
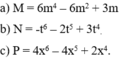
a) M =
3
m
(...">
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời. a, ĐKXĐ : \(x-1\ne0\) => \(x\ne1\) TH1 : \(x-2\ge0\left(x\ge2\right)\) => \(\left|x-2\right|=x-2=1\) => \(x=3\left(TM\right)\) - Thay x = 3 vào biểu thức P ta được : \(P=\frac{3+2}{3-1}=\frac{5}{2}\) TH2 : \(x-2< 0\left(x< 2\right)\) => \(\left|x-2\right|=2-x=1\) => \(x=1\left(KTM\right)\) Vậy giá trị của P là \(\frac{5}{2}\) . a) \(P=\frac{x+2}{x-1}\) \(\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne1\right)\) Ta có: \(\left|x-2\right|=1\text{⇔}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=1\\x-2=-1\end{matrix}\right.\text{⇔}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\) (loại x = 1 vì x ≠ 1) Thay \(x=3\) vào P, ta có: \(P=\frac{3+2}{3-2}=\frac{5}{1}=5\) Vậy P = 5 tại x = 3. b) \(Q=\frac{x-1}{x}+\frac{2x+1}{x^2+x}=\frac{x-1}{x}+\frac{2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{x^2-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\) (ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 0, x ≠ -1) \(=\frac{x^2+2x}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{x\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{x+2}{x+1}\) a, \(C=5\left(2x-1\right)^2+4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)-2\left(5-3x\right)^2\) \(C=5.\left(4x^2-4x+1\right)+4\left(x^2+3x-x-3\right)-2.\left(25-75x+9x^2\right)\) \(C=20x^2-20x+5+4x^2+8x-12-50+150x-18x^2\) \(=\left(20x^2+4x^2-18x^2\right)+\left(-20x+8x+150x\right)+\left(5-12-50\right)\) \(C=6x^2+138x-57\) Chúc bạn học tốt!!! Cũng không chắc có đúng hay sai nữa do cồng kềnh quá ! \(P=\left(\frac{x-1}{x+3}+\frac{2}{x-3}+\frac{x^2+3}{9-x^2}\right):\left(\frac{2x-1}{2x+1}-1\right)\)\(\left(đkcđ:x\ne\pm3;x\ne-\frac{1}{2}\right)\) \(=\left(\frac{\left(x-1\right).\left(x-3\right)+2.\left(x+3\right)-\left(x^2+3\right)}{x^2-9}\right):\left(\frac{2x-1-\left(2x+1\right)}{2x+1}\right)\) \(=\frac{x^2-4x+3+2x+6-x^2-3}{x^2-9}:\frac{-2}{2x+1}\) \(=\frac{-2x-6}{x^2-9}.\frac{2x+1}{-2}\) \(=\frac{-2\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right).\left(x+3\right)}.\frac{2x+1}{-2}\) \(=\frac{2x+1}{x-3}\) b)\(\left|x+1\right|=\frac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=\frac{1}{2}\\x+1=-\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{2}\left(koTMđkxđ\right)\\x=-\frac{3}{2}\left(TMđkxđ\right)\end{cases}}}\) thay \(x=-\frac{3}{2}\) vào P tâ đc: \(P=\frac{2x+1}{x-3}=\frac{2.\left(-\frac{3}{2}\right)+1}{-\frac{3}{2}-3}=\frac{4}{9}\) c)ta có:\(P=\frac{x}{2}\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x+1}{x-3}=\frac{x}{2}\) \(\Rightarrow2.\left(2x+1\right)=x.\left(x-3\right)\) \(\Leftrightarrow4x+2=x^2-3x\) \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-7x-2=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2.\frac{7}{2}+\frac{49}{4}-\frac{57}{4}=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{7}{2}\right)^2-\frac{57}{4}=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{7}{2}-\frac{\sqrt{57}}{2}\right).