
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Câu 3:
Thay x=-1 và y=0 vào (d), ta được:
-m+2m-1=0
hay m=1

a: Thay \(x=9+4\sqrt{2}\) vào A, ta được:
\(A=\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}+1+7}{2\sqrt{2}+1-1}=\dfrac{8+2\sqrt{2}}{2\sqrt{2}}=2\sqrt{2}+1\)


\(a,m=3\Leftrightarrow y=2x+2\\ A\left(a;-4\right)\in\left(d\right)\Leftrightarrow2a+2=-4\Leftrightarrow a=-3\)
\(b,\) PT giao Ox của (d) là \(2x+m-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1-m}{2}\Leftrightarrow M\left(\dfrac{1-m}{2};0\right)\Leftrightarrow OM=\dfrac{\left|1-m\right|}{2}\)
PT giao Oy của (d) là \(x=0\Leftrightarrow y=m-1\Leftrightarrow N\left(0;m-1\right)\Leftrightarrow ON=\left|m-1\right|\)
Để \(S_{OMN}=1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}OM\cdot ON=1\Leftrightarrow OM\cdot ON=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left|\left(1-m\right)\left(m-1\right)\right|}{2}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow\left|-\left(m-1\right)^2\right|=2\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(m-1\right)^2=2\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=1+\sqrt{2}\\m=1-\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

câu 1:
đường thẳng (d) song song với đường thẳng y=3x+1 khi a=3
vậy hệ số góc của đường thẳng (d) song song với đường thẳng y=3x+1 là 3
câu 2:
vì góc tạo bởi đường thẳng (d):y=ax+b(a≠0) với trục Ox là 30o nên
\(a=\tan30^o=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\)
vậy hệ số góc của đường thẳng (d) tạo với trục Ox là\(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\)

8.
Gọi \(A\left(x_0;y_0\right)\) là điểm cố định mà đt luôn đi qua với mọi m
\(\Leftrightarrow mx_0+2y_0-3my_0+m-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m\left(x_0-3y_0+1\right)+\left(2y_0-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_0-3y_0+1=0\\2y_0-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_0=\dfrac{1}{2}\\y_0=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow A\left(\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\)
Vậy đt luôn đi qua \(A\left(\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\) với mọi m
9.
PT giao Ox là \(y=0\Leftrightarrow mx+m-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1-m}{m}\Leftrightarrow A\left(\dfrac{1-m}{m};0\right)\Leftrightarrow OA=\left|\dfrac{1-m}{m}\right|\)
PT giao Oy là \(x=0\Leftrightarrow\left(2-3m\right)y+m-1=0\Leftrightarrow y=\dfrac{1-m}{2-3m}\Leftrightarrow B\left(0;\dfrac{1-m}{2-3m}\right)\Leftrightarrow OB=\left|\dfrac{1-m}{2-3m}\right|\)
Để \(\Delta OAB\) cân thì \(OA=OB\Leftrightarrow\left|\dfrac{1-m}{m}\right|=\left|\dfrac{1-m}{2-3m}\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|m\right|=\left|2-3m\right|\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=2-3m\\m=3m-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=\dfrac{1}{2}\\m=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=\dfrac{1}{2}\\m=1\end{matrix}\right.\) thỏa mãn đề



