
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.




\(\dfrac{1}{n\left(n+1\right)}=\dfrac{1+n-n}{n\left(n+1\right)}=\dfrac{n+1}{n\left(n+1\right)}-\dfrac{n}{n\left(n+1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{n}-\dfrac{1}{n+1}\)

Bài 2:
a; \(x\) - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = \(\dfrac{3}{10}\).\(\dfrac{5}{6}\)
\(x\) - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Vậy \(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{4}\)
b; \(\dfrac{x}{5}\) = \(\dfrac{-3}{14}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{7}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{x}{5}\) = \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\) \(\times\) 5
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{-5}{2}\)
Vậy \(x\) = \(\dfrac{-5}{2}\);
c; \(x\) : \(\dfrac{4}{11}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{4}\) \(\times\) 2
\(x\) : \(\dfrac{4}{11}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{2}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{11}{2}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{4}{11}\)
\(x\) = 2
Vậy \(x\) = 2
d; \(x^2\) + \(\dfrac{9}{-25}\) = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\) : \(\dfrac{5}{8}\)
\(x^2\) - \(\dfrac{9}{25}\) = \(\dfrac{16}{25}\)
\(x^2\) = \(\dfrac{16}{25}\) + \(\dfrac{9}{25}\)
\(x^2\) = \(\dfrac{25}{25}\)
\(x^2\) = 1
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\)\(\in\) {-1; 1}
Bài 3:
a; A = \(\dfrac{2}{13}\)\(\times\) \(\dfrac{5}{9}\)+ \(\dfrac{2}{13}\)\(\times\)\(\dfrac{4}{9}\) + \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
A = \(\dfrac{2}{13}\) \(\times\)(\(\dfrac{5}{9}\) + \(\dfrac{4}{9}\)) + \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
A = \(\dfrac{2}{13}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{9}{9}\) + \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
A = \(\dfrac{2}{13}\) + \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
A = 1
b; B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\).\(\dfrac{4}{11}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{10}\).\(\dfrac{8}{11}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{10}\).\(\dfrac{1}{11}\)
B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) x (\(\dfrac{4}{11}\) + \(\dfrac{8}{11}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{11}\))
B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) x (\(\dfrac{12}{11}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{11}\))
B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) x \(\dfrac{11}{11}\)
B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\)

a) \(\dfrac{5}{11}\cdot\dfrac{5}{7}+\dfrac{5}{11}\cdot\dfrac{2}{7}+\dfrac{6}{11}=\dfrac{5}{11}\cdot\left(\dfrac{5}{7}+\dfrac{2}{7}\right)+\dfrac{6}{11}=\dfrac{5}{11}\cdot1+\dfrac{6}{11}=\dfrac{5}{11}+\dfrac{6}{11}=\dfrac{11}{11}=1\)
b) \(\dfrac{3}{13}\cdot\dfrac{6}{11}+\dfrac{3}{13}\cdot\dfrac{9}{11}-\dfrac{3}{13}\cdot\dfrac{4}{11}=\dfrac{3}{13}\cdot\left(\dfrac{6}{11}+\dfrac{9}{11}-\dfrac{4}{11}\right)=\dfrac{3}{13}\cdot\dfrac{11}{11}=\dfrac{3}{13}\cdot1=\dfrac{3}{13}\)
c) \(\dfrac{-5}{6}\cdot\dfrac{4}{19}+\dfrac{7}{12}\cdot\dfrac{4}{-19}-\dfrac{40}{57}=\dfrac{-5}{6}\cdot\dfrac{4}{19}+\dfrac{-7}{12}\cdot\dfrac{4}{19}-\dfrac{40}{57}=\dfrac{4}{19}\cdot\left(\dfrac{-5}{6}+\dfrac{-7}{12}\right)-\dfrac{40}{57}\)
\(=\dfrac{4}{19}\cdot\dfrac{-17}{12}-\dfrac{40}{47}=\dfrac{-17}{57}-\dfrac{40}{57}=\dfrac{-57}{57}=-1\)
d) \(\left(\dfrac{11}{4}\cdot\dfrac{-5}{9}+\dfrac{4}{9}\cdot\dfrac{11}{-4}\right)\cdot\dfrac{8}{33}=\left(\dfrac{11}{4}\cdot\dfrac{-5}{9}+\dfrac{-4}{9}\cdot\dfrac{11}{4}\right)\cdot\dfrac{8}{33}=\dfrac{11}{4}\cdot\dfrac{8}{33}\cdot\left(\dfrac{-5}{9}+\dfrac{-4}{9}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{11}{4}\cdot\dfrac{8}{33}\cdot1=\dfrac{11\cdot8}{4\cdot33}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
e) \(\left(\dfrac{12}{61}-\dfrac{31}{22}+\dfrac{14}{91}\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{6}\right)=\left(\dfrac{12}{61}-\dfrac{31}{22}+\dfrac{14}{91}\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{6}-\dfrac{1}{6}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{12}{61}-\dfrac{31}{22}+\dfrac{14}{91}\right)\cdot0=0\)

