
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\Leftrightarrow2sin^3x+1-sin^2x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin^2x\left(2sinx-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=0\\sinx=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=k\pi\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\left(2\sin x-1\right)\left(2\sin2x+1\right)=3-4\cos^2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2\sin x-1\right)\left(2\sin2x+1\right)=3-4\left(2-\sin^2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2\sin x-1\right)\left(2\sin2x+1\right)=4\sin^2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2\sin x-1\right)\left(2\sin2x+1\right)=\left(2\sin x-1\right)\left(2\sin x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sin2x+1=2\sin x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sin2x=\sin x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sin2x-\sin x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\cos\frac{3}{2}-\cos\frac{x}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\cos\frac{3}{2}=0\\\cos\frac{x}{2}=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\frac{3x}{2}=\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\\frac{x}{2}=\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\end{cases}\left(k\inℤ\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{\pi}{3}+\frac{2\pi}{3}k\\x=\pi+4k\pi\end{cases}\left(k\inℤ\right)}\)

\(2sin^2x+cosx=0\Rightarrow2\left(1-cos^2x\right)+cosx=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-2cos^2x+cosx+2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{17}}{4}\left(loại\right)\\cosx=\dfrac{1-\sqrt{17}}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=arccos\dfrac{1-\sqrt{17}}{4}+k2\pi\\x=-arccos\dfrac{1-\sqrt{17}}{4}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)

Đặt \(\dfrac{x}{4}=t\)
\(2sin^22t-3cost=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8sin^2t.cos^2t-3cost=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8cos^2t\left(1-cos^2t\right)-3cost=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-8cos^4t+8cos^2t-3cost=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-cost\left(8cos^3t-8cost+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cost\left(2cost-1\right)\left(4cos^2t+2cost-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cost=0\\cost=\dfrac{1}{2}\\cost=\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{13}}{4}\\cost=\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{13}}{4}< -1\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)



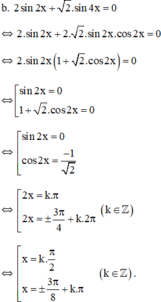
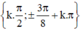 (k ∈ Z)
(k ∈ Z)
\(2sin\left(3x-150^o\right)+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(3x-150^o\right)=-\frac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-150^o=-30^o+k.360^o\\3x-150^o=210^o+k.360^o\end{cases}},k\inℤ\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=40^o+k.120^o\\x=k.120^o\end{cases}},k\inℤ\)