
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


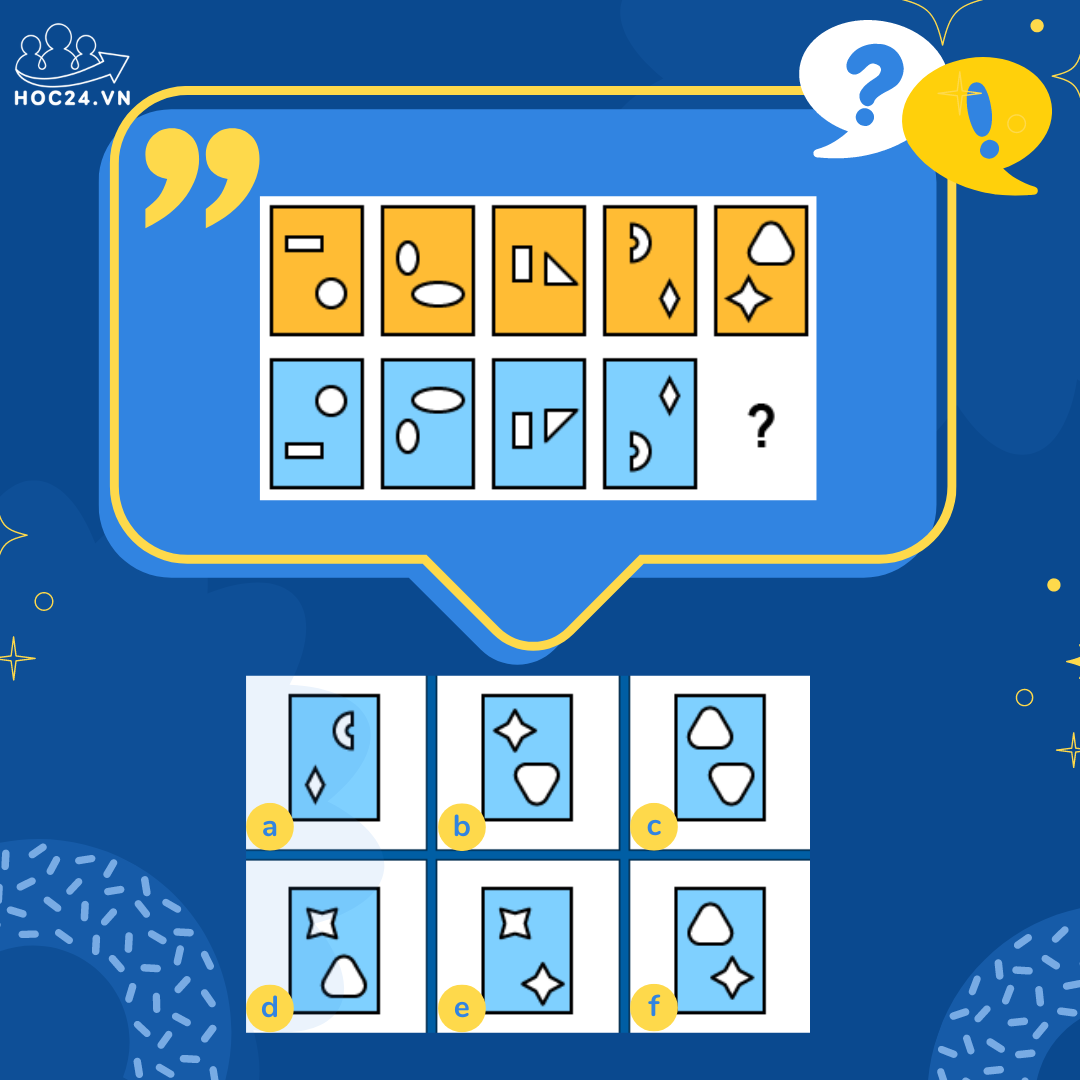
Chắc câu c quá, tại tổng 2 ô vuông của hình chữ nhật có 10 chấm tròn. =)
Em nghĩ là câu c vì thấy tổng của các chấm tròn ở mỗi miếng đều là 10.