Lời giải:
a.
$=\frac{3}{5}-\frac{7}{4}=\frac{12-35}{20}=\frac{-23}{20}$
b.
$=-(2+\frac{5}{8})=-\frac{21}{8}$
c.
$=-(\frac{1}{8}+\frac{5}{9})=-\frac{9+8.5}{8.9}=\frac{-49}{72}$
d.
$=\frac{6}{13}-\frac{14}{39}=\frac{18}{39}-\frac{14}{39}=\frac{4}{39}$
e.
$=\frac{-3}{4}+\frac{5}{7}=\frac{5}{7}-\frac{3}{4}$
$=\frac{20-21}{7.4}=\frac{-1}{28}$

Bài 5
1) x ∈ Ư(18) = {1; 2; 3; 6; 9; 18}
x ∈ B(4) = {0; 4; 8; 12; 16; 20; ...}
Vậy không tìm được x thỏa mãn đề bài
2) x ∈ Ư(20) = {1; 2; 4; 5; 10; 20}
x ∈ B(2) = {0; 2; 4; 6; 8; 10; 12; 14; 16; 18; 20; ...}
⇒ x ∈ {2; 4; 10; 20}
3) x ∈ B(12) = {0; 12; 24; 36; 48; ...; 96; 108; ...}
Mà 30 ≤ x ≤ 100
⇒ x ∈ {36; 48; ...; 96}
4) x ∈ Ư(150) = {1; 2; 3; 5; 6; 10; 15; 25; 30; 50; 75; 150}
Mà x ≤ 50
⇒ x ∈ {1; 2; 3; 5; 6; 10; 15; 25; 30; 50}
5) 70 ⋮ x và 168 ⋮ x
⇒ x ∈ ƯC(70; 168)
Ta có:
70 = 2.5.7
168 = 2³.3.7
⇒ ƯCLN(70; 168) = 2.7 = 14
⇒ x ∈ ƯC(70; 168) = Ư(14) = {1; 2; 7; 14}
Mà x > 10
⇒ x = 14
6) Ta có:
(1995 + 2005 + x) ⋮ 5
1995 ⋮ 5
2005 ⋮ 5
⇒ x ⋮ 5
⇒ x ∈ B(5) = {0; 5; 10; 15; 20; 25; 30; 35; 40; ...}
Mà 23 < x ≤ 35
⇒ x ∈ {25; 30; 35}
Bài 6
1) Do 17x2y chia hết cho 2 và 5 nên y = 0
⇒ Số đã cho có dạng: 17x20
Để 17x20 chia hết cho 3 thì (1 + 7 + x + 2 + 0) ⋮ 3
⇒ (10 + x) ⋮ 3
⇒ x ∈ {2; 5; 8}
Vậy x ∈ {2; 5; 8}; y = 0
2) Do 234xy chia hết cho 2 và 5 nên y = 0
⇒ Số đã cho có dạng: 234x0
Để 234x0 chia hết cho 9 thì (2 + 3 + 4 + x + 0) ⋮ 9
⇒ (9 + x) ⋮ 9
⇒ x ∈ {0; 9}
Vậy x ∈ {0; 9}; y = 0
3) Do 4x6y chia hết cho 2 và 5 nên y = 0
Mà x - y = 4
⇒ x = 4 + y
⇒ x = 4
Vậy x = 4; y = 0
4) Do 57x2y chia hết cho 5 nhưng không chia hết cho 2 nên y = 5
⇒ Số đã cho có dạng 57x25
Để 57x25 chia hết cho 9 thì (5 + 7 + x + 2 + 5) ⋮ 9
⇒ (19 + x) ⋮ 9
⇒ x = 8
Vậy x = 8; y = 5


