
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Chắc câu c quá, tại tổng 2 ô vuông của hình chữ nhật có 10 chấm tròn. =)
Em nghĩ là câu c vì thấy tổng của các chấm tròn ở mỗi miếng đều là 10.

1.
a. Em tự giải
b.
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=4m-1\\3x-2y=-m+9\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+2y=8m-2\\3x-2y=-m+9\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7x=7m+7\\y=\dfrac{3x+m-9}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=m+1\\y=2m-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để \(x+y=7\Rightarrow m+1+2m-3=7\)
\(\Rightarrow3m=9\Rightarrow m=3\)
2.
a. Em tự giải
b.
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm khi:
\(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(2m+10\right)=m^2-9\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m\ge3\\m\le-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi đó theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1x_2=2m+10\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có:
\(P=x_1^2+x_2^2+8x_1x_2=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2+6x_1x_2\)
\(=4\left(m+1\right)^2+6\left(2m+10\right)=4m^2+20m+64\)
\(=4\left(m^2+5m+6\right)+40=4\left(m+2\right)\left(m+3\right)+40\)
Do \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m\ge3\\m\le-3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left(m+2\right)\left(m+3\right)\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow P\ge40\)
Vậy \(P_{min}=40\) khi \(m=-3\)
(Nếu bài này giải là \(4m^2+20m+64=\left(2m+5\right)^2+39\ge39\) là sai vì dấu = khi đó xảy ra tại \(m=-\dfrac{5}{2}\) ko thỏa mãn điều kiện \(\Delta\) để pt có nghiệm)

a. Câu này đơn giản em tự giải
b.
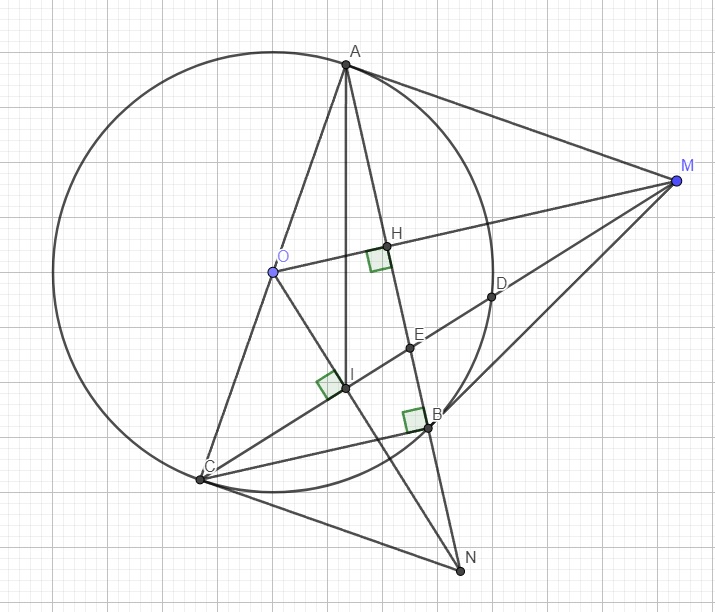
Xét hai tam giác OIM và OHN có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{OIM}=\widehat{OHN}=90^0\\\widehat{MON}\text{ chung}\\\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta OIM\sim\Delta OHN\left(g.g\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{OI}{OH}=\dfrac{OM}{ON}\Rightarrow OI.ON=OH.OM\)
Cũng từ 2 tam giác đồng dạng ta suy ra \(\widehat{OMI}=\widehat{ONH}\)
Tứ giác OAMI nội tiếp (I và A cùng nhìn OM dưới 1 góc vuông)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OAI}=\widehat{OMI}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OAI}=\widehat{ONH}\) hay \(\widehat{OAI}=\widehat{ONA}\)
c.
Xét hai tam giác OAI và ONA có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{OAI}=\widehat{ONA}\left(cmt\right)\\\widehat{AON}\text{ chung}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta OAI\sim\Delta ONA\left(g.g\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{OA}{ON}=\dfrac{OI}{OA}\Rightarrow OI.ON=OA^2=OC^2\) (do \(OA=OC=R\))
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{OC}{ON}=\dfrac{OI}{OC}\)
Xét hai tam giác OCN và OIC có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{OC}{ON}=\dfrac{OI}{OC}\\\widehat{CON}\text{ chung}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta OCN\sim\Delta OIC\left(g.g\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OCN}=\widehat{OIC}=90^0\) hay tam giác ACN vuông tại C
\(\widehat{ABC}\) là góc nt chắn nửa đường tròn \(\Rightarrow BC\perp AB\)
Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông ACN với đường cao BC:
\(BC^2=BN.BA=BN.2BH=2BN.BH\) (1)
O là trung điểm AC, H là trung điểm AB \(\Rightarrow OH\) là đường trung bình tam giác ABC
\(\Rightarrow OH=\dfrac{1}{2}BC\)
Xét hai tam giác OHN và EBC có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{OHN}=\widehat{EBC}=90^0\\\widehat{ONH}=\widehat{ECB}\left(\text{cùng phụ }\widehat{IEB}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta OHN\sim\Delta EBC\left(g.g\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{OH}{EB}=\dfrac{HN}{BC}\Rightarrow HN.EB=OH.BC=\dfrac{1}{2}BC^2\)
\(\Rightarrow BC^2=2HN.EB\) (2)
(1);(2) \(\Rightarrow BN.BH=HN.BE\)
\(\Rightarrow BN.BH=\left(BN+BH\right).BE\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{BE}=\dfrac{BN+BH}{BN.BH}=\dfrac{1}{BH}+\dfrac{1}{BN}\) (đpcm)