\left(x-\frac{7}{2}+\frac{\sqrt{57}}{2}\right)\) bạn tự giải nốt nhé!! d)\(x\in Z;P\in Z\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x+1}{x-3}\in Z\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x-6+7}{x-3}=2+\frac{7}{x-3}\in Z\) \(2\in Z\Rightarrow\frac{7}{x-3}\in Z\Leftrightarrow x-3\inƯ\left(7\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm7\right\}\) bạn tự làm nốt nhé a, \(\left(\dfrac{x^2-4x+3+2x+6-x^2-3}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\right):\left(\dfrac{2x-1-2x-1}{2x+1}\right)\) \(=\dfrac{-2x+6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}:\dfrac{-2}{2x+1}=\dfrac{-2\left(x-3\right)\left(2x+1\right)}{-2\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{2x+1}{x+3}\) b, \(\left|x+1\right|=\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{2}-1\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(ktmđk\right)\\x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) Thay x = -3/2 ta được \(\dfrac{2\left(-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)+1}{-\dfrac{3}{2}+3}=\dfrac{-2}{\dfrac{3}{2}}=-\dfrac{4}{3}\) 2, a,đkxđ \(x\ne-3;x\ne2\) mình giải luôn nhé k ghi lại đề nữa \(=\frac{x+2}{x+3}-\frac{5}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\frac{1}{x-2}\) \(=\frac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)-5-1\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\) \(=\frac{x^2-4-5-x-3}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\) \(=\frac{x^2-x-12}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\) \(=\frac{x^2+3x-4x-12}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\) \(=\frac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-4\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\) \(=\frac{x-4}{x-2}\) b,\(M=\frac{x-4}{x-2}=\frac{x-2-2}{x-2}=1-\frac{2}{x-2}\) để M nguyên thì \(\frac{2}{x-2}\) nguyên=>x - 2 là ước của 2,\(Ư_{\left(2\right)}=\left\{-2;-1;1;2\right\}\) x - 2 = -2 <=> x = 0 x - 2 = -1 <=> x = 1 x - 2 = 1 <=> x = 3 x - 2 =2 <=> x = 4 vậy x = {0;1;3;4} a) \(\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2-1}:\frac{x-1+x^2+x+2}{x^2-1}\) =\(\frac{2x+2}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\frac{2\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=2\) Bài 1: \(2x^2+4x^3-7=4x^2(x-3)+14x(x-3)+42(x-3)+119\) \(=(x-3)(4x^2+14x+42)+119\) Do đó phép chia $2x^2+4x^3-7$ cho $x-3$ có thương là $4x^2+14x+42$ và dư là $119$ Bài 2: Theo định lý Bê-du về phép chia đa thức thì phép chia đa thức $f(x)$ cho $x-a$ có dư là $f(a)$ Áp dụng vào bài toán: \(f(2)=-23\) \(\Leftrightarrow 2^3-4.2^2+5.2+a=-23\) \(\Leftrightarrow 2+a=-23\Rightarrow a=-25\) Bài 3: Ta có: \(x^3+ax+b=x(x^2+2x+1)-2x^2-x+ax+b\) \(=x(x^2+2x+1)-2(x^2+2x+1)+3x+2+ax+b\) \(=(x-2)(x+1)^2+x(a+3)+(b+2)\) Vậy $x^3+ax+b$ khi chia $(x+1)^2$ có dư là $x(a+3)+(b+2)$ \(\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix}
a+3=2\\
b+2=1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow a=-1; b=-1\) Bài 4: \(x^2+y^2-4y+5=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+(y^2-4y+4)+1=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+(y-2)^2+1=0\) \(\Rightarrow x^2+(y-2)^2=-1\) Rõ ràng vế trái luôn không âm, mà vế phải âm nên vô lý Vậy pt vô nghiệm, không tồn tại $x,y$ thỏa mãn. Câu 1: \(a,2xy\left(3x^2+2y-1\right)\) \(=2xy.3x^2+2xy.2y-2xy.1\) \(=6x^3y+4xy^2-2xy\) \(b,\left(x^2+3xy\right)\left(x^2y-3xy^2-7\right)\) \(=x^2.x^2y-x^2.3xy^2-x^2.7+3xy.x^2y-3xy.3xy^2-3xy.7\) \(=x^4y-3x^3y^2-7x^2+3x^3y^2-9x^2y^3-21xy\) \(=x^4y-7x^2-9x^2y^3-21xy\) Câu 2: \(a,x^3-9x\) \(=x\left(x^2-9\right)\) \(=x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)\) \(b,x^2\left(x+3\right)+12-4x\) ( sai đề ) Sửa : \(x^2\left(x+3\right)-12-4x\) \(=x^2\left(x+3\right)-\left(12+4x\right)\) \(=x^2\left(x+3\right)-4\left(x+3\right)\) \(=\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2-4\right)\) \(=\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\) \(c,x\left(x+2\right)-x-2\) \(=x\left(x+2\right)-\left(x+2\right)\) \(=\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\) 





Ta có: