Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

some: some important differences; some hobbies
any: any countries or continents; any coal or oil; any food; any special missions
LEARN THIS! some and any
We use some and any with uncountable and plural countable nouns. (Chúng ta dùng some và any với những danh từ không đếm được và danh từ đếm được ở dạng số nhiều.)
a. We use some in affirmative sentences. (Ta dùng some cho câu khẳng định.)
b. We use any in negatives sentences and questions. (Ta dùng any cho câu phủ định và câu nghi vấn.)

a. In non-defining relative clauses, we use who, which, where and whose, but we do not use that.
(Trong mệnh đề quan hệ không xác định, ta dùng, who, which, where và whose, và chúng ta không dùng that.)
b. A non-defining relative clause:
(Một mệnh đề quan hệ không xác định là:)
comes immediately (1) after a noun and gives us information about that noun.
(theo ngay sau một danh từ và cho biết thông tin về danh từ đó.)
adds extra information to the sentence; the sentence (2) makes sense without it.
(thêm thông tin vào câu; câu vẫn có nghĩa khi không có nó.)
(3) has a comma at the start. It has a comma or a full stop at the end.
(có một dấu phẩy ngay lúc bắt đầu. Có một dấu chấm hoặc dấu phẩy vào cuối câu.)

Rule a:
+ Harris Aslam is an ambitious young man who left school at the age of thirteen to work in his family's grocery business.
(Harris Aslam là một chàng trai trẻ đầy tham vọng, bỏ học năm 13 tuổi để làm việc trong công việc kinh doanh tạp hóa của gia đình.)
+ Now, at the age of eighteen, he owns three shops in Kirkcaldy, Scotland, the town where he was born and broupht up.
(Bây giờ, ở tuổi mười tám, anh sở hữu ba cửa hàng ở Kirkcaldy, Scotland, thị trấn nơi anh sinh ra và lớn lên.)
+ The job he is now applying for is CEO of Nisa Retail, a grocery business whose annual sales are about £1.6 billion!
(Công việc hiện anh đang ứng tuyển là Giám đốc điều hành của Nisa Retail, một công ty kinh doanh tạp hóa có doanh thu hàng năm khoảng 1,6 tỷ bảng Anh!)

LEARN THIS! Past perfect (Thì quá khứ hoàn thành)
a. We form the past perfect with (1) had or (2) hadn’t and the past participle.
(Chúng ta tạo thì quá khứ hoàn thành với had hoặc hadn’t với động từ ở thể quá khứ phân từ.)
b. We use the past perfect when we are already talking about past events and we want to talk about an even earlier event.
(Chúng ta dùng thì quá khứ hoàn thành khi ai đó đang nói về những sự kiện xảy ra trong quá khứ và chúng ta muốn nói đến những sự kiện trước đó nữa.)
When I got to the classroom, the lesson had started.
(Khi mình đến lớp thì bài học đã bắt đầu.)
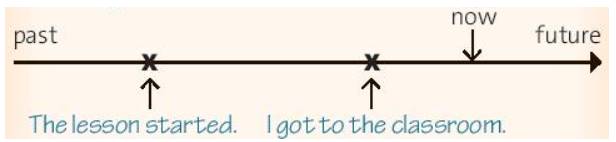
c. We often use the past perfect with after, before or when.
(Chúng ta thường dùng thì quá khứ hoàn thành với after, before hoặc when.)
Before I got to the bus station, the bus had already left.
(Trước khi mình đến trạm xe buýt, thì xe buýt đã đi mất.)
After I’d called Maggie, I watched a film on TV.
(Sau khi mình gọi cho Maggie, mình xem một bộ phim trên TV.)
had thrown … away; had risen; had increased; had spilled; had kept; had sold; had thrown; had … forgotten; hadn’t saved

1. present simple
2. present continuous
3. present continuous
4. present simple
5. present simple
6. present continuous

Nearly a billion mobile phones are sold ... (a)
The first mobile phone call was made ...
The call was answered ...
The first mobiles were powered ... (a)
Voicemail was added ...
Internet access was not added ... (b)
The first text message was sent ...
It was not typed ... (b)
The camera phone was invented ...
Photos of his newborn daughter were shared ... (a)
In the UK, a mobile phone is stolen ...
What are mobile phones used for the most? (c)

She told me that her right ankle was hurting ...; She said she hadn’t twisted it... she couldn’t put any weight on it; ... I had watched a really good video clip ... the day before; I told her she must watch it; she said she had come across ...; She said that after she’d finished watching it, she had thought about sending me the link.
- Changes to pronouns (Thay đổi đại từ): I → she
- Changes to possessive (Thay đổi tính từ sở hữu) : my → her,
- Changes to references to time (Thay đổi tham chiếu thời gian): yesterday → the day before

LEARN THIS! not much, not many, a lot of. a little, a few
a. We use not much or a little + uncountable noun for a small quantity of something.
(Ta dùng not much hoặc a little + danh từ không đếm được cho một lượng nhỏ của một thứ gì đó.
b. We use not many or a few + plural noun for a small number of something.
(Ta dùng not many hoặc a few + danh từ số nhiều cho số lượng nhỏ của một thứ gì đó.)
c. We use much + uncountable noun for a large quantity of something.
(Ta dùng much + danh từ không đếm được cho một lượng lớn của một thứ gì đó.)
d We use many + plural noun for a large number of something.
(Ta dùng many + danh từ số nhiều cho một số lượng lớn của một thứ gì đó.)
e. We use a lot of + uncountable or plural noun for a large quantity or number of something.
(Ta dùng a lot of + danh từ không đếm được hoặc danh từ số nhiều cho một lượng lớn hoặc một số lượng của một thứ gì đó.)
f. We use how much …? + uncountable noun or how many …? + plural noun for questions about quantity or number.
(Ta dùng how much…? + danh từ không đếm được hoặc how many…? + danh từ đếm được cho câu hỏi về lượng hoặc số lượng.)
- rule d: She told me that her right ankle was hurting ...; She said she hadn’t twisted it. but told me she couldn’t put any weight on it; I told Harriet that I had watched ...; I said that I would send her...; I told her she must watch it; ... she said she had come across the same clip ...; She said that after she’d finished watching it...
- rule e: She said she hadn’t twisted it. but told me she couldn’t put any weight on it; I told her she must watch it; ... she said she had come across the same clip ...