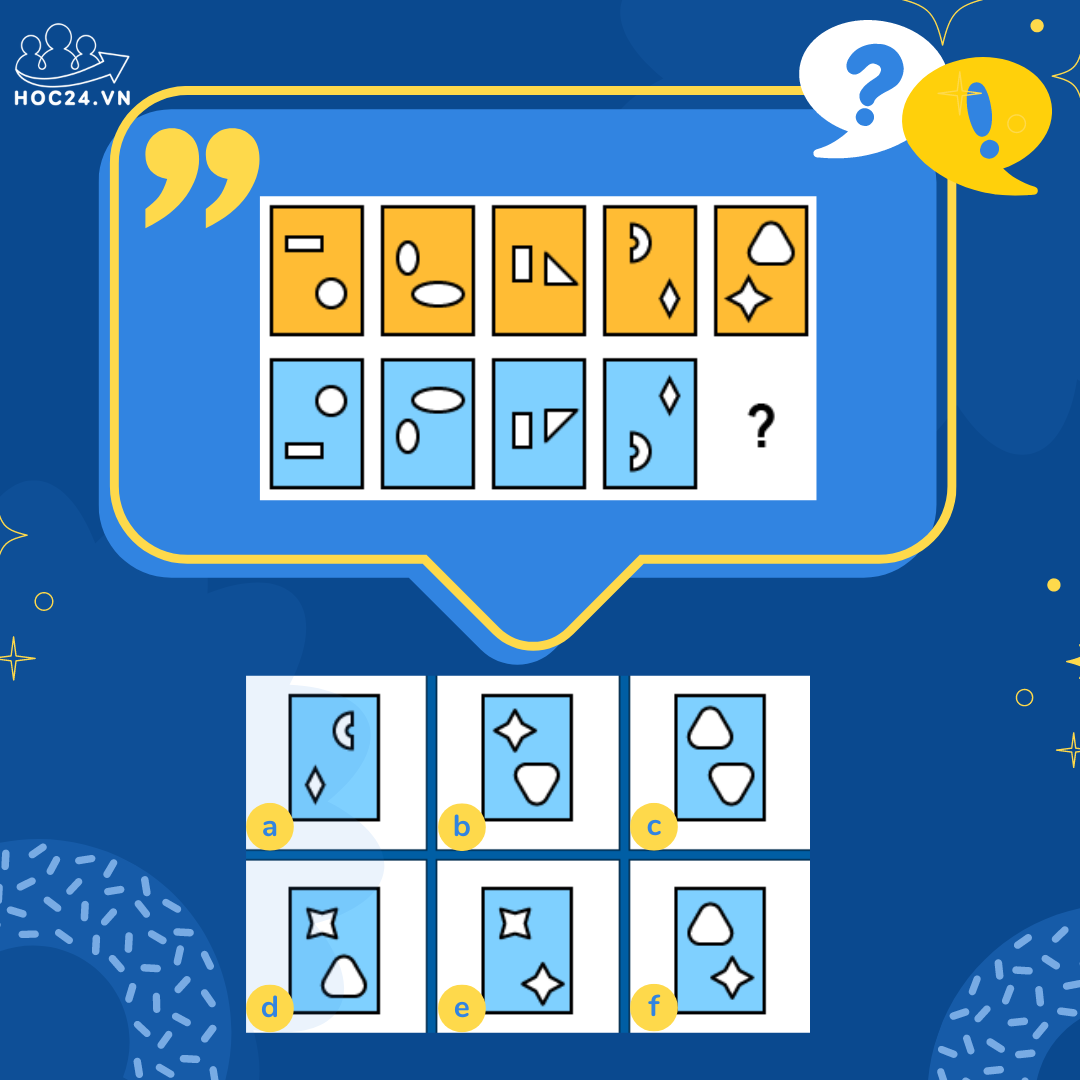
Đáp án b
Các hình màu xanh là phản chiếu của các hình máu cam trong gương.
Nhìn sơ sơ đoán là chọn B
Kiểu 2 hình ở gần (đáy hình cam trên và đỉnh hình xanh dưới sẽ giống nhau), 2 hình còn lại giống nhau tại vị trí đỉnh trên hình cam và đáy dưới hình xanh

