
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



a: 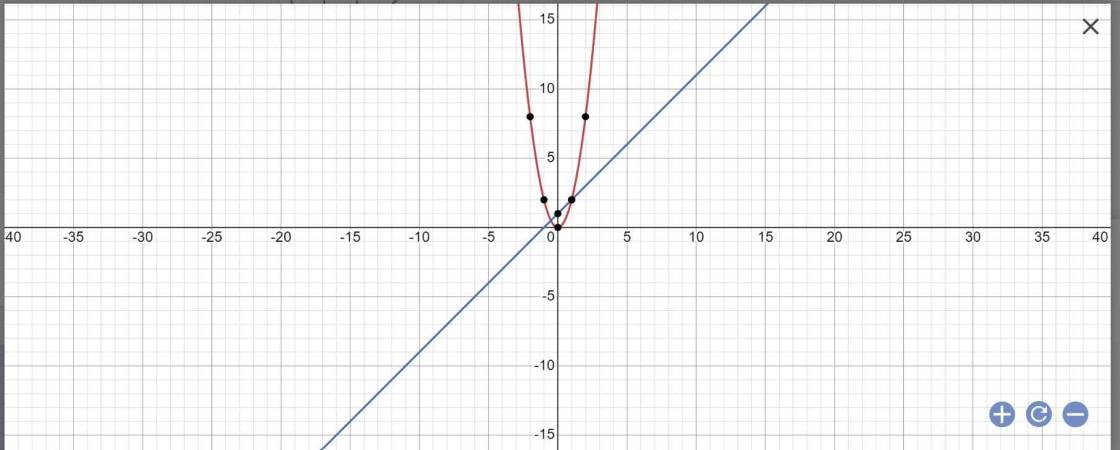
b: PTHĐGĐ là:
2x^2=x+1
=>2x^2-x-1=0
=>2x^2-2x+x-1=0
=>(X-1)(2x+1)=0
=>x=-1/2 hoặc x=1
=>y=2*1/4=1/2 hoặc y=2

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(P\right):y=x^2\\\left(d\right):y=-x+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
a) Tọa độ giao điểm của (P) và (Q) là nghiệm của hệ phương trình
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=x^2\\y=-x+2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=x^2\\x^2=-x+2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=x^2\\x^2+x-2=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(pt\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\left(a+b+c=1+1-2=0\right)\)
\(hpt\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\y=4\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy tọa độ giao điểm của (P) và (Q) là \(A\left(1;1\right)\&B\left(-2;4\right)\)
a) Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm :
x2 = - x + 2
<=> (x - 1)(x + 2) = 0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với x = 1 ta được y = 1
Với x = -2 ta được y = 4
Vậy tọa độ giao điểm là A(1; 1) ; B(-2;4)
b) Gọi C(-2 ; 0) ; D(1;0)
ta được \(S_{AOB}=S_{ABCD}-S_{BOC}-S_{AOD}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(BC+AD\right).CD}{2}-\dfrac{BC.CO}{2}-\dfrac{AD.DO}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(4+1\right).3}{2}+\dfrac{4.2}{2}+\dfrac{1.1}{2}=12\) (đvdt)