
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)

Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(2\left(3-4x\right)=10-\left(2x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-8x-10+2x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x+11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-11\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{11}{6}\)
b) Ta có: \(3\left(2-4x\right)=11-\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-12x-11+3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x=6\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)

(2x + 1)(3x – 2) = (5x – 8)(2x + 1)
⇔ (2x + 1)(3x – 2) – (5x – 8)(2x + 1) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1).[(3x – 2) – (5x – 8)] = 0
⇔ (2x + 1).(3x – 2 – 5x + 8) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)(6 – 2x) = 0
⇔ 2x + 1 = 0 hoặc 6 – 2x = 0
+ 2x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 2x = -1 ⇔ x = -1/2.
+ 6 – 2x = 0 ⇔ 6 = 2x ⇔ x = 3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 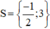

`3x+7=0`
`<=>3x=-7`
`<=>x=-7/3`
Vậy `S={-7/3}`
______________________
`2x(x-2)+2x(5-3x)=0`
`<=>2x(x-2+5-3x)=0`
`<=>2x(3-2x)=0`
`@TH1:2x=0<=>x=0`
`@TH2: 3-2x=0<=>2x=3<=>x=3/2`
Vậy `S={0;3/2}`
3x+7=0
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-7\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{7}{3}\)
2x(x-2)+2x(5-3x)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-2+5-3x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(-2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=0\\-2x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{-3}{-2}=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a,\left(x-6\right)\left(2x-5\right)\left(3x+9\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\Leftrightarrow x=6\\2x-5=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\3x+9=0\Leftrightarrow x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,2x\left(x-3\right)+5\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\\2x+5=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,x^2-4-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x=-7\left(2m-5\right)x-2m^2+8\Leftrightarrow x+7\left(2m-5\right)=8-2m^2\Leftrightarrow x\left(14m-34\right)=8-2m^2\)
\(ycđb\Leftrightarrow14m-34\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne\dfrac{34}{14}\)\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8-2m^2}{14m-34}\)
\(3.17\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow4x^2-6x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(4x-6\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3.15:
a, \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\2x-5=0\\3x+9=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{9}{3}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\2x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3.16
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-5\right).-7-2m^2+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14m+35-2m^2+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14m-2m^2+43=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(7m+m^2\right)=-43\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(7-m\right)=\dfrac{43}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{m\left(7-m\right)}{1}-\dfrac{43}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14m-2m^2}{2}-\dfrac{43}{2}=0\)
pt vô nghiệm

\(a,2x\left(x-5\right)+4\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\2x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;-2\right\}\)
\(b,3x-15=2x\left(x-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x-5\right)-2x\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(-2x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\-2x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
\(c,\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)=\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)-\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2-5x+8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(-2x+6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\-2x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-1\\2x=6\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};3\right\}\)
Câu d xem lại đề

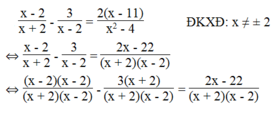
⇔ (x – 2)(x – 2) – 3(x + 2) = 2x – 22
⇔ x 2 – 2x – 2x + 4 – 3x – 6 = 2x – 22
⇔ x 2 – 2x – 2x – 3x – 2x + 4 – 6 + 22 = 0
⇔ x 2 – 9x + 20 = 0
⇔ x 2 – 5x – 4x + 20 = 0
⇔ x(x – 5) – 4(x – 5) = 0
⇔ (x – 4)(x – 5) = 0
⇔ x – 4 = 0 hoặc x – 5 = 0
x – 4 = 0 ⇔ x = 4
x – 5 = 0 ⇔ x = 5
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = 4 hoặc x = 5.

1:
a: =>3x=6
=>x=2
b: =>4x=16
=>x=4
c: =>4x-6=9-x
=>5x=15
=>x=3
d: =>7x-12=x+6
=>6x=18
=>x=3
2:
a: =>2x<=-8
=>x<=-4
b: =>x+5<0
=>x<-5
c: =>2x>8
=>x>4

a) |3x| = x + 6 (1)
Ta có 3x = 3x khi x ≥ 0 và 3x = -3x khi x < 0
Vậy để giải phương trình (1) ta quy về giải hai phương trình sau:
+ ) Phương trình 3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x ≥ 0
Ta có: 3x = x + 6 ⇔ 2x = 6 ⇔ x = 3 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = 3 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
+ ) Phương trình -3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x < 0
Ta có -3x = x + 6 ⇔ -4x + 6 ⇔ x = -3/2 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = -3/2 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho S = {3; -3/2}
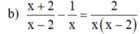
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 0, x ≠ 2
Quy đồng mẫu hai vễ của phương trình, ta được:
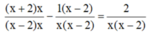
![]()
![]()
![]()
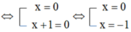
![]()
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {-1}
c) (x + 1)(2x – 2) – 3 > –5x – (2x + 1)(3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 2x + 2x – 2 – 3 > –5x – (6x – 2x2 + 3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 5 ≥ –5x – 6x + 2x2 – 3 + x
⇔ 10x ≥ 2 ⇔ x ≥ 1/5
Tập nghiệm: S = {x | x ≥ 1/5}

=>\(\dfrac{3x^3-9x^2+9x-2x^3+2x^2-6x}{\left(x^2-3x+3\right)\left(x^2-x+3\right)}=-1\)
=>x^3-7x^2+3x=-[(x^2+3)^2-4x(x^2+3)+3x^2]
=>x^3-7x^2+3x+(x^2+3)^2-4x(x^2+3)+3x^2=0
=>x^3-4x^2+3x+x^4+6x^2+9-4x^3-12x=0
=>x^4-3x^3+2x^2-9x+9=0
=>(x-3)(x-1)(x^2+x+3)=0
=>x=3;x=1