1.
a. Em tự giải
b.
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=4m-1\\3x-2y=-m+9\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+2y=8m-2\\3x-2y=-m+9\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7x=7m+7\\y=\dfrac{3x+m-9}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=m+1\\y=2m-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để \(x+y=7\Rightarrow m+1+2m-3=7\)
\(\Rightarrow3m=9\Rightarrow m=3\)
2.
a. Em tự giải
b.
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm khi:
\(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(2m+10\right)=m^2-9\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m\ge3\\m\le-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi đó theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1x_2=2m+10\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có:
\(P=x_1^2+x_2^2+8x_1x_2=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2+6x_1x_2\)
\(=4\left(m+1\right)^2+6\left(2m+10\right)=4m^2+20m+64\)
\(=4\left(m^2+5m+6\right)+40=4\left(m+2\right)\left(m+3\right)+40\)
Do \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m\ge3\\m\le-3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left(m+2\right)\left(m+3\right)\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow P\ge40\)
Vậy \(P_{min}=40\) khi \(m=-3\)
(Nếu bài này giải là \(4m^2+20m+64=\left(2m+5\right)^2+39\ge39\) là sai vì dấu = khi đó xảy ra tại \(m=-\dfrac{5}{2}\) ko thỏa mãn điều kiện \(\Delta\) để pt có nghiệm)

Đáp án b
Các hình màu xanh là phản chiếu của các hình máu cam trong gương.
Nhìn sơ sơ đoán là chọn B
Kiểu 2 hình ở gần (đáy hình cam trên và đỉnh hình xanh dưới sẽ giống nhau), 2 hình còn lại giống nhau tại vị trí đỉnh trên hình cam và đáy dưới hình xanh

a. Câu này đơn giản em tự giải
b.
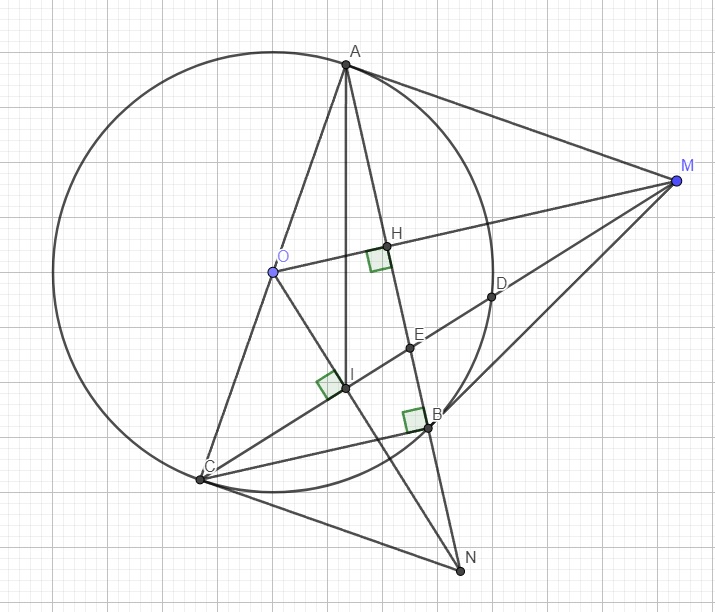
Xét hai tam giác OIM và OHN có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{OIM}=\widehat{OHN}=90^0\\\widehat{MON}\text{ chung}\\\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta OIM\sim\Delta OHN\left(g.g\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{OI}{OH}=\dfrac{OM}{ON}\Rightarrow OI.ON=OH.OM\)
Cũng từ 2 tam giác đồng dạng ta suy ra \(\widehat{OMI}=\widehat{ONH}\)
Tứ giác OAMI nội tiếp (I và A cùng nhìn OM dưới 1 góc vuông)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OAI}=\widehat{OMI}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OAI}=\widehat{ONH}\) hay \(\widehat{OAI}=\widehat{ONA}\)
c.
Xét hai tam giác OAI và ONA có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{OAI}=\widehat{ONA}\left(cmt\right)\\\widehat{AON}\text{ chung}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta OAI\sim\Delta ONA\left(g.g\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{OA}{ON}=\dfrac{OI}{OA}\Rightarrow OI.ON=OA^2=OC^2\) (do \(OA=OC=R\))
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{OC}{ON}=\dfrac{OI}{OC}\)
Xét hai tam giác OCN và OIC có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{OC}{ON}=\dfrac{OI}{OC}\\\widehat{CON}\text{ chung}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta OCN\sim\Delta OIC\left(g.g\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OCN}=\widehat{OIC}=90^0\) hay tam giác ACN vuông tại C
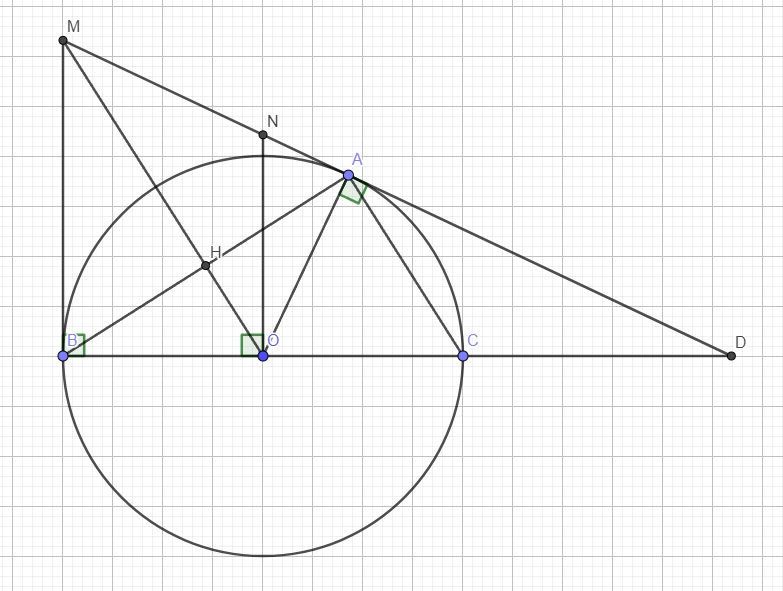
\(\widehat{ABC}\) là góc nt chắn nửa đường tròn \(\Rightarrow BC\perp AB\)
Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông ACN với đường cao BC:
\(BC^2=BN.BA=BN.2BH=2BN.BH\) (1)
O là trung điểm AC, H là trung điểm AB \(\Rightarrow OH\) là đường trung bình tam giác ABC
\(\Rightarrow OH=\dfrac{1}{2}BC\)
Xét hai tam giác OHN và EBC có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{OHN}=\widehat{EBC}=90^0\\\widehat{ONH}=\widehat{ECB}\left(\text{cùng phụ }\widehat{IEB}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta OHN\sim\Delta EBC\left(g.g\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{OH}{EB}=\dfrac{HN}{BC}\Rightarrow HN.EB=OH.BC=\dfrac{1}{2}BC^2\)
\(\Rightarrow BC^2=2HN.EB\) (2)
(1);(2) \(\Rightarrow BN.BH=HN.BE\)
\(\Rightarrow BN.BH=\left(BN+BH\right).BE\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{BE}=\dfrac{BN+BH}{BN.BH}=\dfrac{1}{BH}+\dfrac{1}{BN}\) (đpcm)

4c.
Do M là giao điểm 2 tiếp tuyến tại A và B, theo tính chất hai tiếp tuyến cắt nhau
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OMN}=\widehat{OMB}\)
Mà \(MB||NO\) (cùng vuông góc BC) \(\Rightarrow\widehat{OMB}=\widehat{MON}\) (so le trong)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OMN}=\widehat{MON}\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta OMN\) cân tại N
\(\Rightarrow MN=ON\)
Cũng theo 2 t/c 2 tiếp tuyến cắt nhau \(\Rightarrow MA=MB\)
Do MD là tiếp tuyến của (O) tại A \(\Rightarrow OA\perp MD\)
Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông OND với đường cao OA:
\(ON^2=NA.ND\Rightarrow MN^2=NA.ND\)
\(\Rightarrow MN^2=\left(MA-MN\right).ND=\left(MB-MN\right).ND\)
\(\Rightarrow MN^2=MB.ND-MN.ND\)
\(\Rightarrow MB.ND-MN^2=MN.ND\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{MB.ND-MN^2}{MN.ND}=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{MB}{MN}-\dfrac{MN}{ND}=1\) (đpcm)

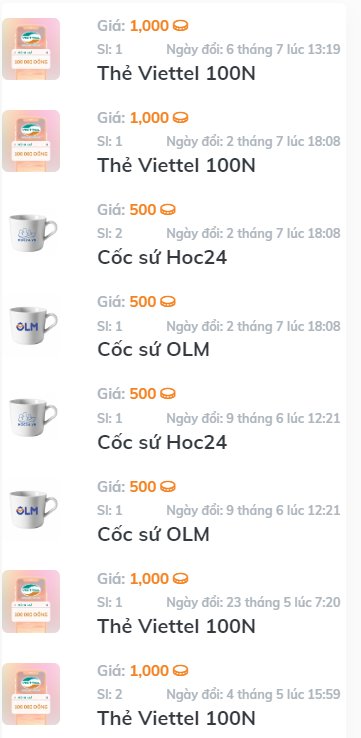

Các phần quà em nhận được đến giừo là 11 thẻ cào và 5 chiếc cốc và 1 bình giữ nhiệt ạ

