Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a, f(10) = \(10^4\) + \(10^3\)- \(12.10^2\)+ 4.10 + 16
f(10) = ......

a) Vẽ đồ thị hàm số y = x2.
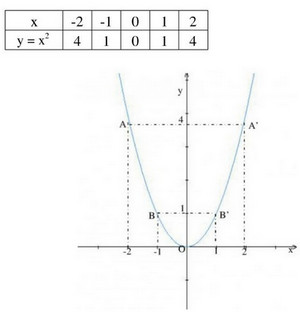
b) Ta có y = f(x) = x2 nên
f(-8) = (-8)2 = 64; f(-1,3) = (-1,3)2 = 1,69; f(-0,75) = (-0,75)2 = 0,5625; f(1,5) = 1,52 = 2,25.
c) Theo đồ thị ta có:
(0,5)2 ≈ 0,25
(-1,5)2 ≈ 2,25
(2,5)2 ≈ 6,25
d) Theo đồ thị ta có: Điểm trên trục hoành √3 thì có tung độ là y = (√3)2 = 3. Suy ra điểm biểu diễn √3 trên trục hoành bằng 1,7. Tương tự điểm biểu diễn √7 gồm bằng 2,7.


a) Để hàm xác định thì \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge0\\\sqrt{x}-1\ne0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge0\\x\ne1\end{cases}}\)
b) Ta có: \(f\left(x\right)=\frac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(4-2\sqrt{3}\right)=\frac{\sqrt{4-2\sqrt{3}}+1}{\sqrt{4-2\sqrt{3}}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)^2}+1}{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)^2}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-2}\)
và \(f\left(a^2\right)=\frac{\sqrt{a^2}+1}{\sqrt{a^2}-1}=\frac{\left|a\right|+1}{\left|a\right|-1}\)(với \(a\ne\pm1\))
* Nếu \(a\ge0;a\ne1\)thì \(f\left(a^2\right)=\frac{a+1}{a-1}\)
* Nếu \(a< 0;a\ne-1\)thì \(f\left(a^2\right)=\frac{a-1}{a+1}\)
c) \(f\left(x\right)=\frac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{x}-1+2}{\sqrt{x}-1}=1+\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
Để f(x) nguyên thì \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)nguyên hay \(2⋮\sqrt{x}-1\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}-1\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2\right\}\)
Mà \(\sqrt{x}-1\ge-1\)nên ta xét ba trường hợp:
+) \(\sqrt{x}-1=-1\Rightarrow x=0\left(tmđk\right)\)
+) \(\sqrt{x}-1=1\Rightarrow x=4\left(tmđk\right)\)
+) \(\sqrt{x}-1=2\Rightarrow x=9\left(tmđk\right)\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;4;9\right\}\)thì f(x) có giá trị nguyên
d) \(f\left(x\right)=\frac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\); \(f\left(2x\right)=\frac{\sqrt{2x}+1}{\sqrt{2x}-1}\)
f(x) = f(2x) khi \(\frac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{2x}+1}{\sqrt{2x}-1}\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{2x}-1\right)=\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{2x}+1\right)\)\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}x+\sqrt{2x}-\sqrt{x}-1=\sqrt{2}x-\sqrt{2x}+\sqrt{x}-1\)\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x}-\sqrt{x}=-\sqrt{2x}+\sqrt{x}\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{2x}=2\sqrt{x}\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x}=\sqrt{x}\Leftrightarrow x=0\)(tmđk)
Vậy x = 0 thì f(x) = f(2x)

a: ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2< =x< =2\\x< >0\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: \(f\left(-x\right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{2-\left(-x\right)}-\sqrt{2+\left(-x\right)}}{-x}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2+x}-\sqrt{2-x}}{-x}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2-x}-\sqrt{2+x}}{x}=f\left(x\right)\)

Câu 2:
c) Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của (P) và (d) là:
\(\dfrac{1}{2}x^2=2x+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}x^2-2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+4=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=4\\x-2=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay x=6 vào (P), ta được:
\(y=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot6^2=18\)
Thay x=-2 vào (P), ta được:
\(y=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\left(-2\right)^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot4=2\)
Vậy: Tọa độ giao điểm của (P) và (d) là (6;18) và (-2;2)
Câu 3:
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-et, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-b}{a}=\dfrac{-\left(-2\right)}{1}=2\\x_1\cdot x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{-1}{1}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(P=x_1^3+x_2^3\)
\(=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^3-3\cdot x_1x_2\left(x_1+x_2\right)\)
\(=2^3-3\cdot\left(-1\right)\cdot2\)
\(=8+3\cdot2\)
\(=8+6=14\)
Vậy: P=14