Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\int e^x.\cos xdx\)
= \(\int\cos xd\left(e^x\right)\)
= ex . cos x - \(\int e^xd\left(\cos x\right)\)
= ex cos x + \(\int\sin x.e^xdx\)
= ex cos x + \(\int\sin xd\left(e^x\right)\)
= ex cos x + sin x . ex - \(\int e^xd\left(\sin x\right)\)
= ex ( cos x - sin x ) - \(\int e^x.\cos xdx\)
= \(\int e^x.\cos x=\dfrac{e^x\left(\cos x+\sin x\right)}{2}\)
Vậy a = b = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)

Lời giải:
Ta có:
\(F(x)=\int f(x)dx=\int e^x\cos xdx\)
Đặt \(\left\{\begin{matrix} u=e^x\\ dv=\cos xdx\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} du=e^xdx\\ v=\int \cos xdx=\sin x\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do đó:
\(F(x)=\int e^x\cos xdx=e^x\sin x-\int \sin x.e^xdx+c\) (1)
Đặt \(\left\{\begin{matrix} u=e^x\\ dv=\sin xdx\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} du=e^xdx\\ v=\int \sin xdx=-cos x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow \int \sin x.e^xdx=-\cos x.e^x+\int \cos x.e^xdx+c\) (2)
Từ (1)(2) suy ra:
\(F(x)=e^x.\sin x+\cos x.e^x-\int \cos x.e^xdx+c\)
\(\Leftrightarrow F(x)=e^x\sin x+e^x\cos x-F(x)+c\)
\(\Leftrightarrow F(x)=\frac{1}{2}e^x(\sin x+\cos x)+c\)
Do đó: \(a=b=\frac{1}{2}\)

Chọn A.
F ' ( x ) = sin x - cos x ' sin x - cos x = cos x + sin x sin x - cos x

Đáp án A
Phương pháp :
Sử dụng bảng nguyên hàm cơ bản.
Cách giải:
Ta có:
![]()
![]()
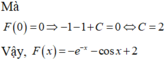

Biến đổi :
\(5\sin x=a\left(2\sin x-\cos x+1\right)+b\left(2\cos x+\sin x\right)+c\)
= \(\left(2a+b\right)\sin x+\left(2b-a\right)\cos x+a+c\)
Đồng nhất hệ số hai tử số :
\(\begin{cases}2a+b=5\\2b-a=0\\a+c=0\end{cases}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}a=2\\b=1\\c=-2\end{cases}\)
Khi đó :
\(f\left(x\right)=\frac{2\left(2\sin x-\cos x+1\right)+\left(2\cos x+\sin x\right)-2}{2\sin x-\cos x+1}\)
= \(2+\frac{2\cos x+\sin x}{2\sin x-\cos x+1}-\frac{2}{2\sin x-\cos x+1}\)
Do vậy :
\(I=2\int dx+\int\frac{\left(2\cos x+\sin x\right)dx}{2\sin x-\cos x+1}-2\int\frac{dx}{2\sin x-\cos x+1}\)
=\(2x+\ln\left|2\sin x-\cos x+1\right|-2J+C\)
Với
\(J=\int\frac{dx}{2\sin x-\cos x+1}\)

Biến đổi :
\(4\sin^2x+1=5\sin^2x+\cos^2x=\left(a\sin x+b\cos x\right)\left(\sqrt{3}\sin x+\cos x\right)+c\left(\sin^2x+\cos^2x\right)\)
\(=\left(a\sqrt{3}+c\right)\sin^2x+\left(a+b\sqrt{3}\right)\sin x.\cos x+\left(b+c\right)\cos^2x\)
Đồng nhấtheej số hai tử số
\(\begin{cases}a\sqrt{3}+c=5\\a+b\sqrt{3}=0\\b+c=1\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}a=\sqrt{3}\\b=-1\\c=2\end{cases}\)

a) Điều kiện x>0. Thực hiện chia tử cho mẫu ta được:
f(x) = =
=
∫f(x)dx = ∫()dx =
+C
b) Ta có f(x) = =
-e-x
; do đó nguyên hàm của f(x) là:
F(x)= =
=
+ C
c) Ta có f(x) =
hoặc f(x) =
Do đó nguyên hàm của f(x) là F(x)= -2cot2x + C
d) Áp dụng công thức biến tích thành tổng:
f(x) =sin5xcos3x = (sin8x +sin2x).
Vậy nguyên hàm của hàm số f(x) là F(x) = -(
cos8x + cos2x) +C
e) ta có
vậy nguyên hàm của hàm số f(x) là F(x) = tanx - x + C
g) Ta có ∫e3-2xdx= -∫e3-2xd(3-2x)= -
e3-2x +C
h) Ta có :
= =

a) \(\int\left(x+\ln x\right)x^2\text{d}x=\int x^3\text{d}x+\int x^2\ln x\text{dx}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^4}{4}+\int x^2\ln x\text{dx}+C\) (*)
Để tính: \(\int x^2\ln x\text{dx}\) ta sử dụng công thức tính tích phân từng phần như sau:
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=\ln x\\v'=x^2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u'=\dfrac{1}{x}\\v=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Suy ra:
\(\int x^2\ln x\text{dx}=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3\ln x-\dfrac{1}{3}\int x^2\text{dx}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3\ln x-\dfrac{1}{3}.\dfrac{1}{3}x^3\)
Thay vào (*) ta tính được nguyên hàm của hàm số đã cho bằng:
(*) \(=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3-\dfrac{1}{3}x^3\ln x+\dfrac{1}{9}x^3+C\)
\(=\dfrac{4}{9}x^3-\dfrac{1}{3}x^3\ln x+C\)
b) Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=x+\sin^2x\\v'=\sin x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u'=1+2\sin x.\cos x\\v=-\cos x\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có:
\(\int\left(x+\sin^2x\right)\sin x\text{dx}=-\left(x+\sin^2x\right)\cos x+\int\left(1+2\sin x\cos^2x\right)\text{dx}\)
\(=-\left(x+\sin^2x\right)\cos x+\int\cos x\text{dx}+2\int\sin x.\cos^2x\text{dx}\)
\(=-\left(x+\sin^2x\right)\cos x+\sin x-2\int\cos^2x.d\left(\cos x\right)\)
\(=-\left(x+\sin^2x\right)\cos x+\sin x-2\dfrac{\cos^3x}{3}+C\)
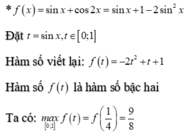
Chọn A
Đặt t = sinx ⇒ dt = cosxdx.