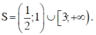Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Từ bất phương trình ban đầu \(\Leftrightarrow25.5^x-5.5^x>9.3^x-3.3^x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20.5^x>6.3^x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\frac{5}{3}\right)^x>\frac{3}{10}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\log_{\frac{5}{3}}\frac{3}{10}\)

a)
x^2 +1 >0 mọi x
BPT \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+3x-10< 0\) {\(\Delta=9+40=49\)}
\(\Rightarrow-5< x< 2\)
b)
5+x^2 > 0 với mọi x BPT \(\Leftrightarrow20-2x-x^2-5>0\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-15< 0\){\(\Delta'=1+15=16\)}
\(\Rightarrow-5< x< 3\)

\(\frac{x}{2x-1}>\frac{x-1}{x+2}\Rightarrow\frac{x}{2x-1}-\frac{x-1}{x+2}>0\Rightarrow\frac{-x^2+5x-1}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}>0\)
| x | \(-\infty\) -2 \(\frac{5-\sqrt{21}}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{5+\sqrt{21}}{2}\) \(+\infty\) |
| -x2 + 5x - 1 | - - 0 + + 0 - |
| 2x - 1 | - - - 0 + + |
| x + 2 | - 0 + + + + |
=> VT : - // + 0 - // + 0 -
Vậy \(S=\left(-2;\frac{5-\sqrt{21}}{2}\right)\cup\left(\frac{1}{2};\frac{5+\sqrt{21}}{2}\right)\)
\(\frac{x}{2x-1}>\frac{x-1}{x+2}\) (1)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\frac{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)-x\left(x+2\right)}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}<0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\frac{x^2-5x+1}{2x^2+3x-2}<0\) (a)
Xét các trường hợp
- Nếu \(2x^2+3x-2<0\) hay là \(x\in\left(-2;\frac{1}{2}\right)\) := (*) thì (a) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x^2-5x+1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x<\frac{5-\sqrt{21}}{2}\) hoặc \(\frac{5-\sqrt{21}}{2}\)< x
Kết hợp với điều kiện \(x\in\) (*) ta được -2<x<\(\frac{5-\sqrt{21}}{2}\)
- Nếu \(2x^2+3x-2>0\) hay \(x\in\left(-\infty;-2\right)\cup\left(\frac{1}{2};+\infty\right)\) : = (* *)
thì (1) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x^2-5x+1<0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\frac{5-\sqrt{21}}{2}\)<x<\(\frac{5+\sqrt{21}}{2}\)
Kết hợp với điều kiện x\(\in\)(* * ) ta được \(\frac{1}{2}\)<x<\(\frac{5+\sqrt{21}}{2}\)
Tóm lại :
(1) có nghiệm -2<x<\(\frac{5-\sqrt{21}}{2}\) hoặc \(\frac{1}{2}\)<x<\(\frac{5+\sqrt{21}}{2}\)

\(\frac{x+2}{x\left(x+1\right)}>1\Rightarrow\frac{x-2-x\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}>0\Rightarrow\frac{x-3-x^2-x}{x\left(x+1\right)}>0\Rightarrow\frac{-x^2-3}{x\left(x+1\right)}>0\)
Lập bảng xét dấu:
| x | \(-\infty\) -1 0 \(+\infty\) |
| -x2 - 3 | + + + |
| x | - - 0 + |
| x + 1 | - 0 + + |
| Vế trái | + // - // + |
Vậy S = (-\(\infty\) ; -1) \(\cup\) (0 ; +\(\infty\))

\(\left(x^2-2x\right)^2-2\left(x-1\right)^2-1\ge0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2x\right)^2-2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)-1\ge0\)
Đặt \(t=x^2-2x\), ta được \(t^2-2t-3\ge0\)
Bất phương trình này có nghiệm \(\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}t\le-1\\t\ge3\end{array}\right.\)
Do đó \(\left(x^2-2x\right)^2-2\left(x-1\right)^2-1\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x^2-2x\le-1\\x^2-2x-3\ge0\end{array}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\) hoặc \(x\le-1\) hoặc \(x\ge3\)
Vậy bất phương trình đã cho có tập nghiệm là
S =(\(-\infty;-1\)] \(\cup\left\{1\right\}\cup\) [3;\(+\infty\))

\(\frac{2x-5}{\left|x-5\right|}+1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x-5}{\left|x-5\right|}\ge-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-5\le-\left|x-5\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-5\right)^2\le\left(-\left|x-5\right|\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-20x+25\le x^2-10x+25\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-10x\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x-10\right)\le0\)
Làm nốt

\(x^2-\left|3x+2\right|+x-1>0\) (1)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}\begin{cases}3x+2\ge0\\x^2-\left(3x+2\right)+x-1=x^2-2x-3>0\end{cases}\\\begin{cases}3x+2<0\\x^2+\left(3x+2\right)+x-1=x^2+4x+1>0\end{cases}\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}-\frac{2}{3}\le x\\x\in\left(-\infty,-1\right)\cup\left(3;+\infty\right)\end{cases}\) hoặc \(\begin{cases}x<-\frac{2}{3}\\x\in\left(-\infty;-2-\sqrt{3}\right)\cup\left(-2+\sqrt{3};+\infty\right)\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x<-2-\sqrt{3}\) hoặc \(x>3\)
Vậy bất phương trình có tập nghiệm T(1) = \(\left(-\infty;-2-\sqrt{3}\right)\cup\left(3;+\infty\right)\)
Điều kiện xác định x ≠ 1 và x ≠ 1/2.
Các nhị thức –x + 3; x – 1; 2x – 1 có nghiệm lần lượt là 3; 1; 1/2.
Dựa vào bảng xét dấu thấy
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là