Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

2x+3=0===> x= -3/2
(x+2)^2=0===>x+2=o===>x=-2
tương tự với cái cn lại
( 2x + 3) ( x + 2) ^2 ( 2x + 5 ) = 0
<=> 2x + 3 = 0 hoặc ( x + 2 ) ^2 = 0 hoặc ( 2x + 5 ) = 0
* 2x + 3 = 0 <=> 2x = -3 <=> x = -3/2
* ( x + 2 ) ^2 = 0 <=> x + 2 = 0 <=> x = -2
* 2x + 5 = 0 <=> 2x = -5 <=> x = -5/2
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = { -3/2 ; -2; -5/2}
k đúng cho mình nha

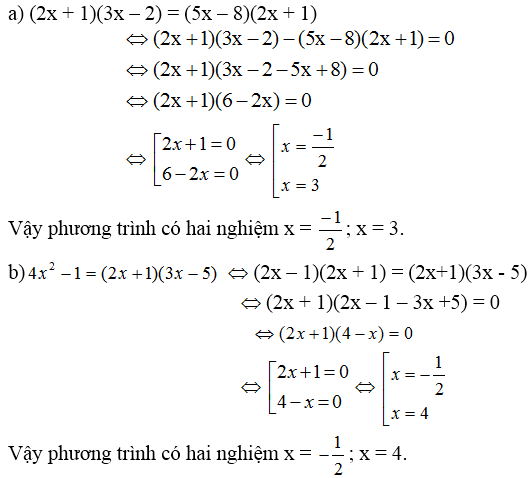
a)(2x+1)(3x-2)=(5x-8)(2x+1)
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2)-(5x-8)(2x+1)=0
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2-5x+8)=0
⇔(2x+1)(-2x+6)=0
⇔2x+1=0 hoặc -2x+6=0
1.2x+1=0⇔2x=-1⇔x=-1/2
2.-2x+6=0⇔-2x=-6⇔x=3
phương trình có 2 nghiệm x=-1/2 và x=3

Bài 3:
a) \(\left(x-6\right).\left(2x-5\right).\left(3x+9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right).\left(2x-5\right).3.\left(x+3\right)=0\)
Vì \(3\ne0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\2x-5=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\2x=5\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=\frac{5}{2}\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập hợp nghiệm là: \(S=\left\{6;\frac{5}{2};-3\right\}.\)
b) \(2x.\left(x-3\right)+5.\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right).\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\2x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\2x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\frac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập hợp nghiệm là: \(S=\left\{3;-\frac{5}{2}\right\}.\)
c) \(\left(x^2-4\right)-\left(x-2\right).\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2^2\right)-\left(x-2\right).\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right).\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\3x=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập hợp nghiệm là: \(S=\left\{2;\frac{1}{3}\right\}.\)
Chúc bạn học tốt!

\(\left(x-5\right)\left(x-1\right)=2x\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-5-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-5\end{cases}}\)
Vậy............
\(5\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x+5\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\left(x^2+x-6\right)-3\left(x^2+7x+10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-16x-60=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-8x-30=0\)
làm tiếp nhé!!!!!

a, \(\frac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{3}-\frac{\left(2x-3\right).\left(2x+3\right)}{8}+\frac{\left(x-4\right)^2}{6}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x^2-4x+4}{3}+\frac{9-4x^2}{8}+\frac{x^2-8x+16}{6}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{8\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+3\left(9-4x^2\right)+4\left(x^2-8x+16\right)}{24}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{8x^2-32x+32+27-12x^2+4x^2-32x+64}{24}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{123-64x}{24}=0\Leftrightarrow123-64x=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{123}{64}\)
(2x+3)(x+2)(x+2)(2x+5)=3
\(\Leftrightarrow\)4(2x+3)(x+2)(x+2)(2x+5)=12
\(\Leftrightarrow\)(2x+3)\(\left(2x+4\right)^2\)(2x+5)=12
đặt 2x+4=yta có phương trình tương đương với:
(y-1)\(y^2\)(y+1)=12
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(y^4\)-\(y^2\)=12
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(y^4-y^2\)-12=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(y^4-4y^2+3y^2-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(y^2-4\right)\)\(\left(y^2+3\right)\)=0\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(y^2-4\)=0 hoặc\(y^2+3\)=0 \(\Rightarrow\)\(y^2\)=-3 mà\(y^2\ge0\forall y\)\(\Rightarrow\)loại
vậy \(y^2\)-4=0\(\Rightarrow y=2\)hoặc -2
với y=2 thì 2x+4=2\(\Leftrightarrow\)2x=-2suy ra x=-1
với y=-2 thì 2x+4=-2\(\Leftrightarrow\)2x=-6suy ra x=-3
vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm là x=-1 và x=-3