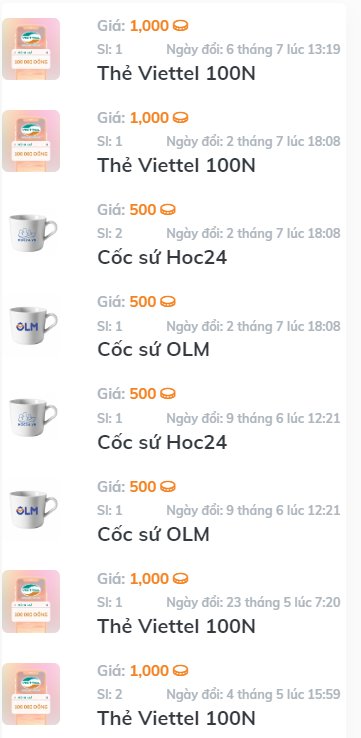

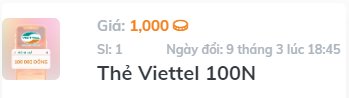
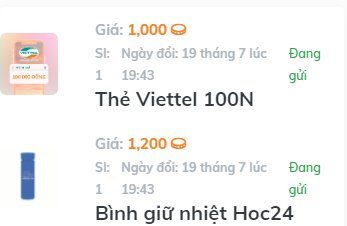
Các phần quà em nhận được đến giừo là 11 thẻ cào và 5 chiếc cốc và 1 bình giữ nhiệt ạ

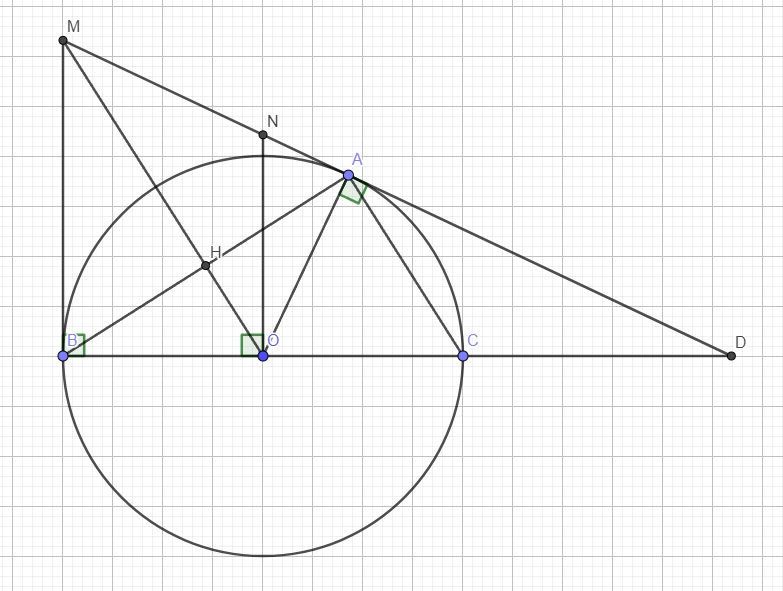
4c.
Do M là giao điểm 2 tiếp tuyến tại A và B, theo tính chất hai tiếp tuyến cắt nhau
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OMN}=\widehat{OMB}\)
Mà \(MB||NO\) (cùng vuông góc BC) \(\Rightarrow\widehat{OMB}=\widehat{MON}\) (so le trong)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OMN}=\widehat{MON}\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta OMN\) cân tại N
\(\Rightarrow MN=ON\)
Cũng theo 2 t/c 2 tiếp tuyến cắt nhau \(\Rightarrow MA=MB\)
Do MD là tiếp tuyến của (O) tại A \(\Rightarrow OA\perp MD\)
Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông OND với đường cao OA:
\(ON^2=NA.ND\Rightarrow MN^2=NA.ND\)
\(\Rightarrow MN^2=\left(MA-MN\right).ND=\left(MB-MN\right).ND\)
\(\Rightarrow MN^2=MB.ND-MN.ND\)
\(\Rightarrow MB.ND-MN^2=MN.ND\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{MB.ND-MN^2}{MN.ND}=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{MB}{MN}-\dfrac{MN}{ND}=1\) (đpcm)

