- Phương pháp: Sử dụng công thức 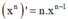 và
và 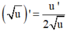 tính f'(x). Từ đó giải bất phương trình.
tính f'(x). Từ đó giải bất phương trình.
- Cách giải:
+ Ta có: 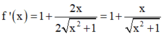
+ Theo đề bài ta có: 2x.f'(x) - f(x) ≥ 0.
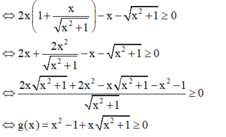
+ Thử các đáp án:
+ Với 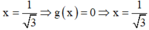 thuộc tập nghiệm của BPT.
thuộc tập nghiệm của BPT.
⇒ Loại đáp án A, B và C.

Đáp án D
- Phương pháp: Sử dụng công thức 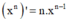 và
và 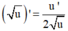 tính f'(x). Từ đó giải bất phương trình.
tính f'(x). Từ đó giải bất phương trình.
- Cách giải:
+ Ta có: 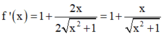
+ Theo đề bài ta có: 2x.f'(x) - f(x) ≥ 0.
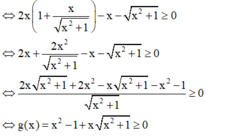
+ Thử các đáp án:
+ Với 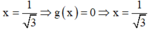 thuộc tập nghiệm của BPT.
thuộc tập nghiệm của BPT.
⇒ Loại đáp án A, B và C.

1.
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\sqrt{x+2}-\sqrt{2-x}}{x}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{2x}{x\left(\sqrt{x+2}+\sqrt{2-x}\right)}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x+2}+\sqrt{2-x}}=\dfrac{2}{2\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
Vậy cần bổ sung \(f\left(0\right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\) để hàm liên tục tại \(x=0\)
2.
a. \(f\left(0\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^-}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^-}\left(x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{\sqrt{x+1}-1}{\sqrt[3]{1+x}-1}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{x\left(\sqrt[3]{\left(x+1\right)^2}+\sqrt[3]{x+1}+1\right)}{x\left(\sqrt[]{x+1}+1\right)}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{\sqrt[3]{\left(x+1\right)^2}+\sqrt[3]{x+1}+1}{\sqrt[]{x+1}+1}=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(0\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^-}f\left(x\right)\) nên hàm liên tục tại \(x=0\)
2b.
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}\dfrac{x^3-x^2+2x-2}{x-1}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}\dfrac{x^2\left(x-1\right)+2\left(x-1\right)}{x-1}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}\dfrac{\left(x^2+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}{x-1}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}\left(x^2+2\right)=3\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}f\left(x\right)=f\left(1\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}\left(3x+a\right)=a+3\)
- Nếu \(a=0\Rightarrow f\left(1\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}f\left(x\right)\) hàm liên tục tại \(x=1\)
- Nếu \(a\ne0\Rightarrow\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}f\left(x\right)\ne\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}f\left(x\right)\Rightarrow\) hàm không liên tục tại \(x=1\)

Đáp án A