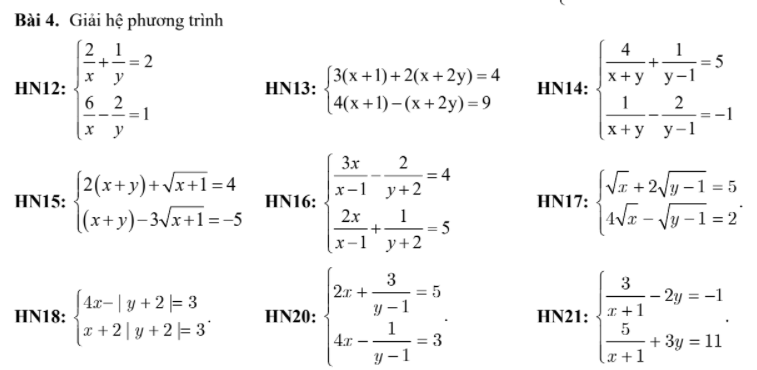
\(a,ĐK:x+y\ne0;x\ne y\\ HPT\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x+y}+\dfrac{4}{x-y}=\dfrac{14}{3}\left(1\right)\\\dfrac{3}{x+y}+\dfrac{4}{x-y}=5\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \left(2\right)-\left(1\right)=\dfrac{1}{x+y}=\dfrac{1}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow x+y=3\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3-y\\ \text{Thay vào }\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{4}{3-2y}=\dfrac{14}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4}{3-2y}=4\\ \Leftrightarrow3-2y=1\\ \Leftrightarrow y=1\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy hệ có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(2;1\right)\)
\(b,ĐK:y\ne-\dfrac{1}{2};x-2y\ne0\\ HPT\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{6}{x-2y}+\dfrac{y}{1+2y}=3\left(1\right)\\\dfrac{6}{x-2y}-\dfrac{8}{1+2y}=-2\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \left(1\right)-\left(2\right)=\dfrac{y+8}{2y+1}=5\\ \Leftrightarrow y+8=10y+5\Leftrightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{3}\\ \text{Thay vào }\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{6}{x-\dfrac{2}{3}}+\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{3}}{\dfrac{5}{3}}=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{6}{x-\dfrac{2}{3}}=\dfrac{14}{5}\\ \Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{15}{7}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{59}{21}\)
Vậy hệ có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(\dfrac{59}{21};\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\)
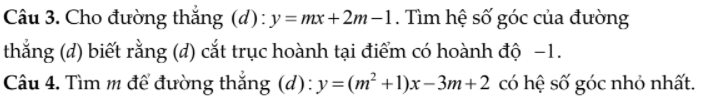 này được
này được 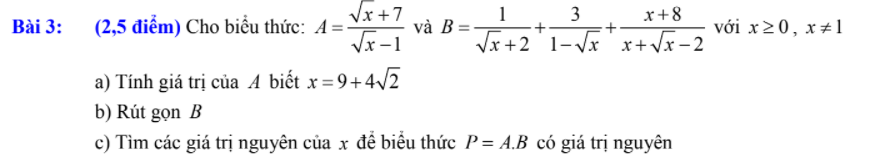 được không ạ, mai em phải nộp rồi, cảm ơn mn nhiều.
được không ạ, mai em phải nộp rồi, cảm ơn mn nhiều. 

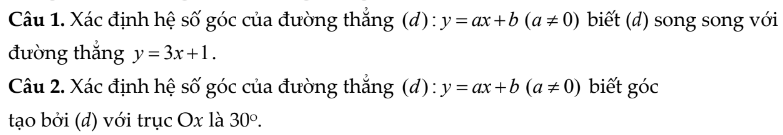


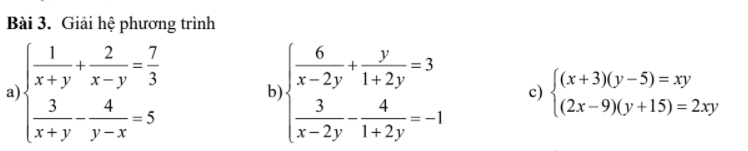
\(a,\Leftrightarrow-m+5\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne5\\ b,\text{Đồng biến }\Leftrightarrow-m+5>0\Leftrightarrow m< 5\\ \text{Nghịch biến }\Leftrightarrow-m+5< 0\Leftrightarrow m>5\)
a) Hàm số trên là hàm số bậc nhất khi: -m+5 ≠ 0 ⇔ m ≠ 5
b) Để hàm số trên là hàm số đồng biến: -m+5 > 0 ⇔ m<5
Để hàm số trên là hàm số nghịch biến: -m+5 <0 ⇔ m>5