
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(1,\\ a,=6x^4y^4-x^3y^3+\dfrac{1}{2}x^4y^2\\ b,=4x^3+5x^2-8x^2-10x+12x+15\\ =4x^3-3x^2+2x+15\\ 2,\\ a,=7\left(x^2-6x+9\right)=7\left(x-3\right)^2\\ b,=\left(x-y\right)^2-36=\left(x-y-6\right)\left(x-y+6\right)\\ 3,\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-0,36\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-0,6\right)\left(x+0,6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=0,6\\x=-0,6\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\sqrt{6-2\sqrt{5}}\)
\(=\sqrt{5-2\sqrt{5}+1}\)
\(=\sqrt{\sqrt{5}^2-2\sqrt{5}+1^2}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)^2}\)
\(=|\sqrt{5}-1|=\sqrt{5}-1\)

\(a^3+b^3+c^3=3abc\)
=>\(\left(a+b\right)^3+c^3-3ab\left(a+b\right)-3abc=0\)
=>\(\left(a+b+c\right)\left[\left(a+b\right)^2-c\left(a+b\right)+c^2\right]-3ab\left(a+b+c\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(a+b+c\right)\left(a^2+2ab+b^2-ac-bc+c^2-3ab\right)=0\)
=>\(a^2+b^2+c^2-ab-ac-bc=0\)
=>\(2a^2+2b^2+2c^2-2ab-2ac-2bc=0\)
=>\(\left(a^2-2ba+b^2\right)+\left(b^2-2cb+c^2\right)+\left(a^2-2ac+c^2\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(a-b\right)^2+\left(b-c\right)^2+\left(a-c\right)^2=0\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a-b=0\\b-c=0\\a-c=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow a=b=c\)
\(A=\dfrac{a^{2023}}{b^{2023}}+\dfrac{b^{2023}}{c^{2023}}+\dfrac{c^{2023}}{a^{2023}}\)
\(=\dfrac{a^{2023}}{a^{2023}}+\dfrac{b^{2023}}{b^{2023}}+\dfrac{c^{2023}}{c^{2023}}\)
=1+1+1
=3

Câu 2:
Gọi số sách Nam mua được là x(sách)(Điều kiện: \(x\in Z^+\))
Số tập Nam mua được là: x+3(tập)
Theo đề, ta có phương trình:
\(12000x+5000\left(x+3\right)=83000\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12000x+5000x+15000=83000\)
\(\Leftrightarrow17000x=68000\)
hay x=4(thỏa ĐK)
Vậy: Bạn Nam mua được 4 quyển sách và 7 cuốn tập

Bài V:
-ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\pm1\).
\(\dfrac{m}{x-1}+\dfrac{x}{x+1}=\dfrac{x^2}{x^2-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{m\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow mx+m+x^2-x=x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(x+1\right)=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{x}{x+1}\)
-Vì m,x nguyên:
\(\Rightarrow x⋮\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1-1\right)⋮\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow-1⋮\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;-2\right\}\) (nhận)
*\(x=0\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{x}{x+1}=\dfrac{0}{0+1}=0\)
\(x=-2\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{x}{x+1}=\dfrac{-2}{-2+1}=1\)
-Vậy với \(m=0\) thì \(S=\left\{0\right\}\)
với \(m=1\) thì \(S=\left\{-2\right\}\)


a)
\(16x^2-\left(4x-5\right)^2=15\)
\(\left(4x-4x+5\right)\left(4x+4x-5\right)=15\)
\(5\left(8x-5\right)=15\)
40x-25=15
40x=40
x=1
b: Ta có: \(\left(2x+3\right)^2-4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+12x+9-4x^2+16=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x=24\)
hay x=2
d: Ta có: \(2\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-\left(x-4\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+4x+2-x^2+9-x^2+8x-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x=5\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{5}{12}\)

 ai giải giúp em mấy bài toán này vs ạ giải chi tiết giúp em ạ
ai giải giúp em mấy bài toán này vs ạ giải chi tiết giúp em ạ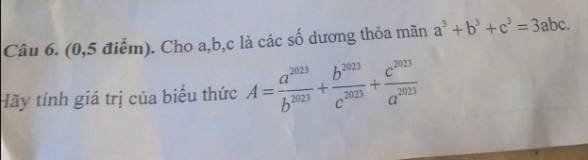


