
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

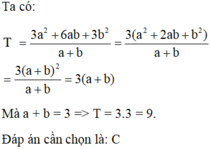

\(a,2x^2-2xt-5x+5y\)
\(=\left(2x^2-5x\right)-\left(2xy-5y\right)\)
\(=x\left(2x-5\right)-y\left(2x-5\right)\)
\(=\left(2x-5\right)\left(x-y\right)\)
\(b,8x^2+4xy-2ax-ay\)
\(=\left(8x^2-2ax\right)+\left(4xy-ay\right)\)
\(=2x\left(4x-a\right)+y\left(4x-a\right)\)
\(=\left(4x-a\right)\left(2x+y\right)\)
\(c,x^3-4x^2+4x\)
\(=x^3-2x^2-2x^2+4x\)
\(=\left(x^3-2x^2\right)-\left(2x^2-4x\right)\)
\(=x^2\left(x-2\right)-2x\left(x-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2-2x\right)=x\left(x-2\right)\left(x-2\right)\)
\(=x\left(x-2\right)^2\)
\(d,2xy-x^2-y^2+16\)
\(=-\left(x^2-2xy+y^2-16\right)\)
\(=-\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-4^2\right]\)
\(=-\left(x-y-4\right)\left(x-y+4\right)\)
\(e,x^2-y^2-2yz-z^2\)
\(=x^2-\left(y^2+2yz+z^2\right)\)
\(=x^2-\left(y+z\right)^2=\left(x-y-z\right)\left(x+y+z\right)\)

Bài 1:
\(B=\frac{0,375-0,3+\frac{3}{11}+\frac{3}{12}}{-0,625+0,5-\frac{5}{11}-\frac{5}{12}}+\frac{1,5+1-0,75}{2,5+\frac{5}{3}-1,25}\)
\(=\frac{3\left(0,125-0,1+\frac{1}{11}+\frac{1}{12}\right)}{-\left(0,625-0,5+\frac{5}{11}+\frac{5}{12}\right)}+\frac{3\left(0,5+\frac{1}{3}-0,25\right)}{5\left(0,5+\frac{1}{3}-0,25\right)}\)
\(=\frac{3\left(0,125-0,1+\frac{1}{11}+\frac{1}{12}\right)}{-\left[5\left(0,125-0,1+\frac{1}{11}+\frac{1}{12}\right)\right]}+\frac{3}{5}\)
\(=\frac{-3}{5}+\frac{3}{5}\)
\(=0\)
Bài 2:
b) Giải:
Ta có: \(\frac{a}{c}=\frac{b}{d}\Rightarrow\frac{a}{b}=\frac{c}{d}\Rightarrow\frac{a^6}{b^6}=\frac{c^6}{d^6}\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
\(\frac{a^6}{b^6}=\frac{c^6}{d^6}=\frac{3a^6}{3b^6}=\frac{c^6}{d^6}=\frac{3a^6+c^6}{3b^6+d^6}\) (1)
\(\frac{a}{b}=\frac{c}{d}=\frac{a+b}{b+d}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(\frac{a}{b}\right)^6=\left(\frac{a+c}{b+d}\right)^6=\frac{a^6}{b^6}=\frac{\left(a+c\right)^6}{\left(b+d\right)^6}\) (2)
Từ (1) và (2) \(\Rightarrow\frac{3a^6+c^6}{3b^6+d^6}=\frac{\left(a+c\right)^6}{\left(b+d\right)^6}\left(đpcm\right)\)