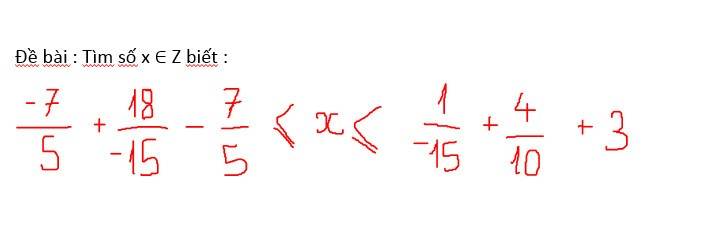

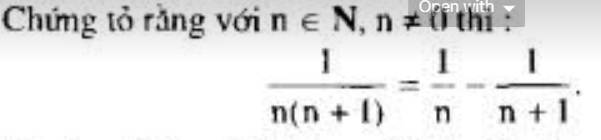
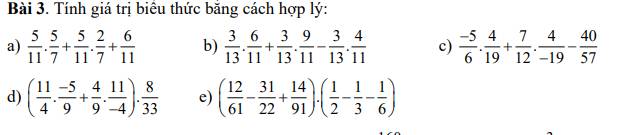
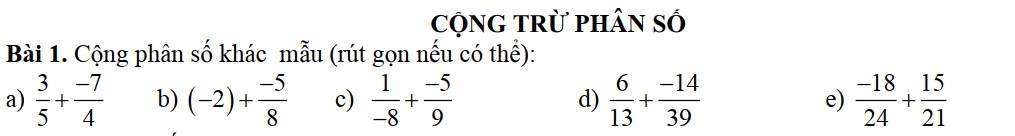

Gọi số học sinh của trường đó là a (với a là số nguyên dương)
Do số học sinh xếp hàng 13 dư 4 nên a chia 13 dư 4
\(\Rightarrow a=13n+4\) (với \(n\in N\)) (1)
Do số học sinh xếp hàng 17 dư 9 nên a chia 17 dư 9
\(\Rightarrow a=17m+9\) (với `m \in N\`)
\(\Rightarrow13n+4=17m+9\)
\(\Rightarrow13n+4-43=17m+9-43\)
\(\Rightarrow13n-39=17m-34\)
\(\Rightarrow13\left(n-3\right)=17\left(m-2\right)\)
Do 13 và 17 nguyên tố cùng nhau suy ra \(n-3\) chia hết 17
\(\Rightarrow n-3=17k\) (với `k \in N`)
\(\Rightarrow n=17k+3\) (2)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra:
\(a=13.\left(17k+3\right)+4\)
\(\Rightarrow a=221k+43=5.\left(44k+8\right)+\left(k+3\right)\) (3)
Do xếp hàng 5 vừa đủ nên a chia hết cho 5 (4)
Từ (3) và (4) suy ra `k+3` chia hết cho 5
Suy ra `k=5b-3` (với `b \in N`)
Suy ra: \(a=221.\left(5k-3\right)+43=1105b-620\)
Do số học sinh của trường vào khoảng 2500 đến 3000 bạn nên:
\(2500< 1105b-620< 3000\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{48}{17}< b< \dfrac{724}{221}\Rightarrow b=3\)
Vậy \(a=1105.3-620=2695\)
Trường đó có 2695 học sinh