
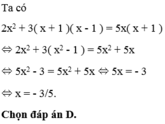
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

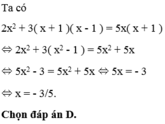

1, \(=\left[\frac{\left(1-x\right)\left(1+x+x^2\right)}{1-x}-x\right]:\frac{1-x^2}{\left(1-x\right)-x^2\left(1-x\right)}\)
\(=\left(1+x+x^2-x\right):\frac{1-x^2}{\left(1-x\right)\left(1-x^2\right)}\)\(=\left(x^2+1\right)\left(1-x\right)\)
2, để B<0 <=> (x2+1)(1-x)<0
vì x^2+1 > 0 với mọi x
=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x^2+1>0\\1-x< 0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x>1}\)
3, \(\left|x-4\right|=5\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=9\\x=-1\left(loại\right)\end{cases}}\)
Thay x=9 vào B ta có: B=(92+1)(1-9)=82.(-8)=-656

B1:dài quá :vv
B2:\(Q=\frac{x^2}{x^4+x^2+1}=\frac{x^2}{x^4+2x^2+1-x^2}=\frac{x^2}{\left(x^2+1\right)-x^2}=\frac{x^2}{\left(x^2-x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x}{x^2-x+1}.\frac{x}{x^2+x+1}=\frac{2}{3}.\frac{x}{x^2+x+1}\)
\(\frac{x}{x^2-x+1}=\frac{2}{3}\Rightarrow\frac{x^2-x+1}{x}=\frac{3}{2}\Rightarrow\frac{x^2-x+1}{x}+2=\frac{3}{2}+2\Rightarrow\frac{x^2+x+1}{x}=\frac{7}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{x}{x^2+x+1}=\frac{2}{7}\Rightarrow Q=\frac{2}{3}.\frac{2}{7}=\frac{4}{21}\)
3.
Ta có: \(a^5-a=a\left(a^4-1\right)=a\left(a^2-1\right)\left(a^2+1\right)=a\left(a+1\right)\left(a-1\right)\left(a^2+1\right)\)
\(=a\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1\right)\left(a^2-4+5\right)=a\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1\right)\left(a^2-4\right)+5a\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1\right)\)
\(=a\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1\right)\left(a-2\right)\left(a+2\right)+5a\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1\right)\)
Do a(a-1)(a+1)(a-2)(a+2) là tích của 5 số hạng liên tiếp nên chia hết cho 2,3 và 5
Lại có a(a-1)(a+1) là tích của 3 số hạng liên tiếp nên chia hết cho 2,3 suy ra 5a(a-1)(a+1) chia hết cho 2,3,5
Từ đó:a(a-1)(a+1)(a-1)(a+2)+5a(a-1)(a+1) chia hết cho 2,3,5 hay a(a-1)(a+1)(a-2)(a+2)+5a(a-1)(a+1) chia hết cho 30 \(\Leftrightarrow a^5-a\) chia hết cho 30
Tương tự ta có\(b^5-b\) chia hết cho 30, \(c^5-c\) chia hết cho 30
Do đó:\(a^5-a+b^5-b+c^5-c⋮30\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^5+b^5+c^5-\left(a+b+c\right)⋮30\)
Mà a+b+c=0 nên;
\(a^5+b^5+c^5⋮30\left(ĐCCM\right)\)

Bài 1:
\(M=\left|x+13\right|+64\)
Vì \(\left|x+3\right|\ge0\)
=> \(\left|x+3\right|+64\ge64\)
Vậy GTNN của M là 64 khi x=-13
\(A=\left|x+3\right|+\left|x+5\right|=\left|-\left(x+3\right)\right|+\left|x+5\right|\)
Áp dụng bđt \(\left|A\right|+\left|B\right|\ge\left|A+B\right|\) ta có:
\(A\ge\left|-x-3+x+5\right|=2\)
Vaayj GTNN của A là 2 khi \(-3\le x\le5\)
Bài 2:
a) \(\left(x+10\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+10=0\Leftrightarrow x=-10\)
b) \(\left(x-\sqrt{121}\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-\sqrt{121}=0\) (vì \(x^2+1>0\) )
\(\Leftrightarrow x=11\)
Bài 1:
a)Ta thấy: \(\left|x+13\right|\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|x+13\right|+64\ge64\)
\(\Rightarrow M\ge64\)
Dấu = khi x=-13
b)\(\left|x+3\right|+\left|x+5\right|=\left|x+3\right|+\left|-x-5\right|\)
Áp dụng Bđt \(\left|a\right|+\left|b\right|\ge\left|a+b\right|\) ta có:
\(\left|x+3\right|+\left|-x-5\right|\ge\left|x+3+\left(-x\right)-5\right|=2\)
\(\Rightarrow A\ge2\)
Dấu = khi \(\left(x+3\right)\left(x+5\right)\ge0\)\(\Rightarrow3\le x\le5\)
\(\Rightarrow\begin{cases}\left(x+3\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\\3\le x\le5\end{cases}\)\(\Rightarrow\)\(\begin{cases}x=-3\\x=-5\end{cases}\)
Vậy MinA=2 khi \(\begin{cases}x=-3\\x=-5\end{cases}\)

