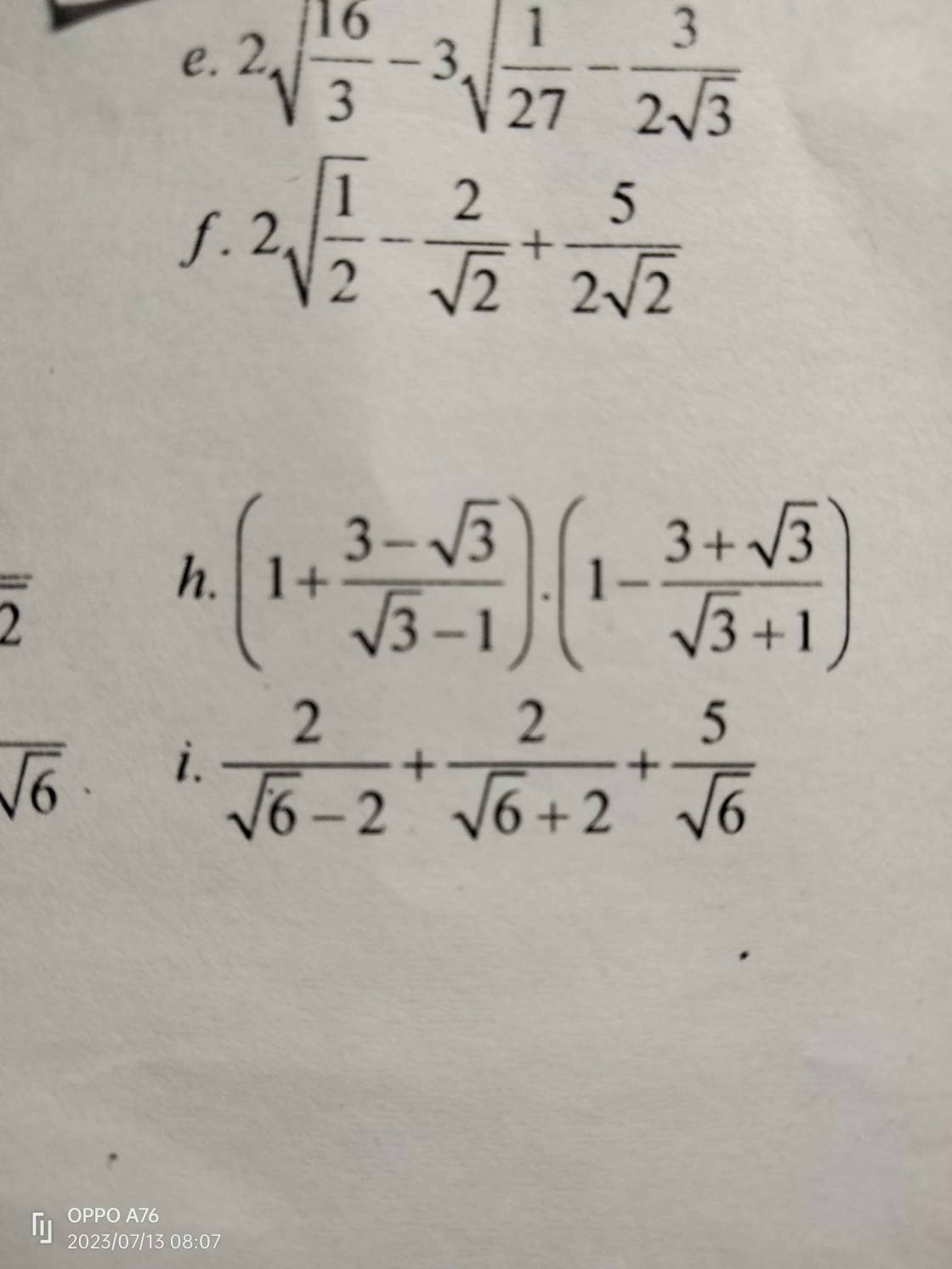Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1) Áp dụng định lí Pytago vào ΔABC vuông tại A, ta được:
\(BC^2=AB^2+AC^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow BC^2=6^2+8^2=100\)
hay BC=10(cm)
Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông vào ΔABC vuông tại A có AH là đường cao ứng với cạnh huyền BC, ta được:
\(AH\cdot BC=AB\cdot AC\)
\(\Leftrightarrow AH\cdot10=6\cdot8=48\)
hay AH=4,8(cm)

ĐKXĐ\(x\ge3\)
<=>\(2\sqrt{9\left(x-3\right)}-\frac{1}{2}\sqrt{4\left(x-3\right)}=10\)
<>\(2.3\sqrt{x-3}-\frac{1}{2}.2\sqrt{x-3}=10\)
<=>\(5\sqrt{x-3}=10\)
<=>\(\sqrt{x-3}=2\)
<=>\(x-3=4\)
<=>\(x=7\)(TMĐKXĐ)

2\(\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}\) - 3\(\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{27}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{8}{\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{3\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{8}{\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{16}{2\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{2}{2\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{11}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{11\sqrt{3}}{6}\)
f, 2\(\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2}}\)- \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2}}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
= \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2}}\) - \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2}}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
= \(\dfrac{5}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
= \(\dfrac{5\sqrt{2}}{4}\)
(1 + \(\dfrac{3-\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-1}\)).(1- \(\dfrac{3+\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}+1}\))
= \(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1+3-\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-1}\).\(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1-3+\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}+1}\)
= \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}-1}\).\(\dfrac{-2}{\sqrt{3}+1}\)
= \(\dfrac{-4}{3-1}\)
= \(\dfrac{-4}{2}\)
= -2

\(1\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{3}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{6}+1\right)\left(5-2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{3}\right)\)
\(=1\left(\sqrt{3}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{6}+1\right)\left(1+3\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6}-\sqrt{3}\right)\)
\(=1\left(\sqrt{6}+1\right)\left(2\sqrt{6}-2\right)\)
\(=2\left(\sqrt{6}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{6}+1\right)=10\)
Cứ nhân lần lược vào rồi rút gọn sẽ được như trên

\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+2+\sqrt{a}-2}{a-4}:\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+2-2}{\sqrt{a}+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\sqrt{a}}{a-4}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+2}{\sqrt{a}}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{a}-2}\)

tick cho mình đi rồi mình gửi bài cho còn không tick thì mình không bày đâu nhé