
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


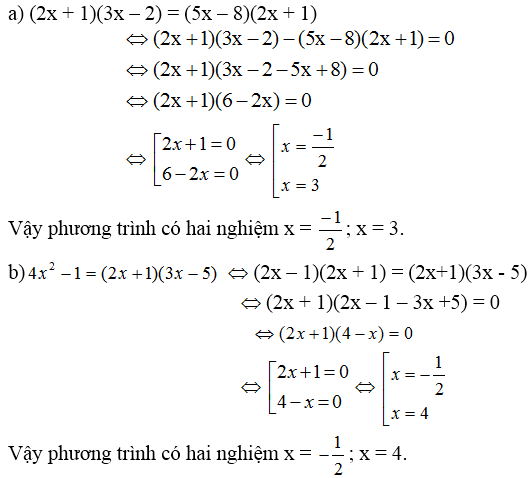
a)(2x+1)(3x-2)=(5x-8)(2x+1)
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2)-(5x-8)(2x+1)=0
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2-5x+8)=0
⇔(2x+1)(-2x+6)=0
⇔2x+1=0 hoặc -2x+6=0
1.2x+1=0⇔2x=-1⇔x=-1/2
2.-2x+6=0⇔-2x=-6⇔x=3
phương trình có 2 nghiệm x=-1/2 và x=3

Từ phương trình, ta có:
\(\frac{1}{2x-3}-\frac{5}{x}=\frac{3}{x\left(2x-3\right)}\)
\(\frac{x}{\left(2x-3\right)x}-\frac{10x-15}{x\left(2x-3\right)}=\frac{3}{x\left(2x-3\right)}\)
\(\frac{-9x-15}{x\left(2x-3\right)}=\frac{3}{x\left(2x-3\right)}\)
\(\frac{-9x-15-3}{x\left(2x-3\right)}=0\)
\(\frac{-9x-18}{x\left(2x-3\right)}=0\)
<=>-9x-18=0
<=>-9x=18
<=>x=-2
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất x=-2
bạn ơi phải là \(\frac{-10x+15}{x\left(2x-3\right)}\) chứ lấy -5(2x-3) thì bằng -10x+15 chứ

\(a,\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-5;3\right\}\)
\(b,\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)=\left(3x+1\right)\left(4x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x+1=0\\3x-1=4x+1\end{cases}}\)
\(c,\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^3-32x\right)+\left(3x^2-48\right)=0\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)+3\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\Leftrightarrow......\)

a) \(x^3+x^2+2x-16\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-2x^2+3x^2-6x+8x-16\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+3x+8\right)\ge0\)
Mà \(x^2+3x+8>x^2+3x+2,25=\left(x+1,5\right)^2\ge0\)
Cho nên \(x-2\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge2\)
a,x^3-2x^2+3x^2-6x+8x-16>=0
(x^2+3x+8)(x-2)>=0
x^2+3x+8>0
=> để lớn hơn hoac bang 0 thì x-2 phải>=0
=>x>=2
b,hình như là vô nghiệm ko chắc chắn lắm

\(\frac{\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)}{3}+5\left(3x+1\right)=\frac{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x+1\right)}{3}+2\left(3x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x+1\right)-\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)}{3}-3\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(4x+2\right)\left(3x+1\right)-\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)}{3}-3\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{12x^2+10x+2-9x^2+6x-3x+2}{3}-9x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3x^2+13x+4-27x-9}{3}=0\Leftrightarrow\frac{3x^2-14x-5}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-14x-5=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2-14x=5\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x-14\right)=5\)
\(.................\)
v: Làm tiếp nè
3x^2 - 14x - 5 = 0
<=> 3x^2 - 15x + x - 5 = 0
<=> ....

a, \(1-\frac{2x-1}{9}=3-\frac{3x-3}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{108-12\cdot\left(2x-1\right)}{108}=\frac{108\cdot3-9\cdot\left(3x-3\right)}{108}\)
\(\Rightarrow108-12\cdot\left(x-1\right)=108\cdot3-9\cdot\left(3x-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow108-24x+12=324-27x+27\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=231\)
\(\Rightarrow x=77\)
c,\(\frac{3}{4x-20}+\frac{15}{50-2x^2}+\frac{7}{6x+30}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3\cdot\left(50-2x^2\right)\cdot\left(6x+30\right)+15\cdot\left(4x-20\right)\cdot\left(6x+30\right)+7\cdot\left(4x-20\right)\cdot\left(50-2x^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow900x+4500-36x^3-180x^2+360x^2+1800x-1800x-9000+1400x-56x^3-7000+280x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-92x^3+460x^2+2300x-11500=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow92x^3-460x^2-2300x+11500=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-5\\x=5\end{cases}}\)
a) Thay x = 3 vào bất phương trình ta được: 2.3 + 3 < 9 <=> 9 < 9 (khẳng định sai)
Vậy x = 3 không là nghiệm của bất phương trình2x + 3 < 9
b) Thay x = 3 vào bất phương trình ta có: -4.3 > 2.3 + 5 => -12 > 11 (khẳng định sai)
Vậy x = 3 không là nghiệm của bất phương trình -4x > 2x + 5
c) Thay x = 3 vào bất phương trình ta có: 5 - 3 > 3.3 -12 => 2 > -3 (khẳng định đúng)
Vậy x = 3 là nghiệm của bất phương trình 5 - x > 3x - 12

a) \(\frac{4x-8}{2x^2+1}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow4x-8=0\left(2x^2+1\ne0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy x=2
b)
\(\frac{x^2-x-6}{x-3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)}{x-3}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
Vậy x=-2
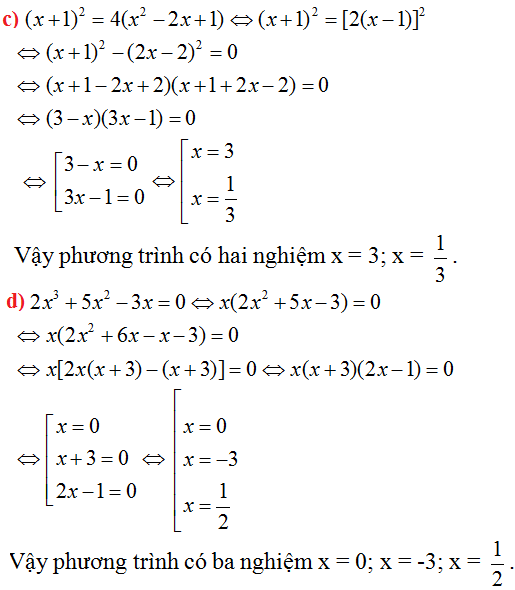
Nhận thấy :
\(3x^2-3x+1=3\left(x^2-x\right)+1=3\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\frac{3}{4}+1=3\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{1}{4}>0\)
Nên phương trình trên
<=> \(3x^2-3x+1=1-2x\)
<=> \(3x^2-x=0\)
<=> \(x\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy .................
Để phương trình trên có nghiệm thì \(1-2x\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\le\frac{1}{2}\)
Ta có: \(3x^2-3x+1=3\left(x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}\right)+\frac{1}{4}=3\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{1}{4}\ge\frac{1}{4}>0\)
Vậy nên \(\left|3x^2-3x+1\right|=3x^2-3x+1\)
Phương trình trở thành:
\(3x^2-3x+1=1-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}\left(tmđk\right)\)
Vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm x = 0 hoặc \(x=\frac{1}{3}.\)