Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Ta có \(f\left(1\right)+f\left(10\right)+f\left(100\right)=1+a+b+100+10a+b+10000+100a+b\)
\(=10101+111a+3b\)
Tương tự \(G\left(1\right)+G\left(10\right)+G\left(100\right)=10101+111m+3n\)
Từ đây ta có \(111a-3b=111m-3n\Rightarrow111\left(a-m\right)-3\left(b-n\right)=0\)
Xét \(h\left(x\right)=f\left(x\right)-G\left(x\right)\) , khi đó \(h\left(x_0\right)=f\left(x_0\right)-G\left(x_0\right)\)
\(=ax_0+b-mx_0-n=\left(a-m\right)x_0+\left(b-n\right)\)
Để \(h\left(x_0\right)=0\Rightarrow\left(a-m\right)x_0+\left(b-n\right)=0\Rightarrow3\left(a-m\right)x_0+3\left(b-n\right)=0\)
Ta đã có \(111a-3b=111m-3n\Rightarrow111\left(a-m\right)-3\left(b-n\right)=0\)
Vậy nên \(3x_0=111\Rightarrow x_0=37\)
Tóm lại \(f\left(37\right)=G\left(37\right)\)

Lời giải:
a)
\(f(-3)=(-3)^2=9; f(-\frac{1}{2})=(\frac{-1}{2})^2=\frac{1}{4}\)
\(f(0)=0^2=0\)
\(g(1)=3-1=2; g(2)=3-2=1; g(3)=3-3=0\)
b)
\(2f(a)=g(a)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 2a^2=3-a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 2a^2+a-3=0\Leftrightarrow (2a+3)(a-1)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} a=\frac{-3}{2}\\ a=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

e) Đặt x4+x2+1=a
=> a2-38a+105=0
=> a2-38a+361 -256=0
=> (a-19)2-162=0
=> (a-19-16)(a-19+16)=0
=> (a-35)(a-3)=0
=>\(\orbr{\begin{cases}a=35\\a=3\end{cases}}\)
Bạn cứ thay a vào và làm tiếp nha!

\(f\left(2\right)=5.2+1=11\)
\(f\left(-1\right)=-5+1=-4\)
\(\Rightarrow a=11+4=15\)
\(\Rightarrow g\left(1\right)=15.1+3=18\)

c) Từ kết quả câu a, b ta được bảng sau:
Nhận xét:
- Các hàm số y = f(x) = 2/3 x và y = g(x) = 2/3 x + 3 là hai hàm số đồng biến vì khi x tăng thì y cũng nhận được các giá trị tương ứng tăng lên.
- Cùng một giá trị của biến x, giá trị của hàm số y = g(x) luôn luôn lớn hơn giá trị tương ứng của hàm số y = f(x) là 3 đơn vị.
a) Cho hàm số : \(y=f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}x\)
Ta có : \(f\left(-2\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.\left(-2\right)=-\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(f\left(-1\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.\left(-1\right)=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(f\left(0\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.0=0\)
\(f\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(f\left(1\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.1=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(f\left(2\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.2=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(f\left(3\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.3=2\)
b) Cho hàm số : \(y=g\left(x\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}x+3\)
\(g\left(-2\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.\left(-2\right)+3=\dfrac{5}{3}\)
\(g\left(-1\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.\left(-1\right)+3=\dfrac{7}{3}\)
\(g\left(0\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.0+3=3\)
\(g\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.\dfrac{1}{2}+3=\dfrac{10}{3}\)
\(g\left(1\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.1+3=\dfrac{11}{3}\)
\(g\left(2\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.2+3=\dfrac{13}{3}\)
\(g\left(3\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.3+3=5\)
c) Khi \(x\)lấy cùng một giá trị thì giá trị của \(g\left(x\right)\) lớn hơn giá trị của \(f\left(x\right)\) là \(3\) đơn vị.

a.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4xy+8x-6y-12=4xy-12x+54\\3xy-3x+3y-3=3xy+3y-12\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}20x-6y=66\\-3x=-9\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1-x\\x^2+xy+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x\left(1-x\right)+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3=0\Rightarrow x=-3\Rightarrow y=4\)
c.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\frac{2x-5}{3}\\x^2-y^2=40\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-\left(\frac{2x-5}{3}\right)^2-40=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2-\left(4x^2-20x+25\right)-360=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x^2+20x-385=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=7\Rightarrow y=3\\x=-11\Rightarrow y=-9\end{matrix}\right.\)
d.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\frac{36-3x}{2}\\\left(x-2\right)\left(y-3\right)=18\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(\frac{36-3x}{2}-3\right)=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(10-x\right)=12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2+12x-32=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\Rightarrow y=12\\x=8\Rightarrow y=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
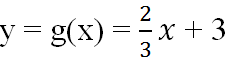
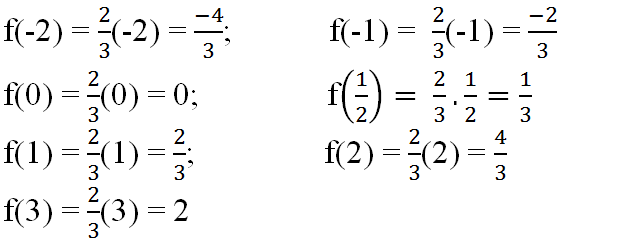
Giải:
Ta có: \(g\left(x\right)=\left(2x+1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow g\left(3\right)=\left(2.3+1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow g\left(3\right)=\left(6+1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow g\left(3\right)=7^2=49\)
Ta có:
\(f\left(x\right)=2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(g\left(3\right)\right)=2.49-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(g\left(3\right)\right)=97\)
Vậy ...
f(g(x))=2.(2x+1)^2-1
f(g(3))=2.(2.3+1)^2-1=97