(x+y)^3=x^3+y^3+3xy(x+y)=1
=>3xy(x+y)+2=1
=>3xy(x+y)=-1?(vì x+y=1)
=>xy=-1/3=M
b) (x+y)^2=x^2+y^2+2xy=1 =>x^2+y^2=1-2xy=1-2.(-1/3)=5/3
(x^2+y^2)(x^3+y^3)=x^5+y^5 +x^2.y^3+x^3.y^2=x^5+y^5+x^2.y^2(x+y)=...(ráp số vô rồi tính ra kết quả nhé :) )

a)\(x+\frac{1}{x}=3\Rightarrow\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^2=9\Rightarrow x^2+2.x.\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{x^2}=9\Rightarrow x^2+2+\frac{1}{x^2}=9\)
=>\(A=x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}=7\)
b)\(x+\frac{1}{x}=3\Rightarrow\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^3=27\Rightarrow x^3+3.x^2.\frac{1}{x}+3.x.\frac{1}{x^2}+\frac{1}{x^3}=27\)
=>\(x^3+3x+3.\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{x^3}=27\Rightarrow x^3+\frac{1}{x^3}+3\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=27\Rightarrow x^3+\frac{1}{x^3}+3.3=27\)
=>\(\Rightarrow x^3+\frac{1}{x^3}+9=27\Rightarrow x^3+\frac{1}{x^3}=18\)
c) Áp dụng kq phần a ta được:
\(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}=7\Rightarrow\left(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}\right)^2=49\Rightarrow x^4+2.x^2.\frac{1}{x^2}+\frac{1}{x^4}=49\Rightarrow x^4+2+\frac{1}{x^4}=49\)
=>\(C=x^4+\frac{1}{x^4}=47\)
d)Ta có:
\(\left(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}\right)\left(x^3+\frac{1}{x^3}\right)=7.18\Rightarrow x^5+\frac{1}{x}+x+\frac{1}{x^5}=126\Rightarrow x^5+3+\frac{1}{x^5}=126\)
=>\(D=x^5+\frac{1}{x^5}=123\)

a, \(Đkxđ:\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne1\\x\ne\pm3\end{cases}}\)
\(P=\left(1+\frac{1}{x-1}\right):\left(\frac{x^2-7}{x^2-4x+3}+\frac{1}{x-1}+\frac{1}{3-x}\right)\)
\(=\left(\frac{x-1}{x-1}+\frac{1}{x-1}\right):\left(\frac{x^2-7}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\frac{1}{x-1}-\frac{1}{x-3}\right)\)
\(=\left(\frac{x-1+1}{x-1}\right):\left(\frac{x^2-7+x-3-\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\right)\)
\(=\frac{x}{x-1}:\frac{x^2-7+x-3-x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x}{x-1}.\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{x^2-9}\)
\(=\frac{x}{x-1}.\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x}{x+3}\)
b, \(|x+2|=5\)
\(\Rightarrow x+2=\hept{\begin{cases}5\Leftrightarrow x+2\ge0\Rightarrow x\ge-2\\-5\Leftrightarrow x+2< 0\Rightarrow x< -2\end{cases}}\)
Nếu \(x\ge-2\Rightarrow x+2=5\)
\(\Rightarrow x=3\)\(\left(ktmđkxđ\right)\)
Nếu \(x< -2\Rightarrow x+2=-5\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-7\)\(\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy \(x=-7\)

\(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\pm1\)
a) \(B=\left(\frac{1-x^3}{1-x}-x\right)\div\frac{1-x^2}{1-x-x^2+x^3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B=\left(\frac{\left(1-x\right)\left(1+x+x^2\right)}{1-x}-x\right):\left(\frac{\left(1-x\right)\left(1+x\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B=\left(1+x+x^2-x\right):\left(\frac{-1}{x-1}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B=-\left(x^2+1\right).\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B=-x^3+x^2-x+1\)
b) Để B < 0
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^3+x^2-x+1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)>0\)
TH1 : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x^2+1>0\left(tm\right)\\x-1>0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x>1}\)
TH2 : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x^2+1< 0\left(ktm\right)\\x-1< 0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)
Vậy để \(B< 0\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
c) Khi \(x-4=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B=-\left(9^3\right)+9^2-9+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B=-729+81-9+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B=-656\)
Vậy khi \(x-4=5\Leftrightarrow B=-656\)