
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



2x² + 5x - 12 = 0
∆ = 25 + 4.2.12 = 121
x₁ = (-5 + 11)/4 = 3/2
x₂ = (-5 - 11)/4 = -4
Bảng xét dấu
x -∞ -4 3/2 +∞
2x²+5x-12 + - +
Các nghiệm nguyên của bpt là: -4; -3; -2; -1; 0; 1
Vậy bpt đã cho có 6 nghiệm nguyên

Câu 1:
\(\left(4x+3\right)\left(3x^2+x-2\right)\left(2x^2-3x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(4x+3\right)\left(3x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-5\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{3}{4}\\x=-1\\x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow A=\left\{-1;-\dfrac{3}{4};\dfrac{2}{3};\dfrac{5}{2}\right\}\)
Câu 2:
\(\left(x^2-4\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow A=\left\{-2;2;3\right\}\\ \left|5x\right|-11\le0\Leftrightarrow\left|5x\right|\le11\Leftrightarrow-11\le5x\le11\\ \Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{11}{5}\le x\le\dfrac{11}{5}\\ \Leftrightarrow B=\left[-\dfrac{11}{5};\dfrac{11}{5}\right]\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A\cap B=\left\{-2;2\right\}\\ A\cup B=\left[-\dfrac{11}{5};3\right]\\ A\B=\left\{3\right\}\)

E trên trục hoành nên E(x;0)
A(6;3); B(-3;6); E(x;0)
\(\overrightarrow{AB}=\left(-9;3\right);\overrightarrow{AE}=\left(x-6;-3\right)\)
Để A,B,E thẳng hàng thì \(\dfrac{x-6}{-9}=\dfrac{-3}{3}=-1\)
=>x-6=9
=>x=15
Vậy: E(15;0)
Do E thuộc trục hoành nên tọa độ có dạng \(E\left(x;0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\overrightarrow{AB}=\left(-9;3\right)\\\overrightarrow{AE}=\left(x-6;-3\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
3 điểm A, B, E thẳng hàng khi:
\(\dfrac{x-6}{-9}=\dfrac{-3}{3}\Rightarrow x-6=9\)
\(\Rightarrow x=15\Rightarrow E\left(15;0\right)\)


Câu 1:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y-2x< =2\\2y-x>=4\\x+y< =5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y< =2x+2\\2y>=x+4\\y< =-x+5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y< =2x+2\\y< =-x+5\\y>=\dfrac{1}{2}x+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
y<=2x+2
=>y-2x-2<=0
Vẽ đường thẳng y=2x+2
Khi x=0 và y=0 thì \(y-2x-2=0-0-2=-2< =0\)(đúng)
=>Miền nghiệm của BPT y<=2x+2 là nửa mặt phẳng vừa chứa biên vừa chứa điểm O(0;0)
y<=-x+5
=>x+y-5<=0
Khi x=0 và y=0 thì \(x+y-5=0+0-5< =0\)(đúng)
=>Miền nghiệm của BPT y<=-x+5 là nửa mặt phẳng vừa chứa biên vừa chứa điểm O(0;0)
y>=1/2x+2
=>\(-\dfrac{1}{2}x+y-2>=0\)
Khi x=0 và y=0 thì \(-\dfrac{1}{2}x+y-2=-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot0+0-2=-2< 0\)
=>O(0;0) không thỏa mãn BPT \(-\dfrac{1}{2}x+y-2>=0\)
=>Miền nghiệm của BPT \(y>=\dfrac{1}{2}x+2\) là nửa mặt phẳng chứa biên nhưng không chứa điểm O(0;0)
Vẽ đồ thị:
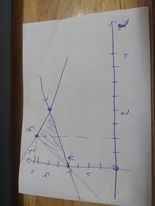
Theo hình vẽ, ta có: Miền nghiệm của hệ BPT sẽ là ΔABC, với A(0;2); B(1;4); C(2;3)
Khi x=0 và y=2 thì F=2-0=2
Khi x=1 và y=4 thì F=4-1=3
Khi x=2 và y=3 thì F=3-2=1
=>Chọn A

a: Hàm số nghịch biến trên R
b: \(\dfrac{f\left(x_1\right)-f\left(x_2\right)}{x_1-x_2}=\dfrac{x_1^2-4x_1+5-x_2^2+4x_2-5}{x_1-x_2}\)
\(=x_1+x_2-4\)
Trường hợp 1: x<=2
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1+x_2-4< =0\)
Vậy: Hàm số nghịch biến khi x<=2

10.
\(\dfrac{sin3x-cos3x}{sinx+cosx}=\dfrac{3sinx-4sin^3x-\left(4cos^3x-3cosx\right)}{sinx+cosx}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(sinx+cosx\right)-4\left(sin^3x+cos^3x\right)}{sinx+cosx}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(sinx+cosx\right)-4\left(sinx+cosx\right)\left(sin^2x+cos^2x-sinx.cosx\right)}{sinx+cosx}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(sinx+cosx\right)-4\left(sinx+cosx\right)\left(1-sinx.cosx\right)}{sinx+cosx}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(sinx+cosx\right)\left(3-4+4sinx.cosx\right)}{sinx+cosx}\)
\(=-1+4sinx.cosx\)
\(=2sin2x-1\)
11.
\(tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{x}{2}\right)\dfrac{1+cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}+x\right)}{sin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}+x\right)}=tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{x}{2}\right).\dfrac{1+sin\left(-x\right)}{cos\left(-x\right)}\)
\(=tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{x}{2}\right).\dfrac{1-sinx}{cosx}=tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{x}{2}\right)\dfrac{sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}+cos^2\dfrac{x}{2}-2sin\dfrac{x}{2}cos\dfrac{x}{2}}{cos^2\dfrac{x}{2}-sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}}\)
\(=tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{x}{2}\right).\dfrac{\left(cos\dfrac{x}{2}-sin\dfrac{x}{2}\right)^2}{\left(cos\dfrac{x}{2}-sin\dfrac{x}{2}\right)\left(cos\dfrac{x}{2}+sin\dfrac{x}{2}\right)}\)
\(=tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{x}{2}\right).\dfrac{cos\dfrac{x}{2}-sin\dfrac{x}{2}}{cos\dfrac{x}{2}+sin\dfrac{x}{2}}\)
\(=tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{x}{2}\right).\dfrac{cos\left(\dfrac{x}{2}+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)}{sin\left(\dfrac{x}{2}+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)}\)
\(=tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{x}{2}\right).cot\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{x}{2}\right)\)
\(=1\)





Thi không giúp được bạn nhé!
Mà có giúp cũng đâu có bài đâu mà giúp ^^
Giúp gì thế em nhỉ?