



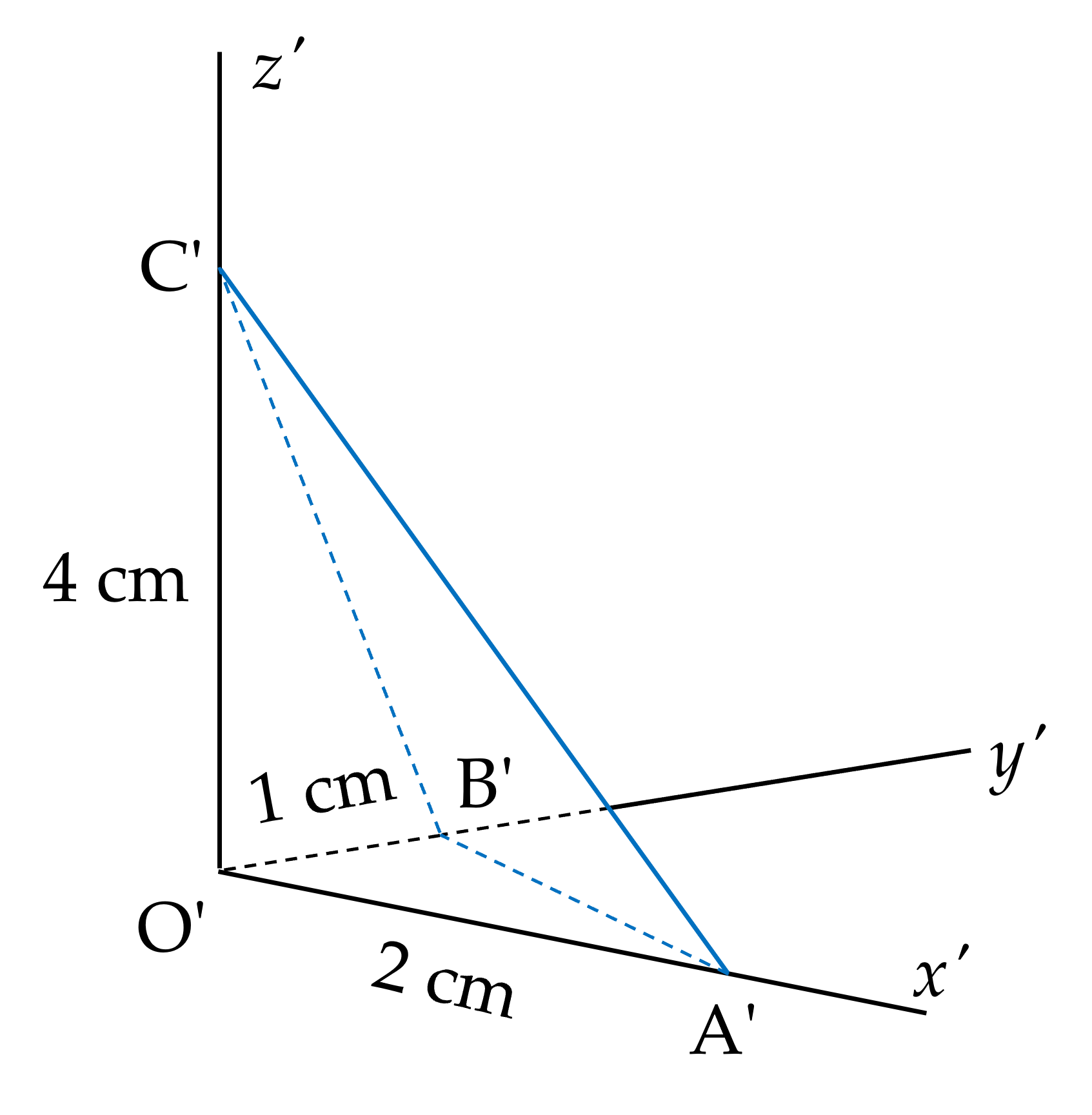
Hệ số biến dạng theo mỗi trục đo O'x', O'y', O'z' lần lượt là:
p=O'A'OA=22=1�=�'�'��=22=1;
q=O'B'OB=13�=�'�'��=13;
r=O'C'OC=46=23�=�'�'��=46=23.