Xét:
\(P^2=\dfrac{\left(a-b\right)^2}{\left(a+b\right)^2}=\dfrac{a^2-2ab+b^2}{a^2+2ab+b^2}=\dfrac{3a^2+3b^2-6ab}{3a^2+3b^2+6ab}=\dfrac{10ab-6ab}{10ab+6ab}=\dfrac{4ab}{16ab}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)Mà \(P>0\Rightarrow P=\dfrac{1}{2}\)

a) a3 + 1 + 3a + 3a2 = ( a + 1)3 = 102 = 100
b) x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 = ( x + 1)3 = 203 = 8000 ( sửa đề)
c) a3 + 3a2 + 3a + 6 = a3 + 3a2 + 3a + 1 + 5 = ( a + 1)3 + 5 = 27005
d) a3 - 3a2 + 3a - 1 = ( a - 1)3 = 1003 = 1000000 ( sửa đề )

\(P=\frac{a^3}{2a+3b}+\frac{b^3}{3a+2b}=\frac{a^4}{2a^2+3ab}+\frac{b^4}{3ab+2b^2}\)
\(P\ge\frac{\left(a^2+b^2\right)^2}{2\left(a^2+b^2\right)+6ab}\ge\frac{\left(a^2+b^2\right)^2}{2\left(a^2+b^2\right)+3\left(a^2+b^2\right)}=\frac{a^2+b^2}{5}=\frac{2}{5}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(a=b=1\)

a) \(a^2+25b^2+17+10b-8a=0\)
\(\Rightarrow a^2-8a+16+25b^2+10b+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(a-4\right)^2+\left(5b+1\right)^2=0\)
Vì \(\left(a-4\right)^2\ge0\) với mọi a
\(\left(5b+1\right)^2\ge0\) với mọi b
\(\Rightarrow\left(a-4\right)^2+\left(5b+1\right)^2\ge0\) với mọi a,b
Mà \(\left(a-4\right)^2+\left(5b+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(a-4\right)^2=0\\\left(5b+1\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a-4=0\\5b+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=4\\5b=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=4\\b=-\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Ta có : \(3a^2+3b^2=10ab\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3a^2-ab-9ab+3b^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a\left(3a-b\right)-3b\left(3a-b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3a-b\right)\left(a-3b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3a-b=0\\a-3b=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}b=3a\left(L\right)\\a=3b\left(N\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thế \(a=3b\) vào P ta được :
\(P=\dfrac{3b-b}{3b+b}=\dfrac{2b}{4b}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)

Bài giải:
1.
a) x2 + 6x + 9 = x2 + 2 . x . 3 + 32 = (x + 3)2
b) 10x – 25 – x2 = -(-10x + 25 +x2) = -(25 – 10x + x2)
= -(52 – 2 . 5 . x – x2) = -(5 – x)2
c) 8x3 - 1818 = (2x)3 – (1212)3 = (2x - 1212)[(2x)2 + 2x . 1212 + (1212)2]
= (2x - 1212)(4x2 + x + 1414)
d) 125125x2 – 64y2 = (15x)2(15x)2- (8y)2 = (1515x + 8y)(1515x - 8y)
2.
a) x3 + 127127 = x3 + (1313)3 = (x + 1313)(x2 – x . 1313+ (1313)2)
=(x + 1313)(x2 – 1313x + 1919)
b) (a + b)3 – (a - b)3
= [(a + b) – (a – b)][(a + b)2 + (a + b) . (a – b) + (a – b)2]
= (a + b – a + b)(a2 + 2ab + b2 + a2 – b2 + a2 – 2ab + b2)
= 2b . (3a3 + b2)
c) (a + b)3 + (a – b)3 = [(a + b) + (a – b)][(a + b)2 – (a + b)(a – b) + (a – b)2]
= (a + b + a – b)(a2 + 2ab + b2 – a2 +b2 + a2 – 2ab + b2]
= 2a . (a2 + 3b2)
d) 8x3 + 12x2y + 6xy2 + y3 = (2x)3 + 3 . (2x)2 . y +3 . 2x . y + y3 = (2x + y)3
e) - x3 + 9x2 – 27x + 27 = 27 – 27x + 9x2 – x3 = 33 – 3 . 32 . x + 3 . 3 . x2 – x3 = (3 – x)3