\(A=\dfrac{2\left(3+\sqrt{5}\right)}{4+\sqrt{6+2\sqrt{5}}}+\dfrac{2\left(3-\sqrt{5}\right)}{4-\sqrt{6-2\sqrt{5}}}=\dfrac{2\left(3+\sqrt{5}\right)}{4+\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)^2}}+\dfrac{2\left(3-\sqrt{5}\right)}{4-\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)^2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(3+\sqrt{5}\right)}{5+\sqrt{5}}+\dfrac{2\left(3-\sqrt{5}\right)}{5-\sqrt{5}}=\dfrac{2\left(3+\sqrt{5}\right)\left(5-\sqrt{5}\right)+2\left(3-\sqrt{5}\right)\left(5+\sqrt{5}\right)}{\left(5-\sqrt{5}\right)\left(5+\sqrt{5}\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{40}{20}=2\)

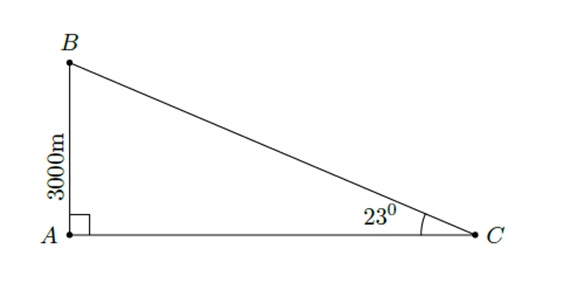
Muốn đạt độ cao 30003000 m so với mặt đất thì máy bay phải bay một đoạn đường dài:
\(BC=\dfrac{AB}{sin\left(23^o\right)}=\dfrac{3000}{sin\left(23^o\right)}\approx7678\left(m\right)\)
Kết luận: Muốn đạt độ cao 30003000 m so với mặt đất thì máy bay phải bay một đoạn đường dài gần 7678m

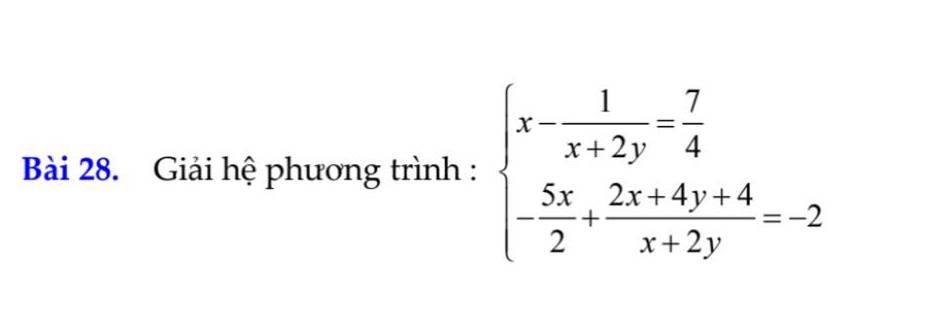
ĐKXĐ: \(x+2y\ne0\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-\dfrac{1}{x+2y}=\dfrac{7}{4}\\-\dfrac{5}{2}x+2+\dfrac{4}{x+2y}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đặt \(\dfrac{1}{x+2y}=z\) ta được hệ:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-z=\dfrac{7}{4}\\-\dfrac{5}{2}x+4z=-4\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\z=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\\dfrac{1}{x+2y}=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x+2y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

 giúp mình câu 2 với ạaaaaa
giúp mình câu 2 với ạaaaaa
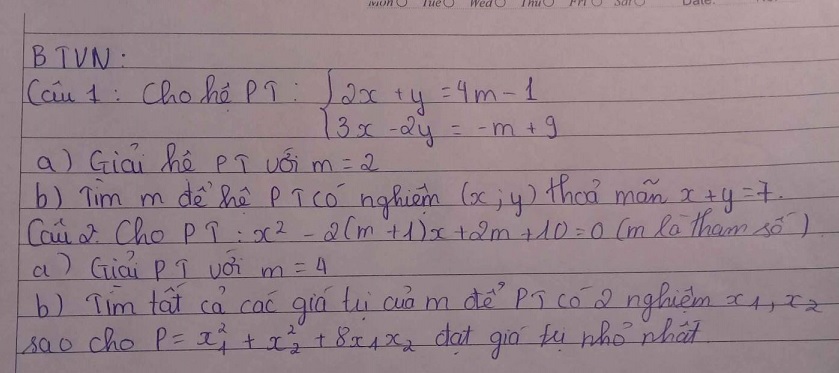


.png)


Câu 2:
=>x=1-y và m(1-y)-y=2m
=>x=1-y và m-my-y=2m
=>x=1-y và y(-m-1)=m
=>x=1-y và y=-m/m+1
=>x=1+m/m+1=(m+2)/m+1 và y=-m/m+1
Để x,y nguyên thì m+1+1 chia hết cho m+1 và -m-1+1 chia hết cho m+1
=>\(m+1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
mà m<>0
nên m=-2