a)

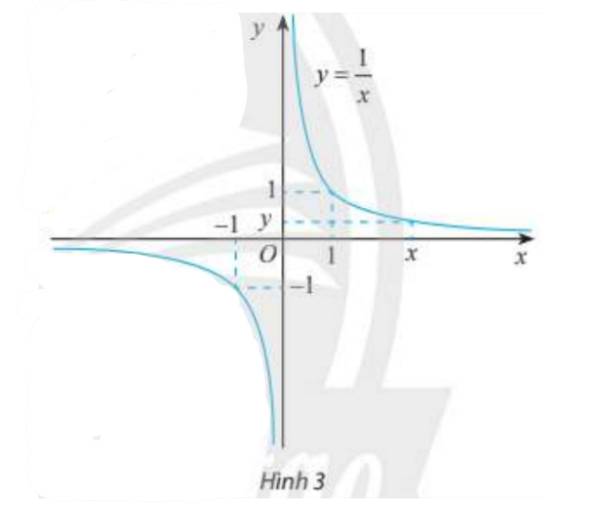
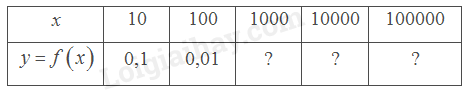
Giá trị \(f\left( x \right)\) dần về 0 khi \(x\) càng lớn (dần tới \( + \infty \)).
b)
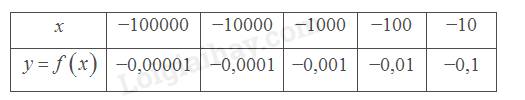
Giá trị \(f\left( x \right)\) dần về 0 khi \(x\) càng bé (dần tới \( - \infty \)).


1.
\(u_{n+1}=4u_n+3.4^n\)
\(\Leftrightarrow u_{n+1}-\dfrac{3}{4}\left(n+1\right).4^{n+1}=4\left[u_n-\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n\right]\)
Đặt \(u_n-\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n=v_n\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}v_1=2-\dfrac{3}{4}.4=-1\\v_{n+1}=4v_n\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow v_n=-1.4^{n-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow u_n=\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n-4^{n-1}=\left(3n-1\right)4^{n-1}\)
2.
\(a_n=\dfrac{a_{n-1}}{2n.a_{n-1}+1}\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}=2n+\dfrac{1}{a_{n-1}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}-n^2-n=\dfrac{1}{a_{n-1}}-\left(n-1\right)^2-\left(n-1\right)\)
Đặt \(\dfrac{1}{a_n}-n^2-n=b_n\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b_1=2-1-1=0\\b_n=b_{n-1}=...=b_1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}=n^2+n\Rightarrow a_n=\dfrac{1}{n^2+n}\)

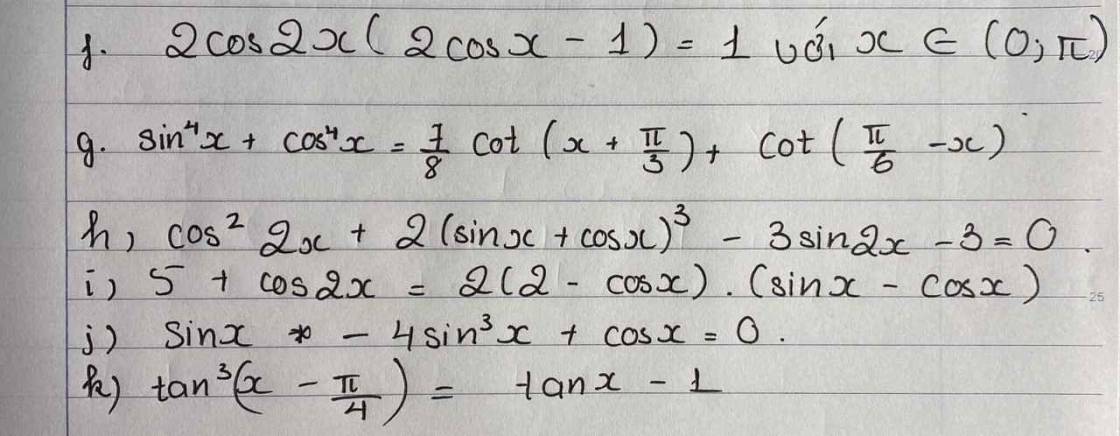

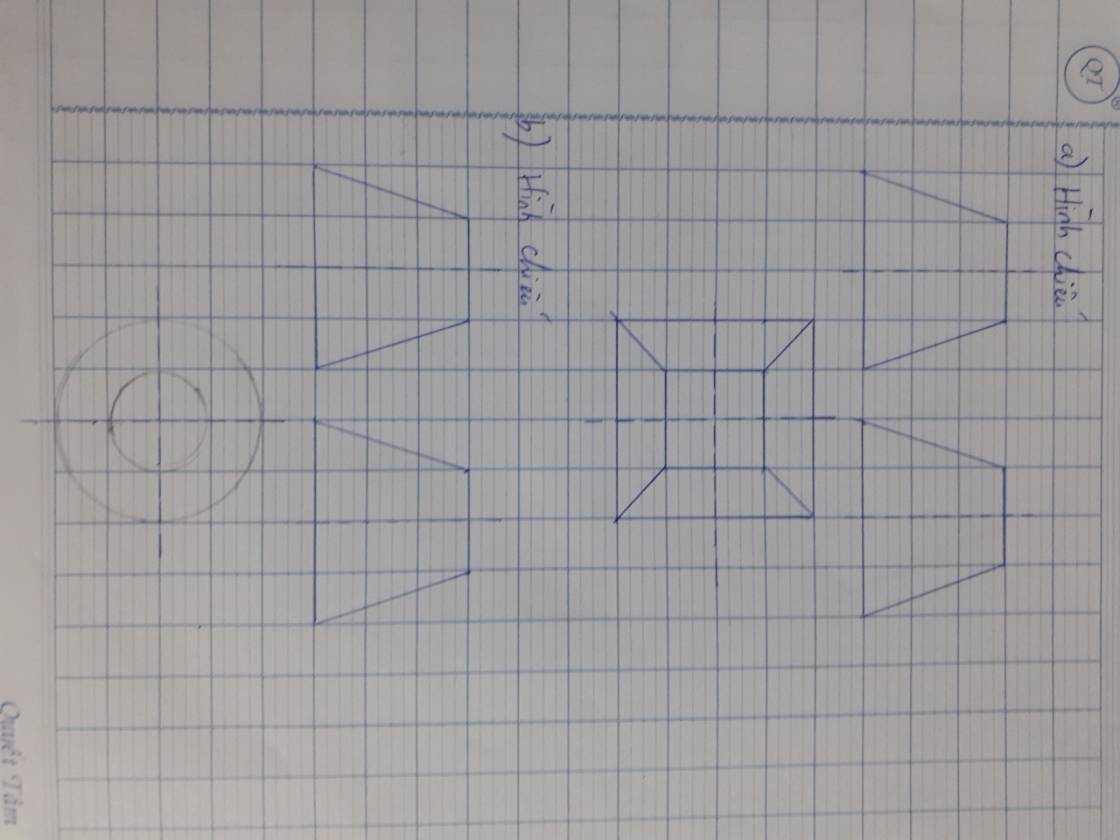
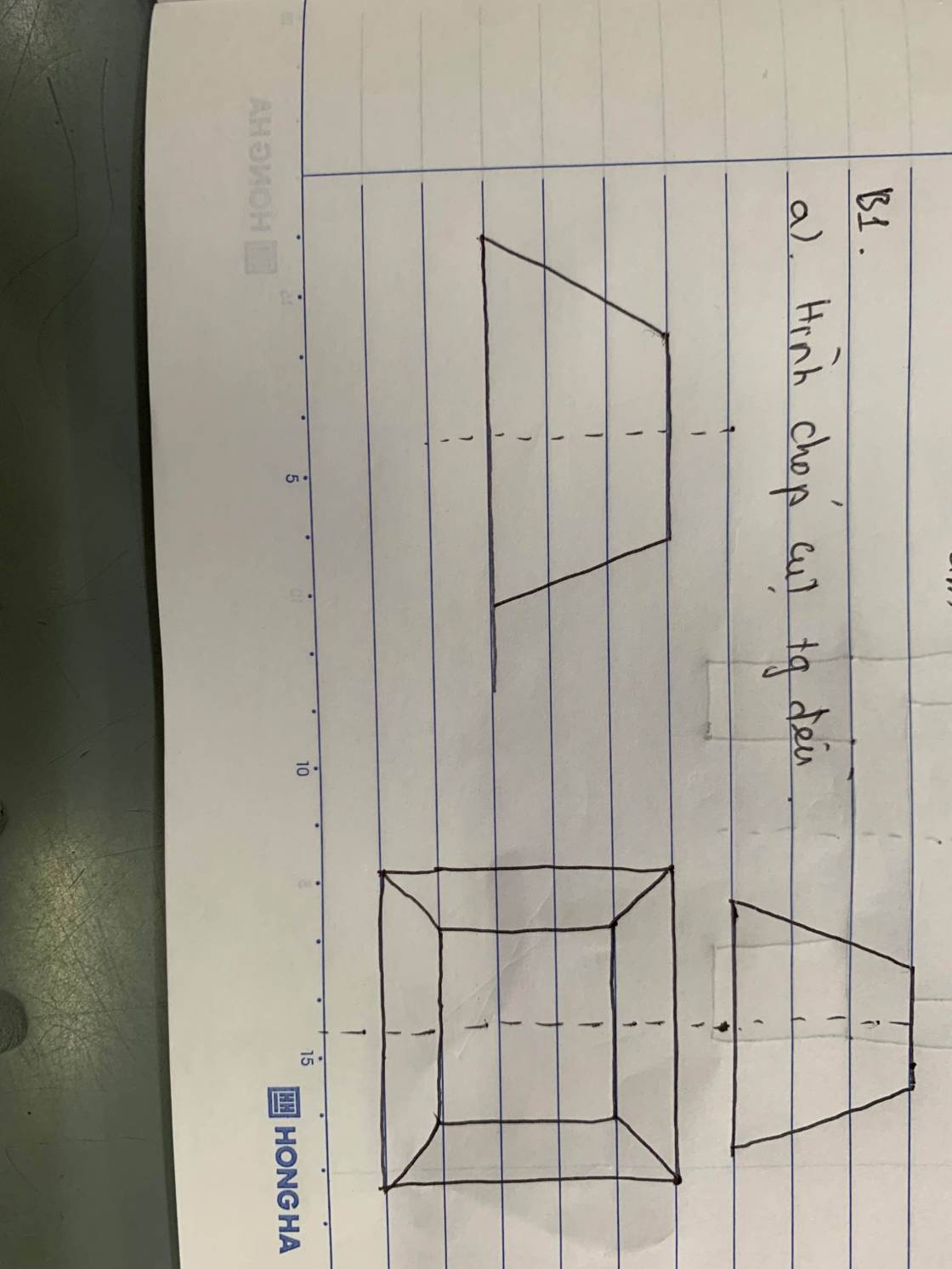
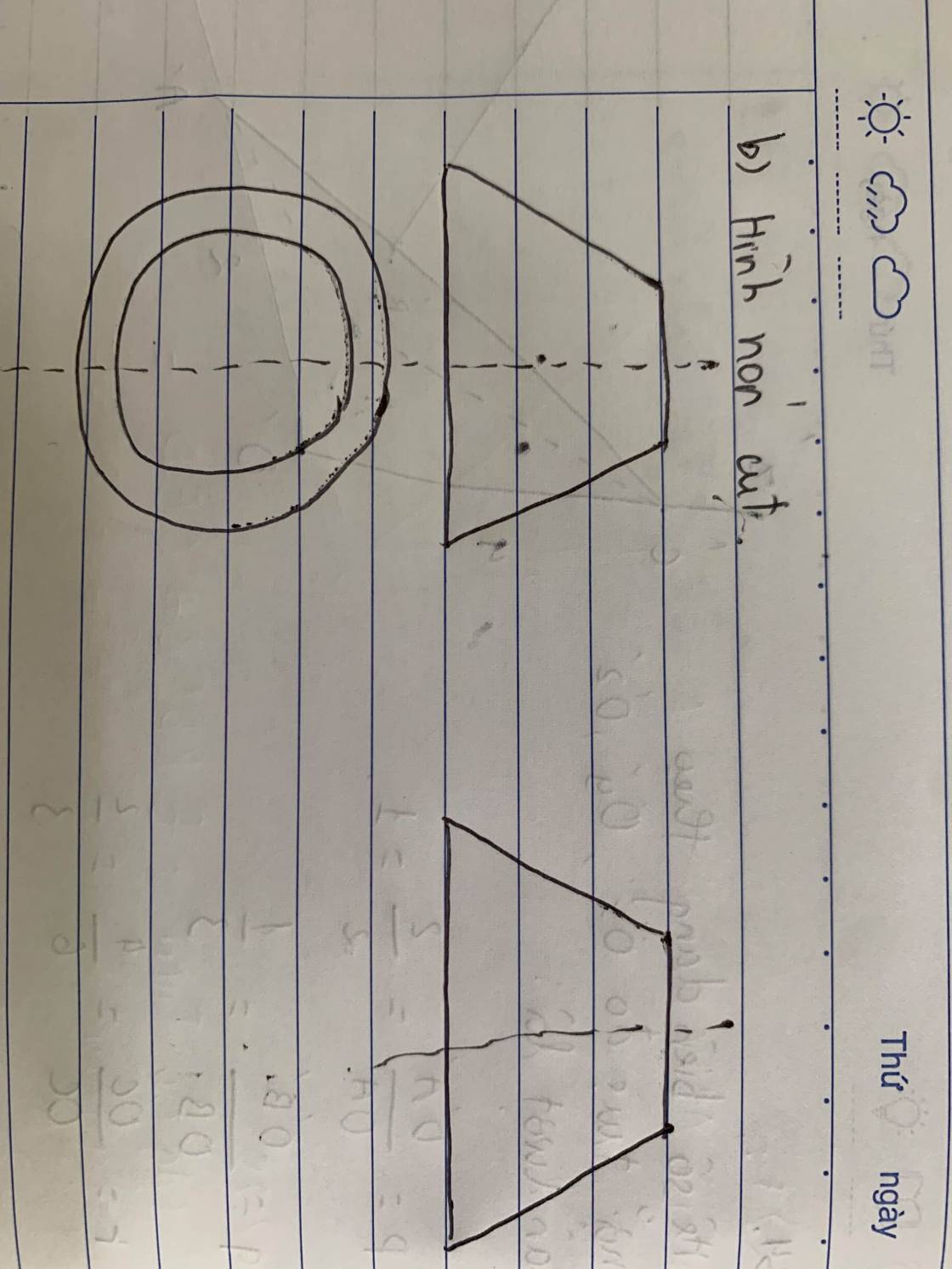
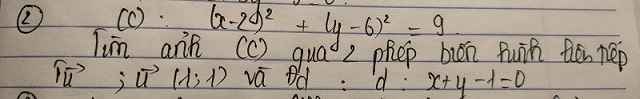

Đặt \(\left(\dfrac{x}{4};\dfrac{y}{2};z\right)=\left(a;b;c\right)\Rightarrow a;b;c\ge0\)
Từ giả thiết \(\Rightarrow16^a+16^b+16^c=34\)
Do \(a;b;c\ge0\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}16^a\ge1\\16^b\ge1\\16^c\ge1\\16^{a+b}\ge1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(16^a-1\right)\left(16^b-1\right)+\left(16^{a+b}-1\right)\left(16^c-1\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16^{a+b}-16^a-16^b+1+16^{a+b+c}-16^{a+b}-16^c+1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16^{a+b+c}\ge16^a+16^b+16^c-2=32\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a+b+c\ge log_{16}32=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(P_{min}=\dfrac{5}{4}\) khi \(\left(a;b;c\right)=\left(0;0;\dfrac{5}{4}\right)\) và hoán vị
Đặt (𝑥4;𝑦2;𝑧)=(𝑎;𝑏;𝑐)⇒𝑎;𝑏;𝑐≥0(4x;2y;z)=(a;b;c)⇒a;b;c≥0
Từ giả thiết ⇒16𝑎+16𝑏+16𝑐=34⇒16a+16b+16c=34
Do 𝑎;𝑏;𝑐≥0⇒{16𝑎≥116𝑏≥116𝑐≥116𝑎+𝑏≥1a;b;c≥0⇒⎩⎨⎧16a≥116b≥116c≥116a+b≥1
⇒(16𝑎−1)(16𝑏−1)+(16𝑎+𝑏−1)(16𝑐−1)≥0⇒(16a−1)(16b−1)+(16a+b−1)(16
Đúng(0)