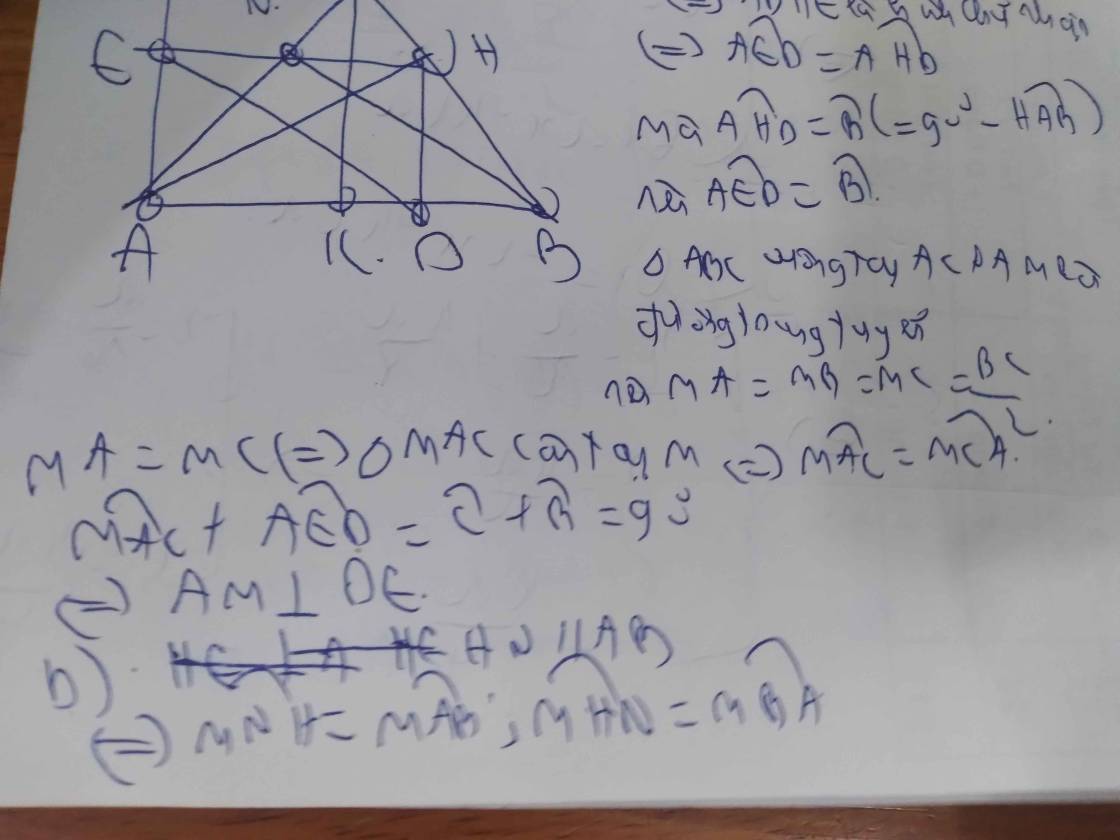




 ai giải giùm em câu 6 vs ạ cho em lời giải chi tiết và vẽ hình giúp em vs ạ cảm ơn mn
ai giải giùm em câu 6 vs ạ cho em lời giải chi tiết và vẽ hình giúp em vs ạ cảm ơn mn
a, Vì \(\widehat{AKH}=\widehat{AIH}=\widehat{KAI}=90^0\) nên HIAK là hcn
b, Do HIAK là hcn nên \(AK=HI\)
Mà D đx H qua I nên \(HI=HD\)
Do đó \(AK=HD\)
Mà HIAK là hcn nên AK//HI hay AK//HD
Vậy DAKI là hbh