\(A=\dfrac{2\left(3+\sqrt{5}\right)}{4+\sqrt{6+2\sqrt{5}}}+\dfrac{2\left(3-\sqrt{5}\right)}{4-\sqrt{6-2\sqrt{5}}}=\dfrac{2\left(3+\sqrt{5}\right)}{4+\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)^2}}+\dfrac{2\left(3-\sqrt{5}\right)}{4-\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)^2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(3+\sqrt{5}\right)}{5+\sqrt{5}}+\dfrac{2\left(3-\sqrt{5}\right)}{5-\sqrt{5}}=\dfrac{2\left(3+\sqrt{5}\right)\left(5-\sqrt{5}\right)+2\left(3-\sqrt{5}\right)\left(5+\sqrt{5}\right)}{\left(5-\sqrt{5}\right)\left(5+\sqrt{5}\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{40}{20}=2\)

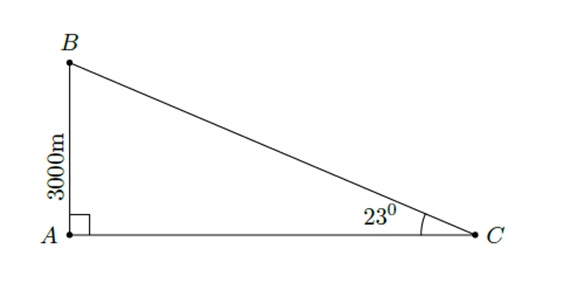
Muốn đạt độ cao 30003000 m so với mặt đất thì máy bay phải bay một đoạn đường dài:
\(BC=\dfrac{AB}{sin\left(23^o\right)}=\dfrac{3000}{sin\left(23^o\right)}\approx7678\left(m\right)\)
Kết luận: Muốn đạt độ cao 30003000 m so với mặt đất thì máy bay phải bay một đoạn đường dài gần 7678m



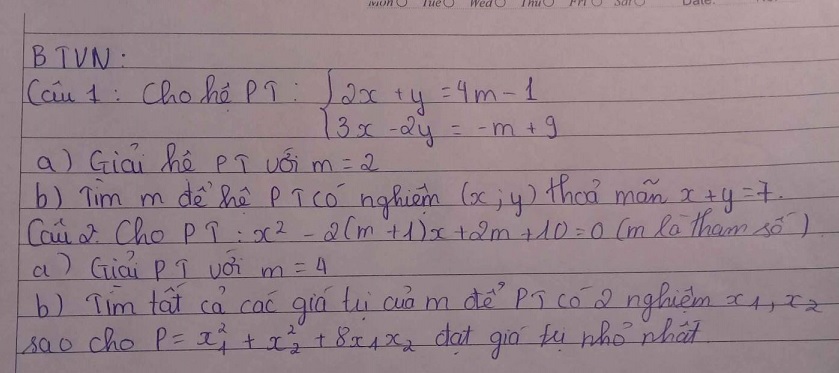



.png)

.png)
Bài 2
1) Để hàm số đã cho là hàm số bậc nhất thì:
5m - 3 ≠ 0
⇔ 5m ≠ 3
⇔ m ≠ 3/5
2) Để hàm số đã cho là hàm số bậc nhất thì:
21m + 7 ≠ 0
⇔ 21m ≠ -7
⇔ m ≠ -1/3
3) Để hàm số đã cho là hàm số bậc nhất thì:
-15m - 3 ≠ 0
⇔ -15m ≠ 3
⇔ m ≠ -1/5
4) Để hàm số đã cho là hàm số bậc nhất thì:
-8m - 4 ≠ 0
⇔ -8m ≠ 4
⇔ m ≠ -1/2
5) Để hàm số đã cho là hàm số bậc nhất thì:
6 - 12m ≠ 0
⇔ 12m ≠ 6
⇔ m ≠ 1/2
6) Để hàm số đã cho là hàm số bậc nhất thì:
-4 - 16m ≠ 0
⇔ 16m ≠ -4
⇔ m ≠ -1/4
Bài 3:
Để hàm số: y=ax+b đồng biến <=> a>0
\(1,HSĐB\Leftrightarrow15m-3>0\Leftrightarrow15m>3\Leftrightarrow m>\dfrac{3}{15}\Leftrightarrow m>\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(2,HSĐB\Leftrightarrow-6m+18>0\Leftrightarrow-6m>-18\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{-18}{-6}\Leftrightarrow m< 3\)
\(3,HSĐB\Leftrightarrow-\left(-20m-10\right)>0\Leftrightarrow-20m-10< 0\\ \Leftrightarrow-20m< 10\Leftrightarrow m>-\dfrac{10}{20}\Leftrightarrow m>-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(4,HSĐB\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{5}{9}m+\dfrac{2}{3}>0\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{5}{9}m>-\dfrac{2}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow m< -\dfrac{2}{3}:\left(-\dfrac{5}{9}\right)\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{6}{5}\)
\(5,HSĐB\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{6}{5}-12m>0\Leftrightarrow12m< \dfrac{6}{5}\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{6}{5}:12\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{1}{10}\)