Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

A = (3x + 7)(2x + 3) – (3x – 5)(2x + 11)
= 3x.2x + 3x.3 + 7.2x + 7.3 – (3x.2x + 3x.11 – 5.2x – 5.11)
= 6 x 2 + 9 x + 14 x + 21 – ( 6 x 2 + 33 x – 10 x – 55 ) = 6 x 2 + 23 x + 21 – 6 x 2 – 33 x + 10 x + 55 = 76
B = x ( 2 x + 1 ) – x 2 ( x + 2 ) + x 3 – x + 3 = x . 2 x + x – ( x 2 . x + 2 x 2 ) + x 3 – x + 3 = 2 x 2 + x – x 3 – 2 x 2 + x 3 – x + 3 = 3
Từ đó ta có A = 76; B = 3 mà 76 = 25.3 + 1 nên A = 25B + 1
Đáp án cần chọn là: C

`1-D`
Vì `7-2x=0` có dạng của ptr bậc nhất một ẩn `ax+b=0` trong đó `a=-2 \ne 0`
_________________________________________________
`2-C`
Vì `-x+1 < 0` có dạng bất ptr bậc nhất một ẩn `ax+b < 0` và `a=-1 \ne 0`
__________________________________________________
`3-A`
`4x-10 > x+2`
`<=>4x-x > 2+10`
`<=>3x > 12`
`<=>x > 4`
_________________________________________________
`4-C`
Vì tỉ số đồng dạng của `2` hai tam giác đồng dạng bằng tỉ số của `2` đường cao tương ứng của `2` tam giác đồng dạng đó

Câu 5: B
Câu 6:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x-2\ne0\)
=>\(x\ne2\)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x+1\ne0\)
=>\(x\ne-1\)
8:
\(A=\dfrac{x^2+4}{3x^2-6x}+\dfrac{5x+2}{3x}-\dfrac{4x}{3x^2-6x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+4-4x}{3x\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{5x+2}{3x}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{3x\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{5x+2}{3x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2+5x+2}{3x}=\dfrac{6x}{3x}=2\)
7:
\(\dfrac{8x^3yz}{24xy^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{8xy\cdot x^2z}{8xy\cdot3y}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2z}{3y}\)

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\)
Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}-\dfrac{5x-50}{2x^2+10x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}-\dfrac{5x-50}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}-\dfrac{5x-50}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50-5x+50}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+5x-x-5}{2\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+5\right)-\left(x+5\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)
b) Để B=0 thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\)
hay x=1(nhận)
Vậy: Để B=0 thì x=1
Để \(B=\dfrac{1}{4}\) thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x-1\right)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-4=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=6\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)(nhận)
Vậy: Để \(B=\dfrac{1}{4}\) thì \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
c) Thay x=3 vào biểu thức \(B=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\), ta được:
\(B=\dfrac{3-1}{2}=\dfrac{2}{2}=1\)
Vậy: Khi x=3 thì B=1
d) Để B<0 thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 1\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Để B<0 thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để B>0 thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1>0\)
hay x>1
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: x>1
Vậy: Để B>0 thì x>1
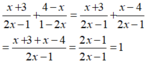
Ta có
B = (2x – 3)(x +7) – 2x(x + 5) – x
= 2x.x + 2x.7 – 3.x – 3.7 – 2x.x – 2x.5 – x
= 2 x 2 + 14x – 3x – 21 – 2 x 2 – 10x – x
= ( 2 x 2 – 2 x 2 ) + (14x – 3x – 10x – x) – 21= -21 < -1
Đáp án cần chọn là: B